Association between Hydroxyzine Use and Reduced Mortality in Patients Hospitalized for Coronavirus Disease 2019: Results from a multicenter observational study
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.10.23.20154302, Oct 2020
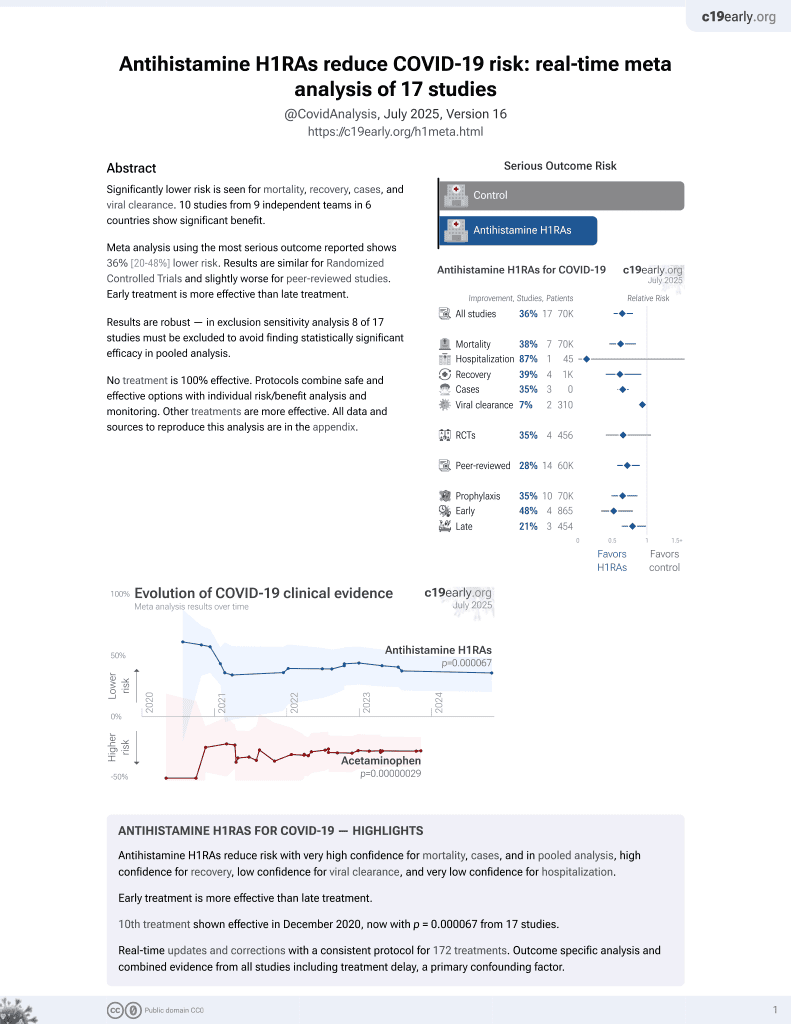
11th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2020, now with p = 0.000052 from 17 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
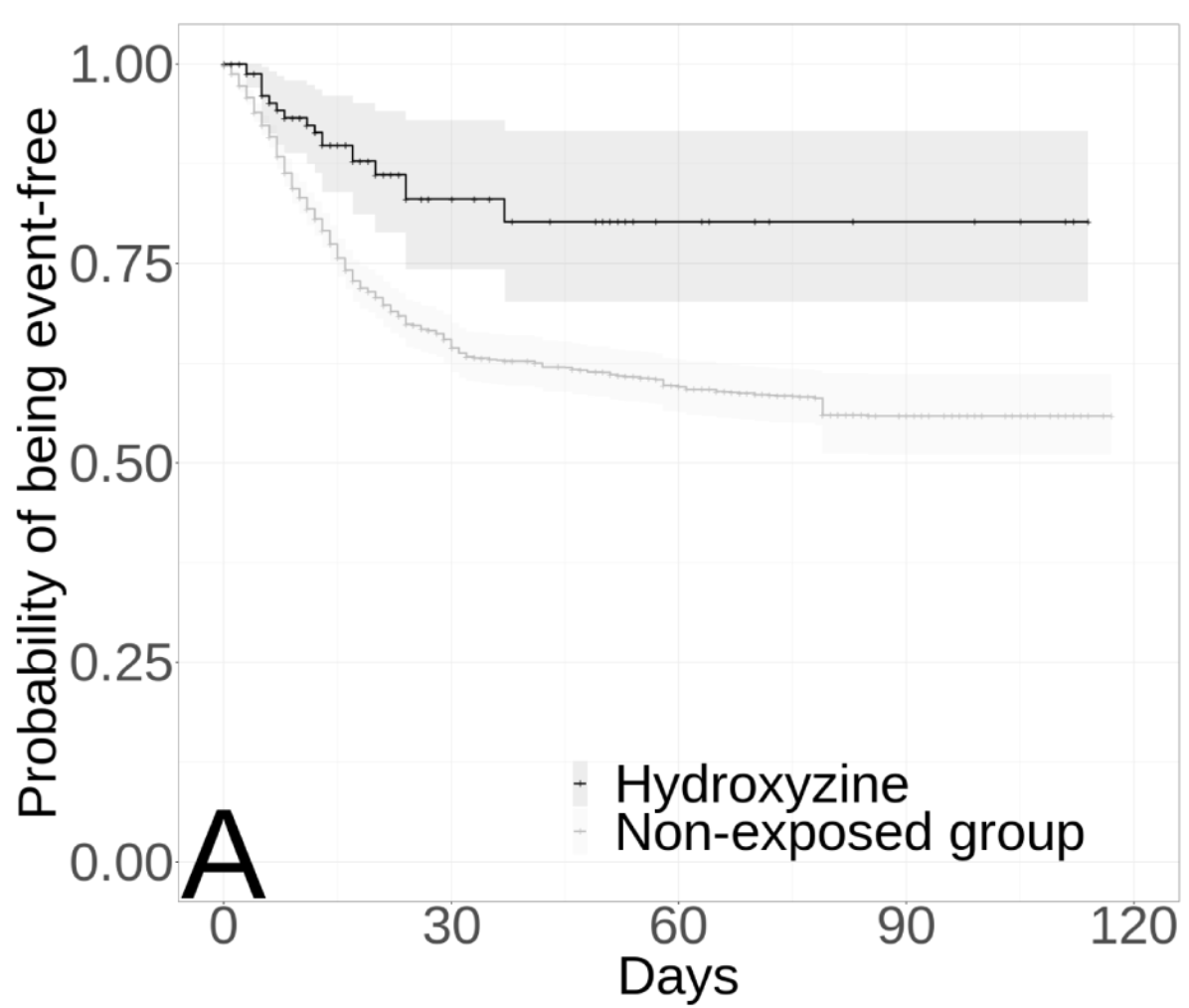
Retrospective 7,345 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in France showing lower mortality with hydroxyzine use, with a significant dose-response relationship. Hydroxyzine was also associated with a faster decrease in inflammatory markers.
|
risk of death, 58.0% lower, HR 0.42, p = 0.001, treatment 138, control 7,207, adjusted per study, propensity score weighting, multivariable.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Hoertel et al., 27 Oct 2020, retrospective, France, preprint, 18 authors, study period 24 January, 2020 - 1 April, 2020.
Contact: nico.hoertel@yahoo.fr, nicolas.hoertel@aphp.fr.
Association between Hydroxyzine Use and Reduced Mortality in Patients Hospitalized for Coronavirus Disease 2019: Results from a multicenter observational study Running title: Hydroxyzine use and Risk of Death in COVID-19
to-C-reactive protein ratio (LCRP), and circulating interleukin 6 levels (IL-6) (all p<0.016), with a significant dose-effect relationship for NLR and LCRP (both p<0.037).
Conclusions: In this retrospective observational study, hydroxyzine use was associated with reduced mortality in patients hospitalized for COVID-19. This association may be partially mediated by specific anti-inflammatory properties of H1 antihistamines. Double-blind controlled randomized clinical trials of hydroxyzine for COVID-19 are needed to confirm these results.
* p-value is significant (p<0.05).
References
Ap-Hp, DSI-WIND
Ap-Hp, None
Austin, Using the standardized difference to compare the prevalence of a binary variable between two groups in observational research, Communications in statisticssimulation and computation
Chevance, Gourion, Hoertel, Ensuring mental health care during the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic in France: a narrative review, L'encephale
Conseil, home or in a care facility of suspected or confirmed Covid-19 patients
Devlin, Chang, Lee, Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding
Efron, Nonparametric standard errors and confidence intervals, canadian Journal of Statistics
Elm, Altman, Egger, The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies
Fa, Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and lymphocyte-to-C-reactive protein ratio in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A metaanalysis, Journal of medical virology
Geleris, Sun, Platt, Observational study of hydroxychloroquine in hospitalized patients with Covid-19, New England Journal of Medicine
Gordon, Jang, Bouhaddou, A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing, Nature
Hoertel, Blachier, Blanco, A stochastic agent-based model of the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic in France, Nature Medicine
Hoertel, Sanchez Rico M, Vernet R, Association between SSRI Antidepressant Use and Reduced Risk of Intubation or Death in Hospitalized Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: a Multicenter Retrospective Observational Study, medRxiv
Hur, Price, Gray, Factors Associated With Intubation and Prolonged Intubation in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19, Otolaryngology--Head and Neck Surgery
Jouffroy, Feldman, Lerner, MedExt: combining expert knowledge and deep learning for medication extraction from French clinical texts
Kaplan, Meier, Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations, Journal of the American statistical association
Liu, Yan, Wan, Viral dynamics in mild and severe cases of COVID-19, The Lancet Infectious Diseases
Liu, Zhang, Joo, NF-κB signaling in inflammation, Signal transduction and targeted therapy
Mandhane, Shah, Bahekar, Characterization of anti-inflammatory properties and evidence for no sedation liability for the novel antihistamine SUN-1334, H. International archives of allergy and immunology
Robins, Hernan, Brumback, Marginal structural models and causal inference in epidemiology, LWW
Ruan, Yang, Wang, Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China, Intensive care medicine
Schneeweiss, Sensitivity analysis and external adjustment for unmeasured confounders in epidemiologic database studies of therapeutics, Pharmacoepidemiology and drug safety
Stebbing, Phelan, Griffin, COVID-19: combining antiviral and antiinflammatory treatments, The Lancet Infectious Diseases
Villoutreix, Beaune, Tamouza, Prevention of COVID-19 by drug repurposing: rationale from drugs prescribed for mental disorders, Drug Discovery Today
Williamson, Walker, Bhaskaran, OpenSAFELY: factors associated with COVID-19-related hospital death in the linked electronic health records of 17 million adult NHS patients, MedRxiv
Yoshida, Solomon, Kim, Active-comparator design and new-user design in observational studies, Nature Reviews Rheumatology
Zhang, Wu, Li, The cytokine release syndrome (CRS) of severe COVID-19 and interleukin-6 receptor (IL-6R) antagonist tocilizumab may be the key to reduce the mortality, International journal of antimicrobial agents
Zhou, Yu, Du, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, The Lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.10.23.20154302",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/2020.10.23.20154302",
"abstract": "<jats:title>ABSTRACT</jats:title><jats:sec><jats:title>Objective</jats:title><jats:p>To examine the association between hydroxyzine use and mortality in patients hospitalized for COVID-19, based on its anti-inflammatory and antiviral properties.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Design</jats:title><jats:p>Multicenter observational retrospective cohort study.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Setting</jats:title><jats:p>Greater Paris University hospitals, France.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Participants</jats:title><jats:p>7,345 adults hospitalized for COVID-19 between 24 January and 1 April 2020, including 138 patients (1.9%) who received hydroxyzine during the visit at a mean dose of 49.8 mg (SD=51.5) for an average of 22.4 days (SD=25.9).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Data source</jats:title><jats:p>Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris Health Data Warehouse.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Main outcome measures</jats:title><jats:p>The study endpoint was death. We compared this endpoint between patients who received hydroxyzine and those who did not in time-to-event analyses adjusting for patient characteristics (such as age, sex, and comorbidities), clinical and biological markers of disease’s severity, and use of other medications. The primary analysis was a multivariable Cox model with inverse probability weighting. Sensitivity analyses included a multivariable Cox model and a univariate Cox regression model in a matched analytic sample in a 1:1 ratio.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>Over a mean follow-up of 20.3 days (SD=27.5), 994 patients (13.5%) had a primary end-point event. The primary multivariable analysis with inverse probability weighting showed a significant association between hydroxyzine use and reduced mortality (HR, 0.42; 95% CI, 0.25 to 0.71; p=0.001) with a significant dose-effect relationship (HR, 0.10; 95% CI, 0.02 to 0.45; p=0.003). This association was similar in sensitivity analyses. In secondary analyses conducted among subsamples of patients, we found a significant association between hydroxyzine use and a faster decrease in biological inflammatory markers associated with COVID-19-related mortality, including neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), lymphocyte-to-C-reactive protein ratio (LCRP), and circulating interleukin 6 levels (IL-6) (all p<0.016), with a significant dose-effect relationship for NLR and LCRP (both p<0.037).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title><jats:p>In this retrospective observational study, hydroxyzine use was associated with reduced mortality in patients hospitalized for COVID-19. This association may be partially mediated by specific anti-inflammatory properties of H1 antihistamines. Double-blind controlled randomized clinical trials of hydroxyzine for COVID-19 are needed to confirm these results.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
27
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7890-1349",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Hoertel",
"given": "Nicolas",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sánchez",
"given": "Marina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vernet",
"given": "Raphaël",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beeker",
"given": "Nathanaël",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7142-6728",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Neuraz",
"given": "Antoine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Blanco",
"given": "Carlos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Olfson",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lemogne",
"given": "Cédric",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Meneton",
"given": "Pierre",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Daniel",
"given": "Christel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Paris",
"given": "Nicolas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gramfort",
"given": "Alexandre",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lemaitre",
"given": "Guillaume",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Salamanca",
"given": "Elisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bernaux",
"given": "Mélodie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bellamine",
"given": "Ali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burgun",
"given": "Anita",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Limosin",
"given": "Frédéric",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2020-10-27T18:01:01Z",
"timestamp": 1603821661000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-25T00:02:02Z",
"timestamp": 1669334522000
},
"group-title": "Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS)",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-20T15:34:07Z",
"timestamp": 1695224047001
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "medRxiv"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 8,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
27
]
]
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1101/2020.10.23.20154302",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "246",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
27
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.1101",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
27
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-1129-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2020103005500463000_2020.10.23.20154302v2.1",
"unstructured": "Hoertel N , Blachier M , Blanco C , et al. A stochastic agent-based model of the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic in France. Nature Medicine 2020:1–5."
},
{
"key": "2020103005500463000_2020.10.23.20154302v2.2",
"unstructured": "Gordon DE , Jang GM , Bouhaddou M , et al. A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing. Nature 2020:1–13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.encep.2020.04.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2020103005500463000_2020.10.23.20154302v2.3",
"unstructured": "Chevance A , Gourion D , Hoertel N , et al. Ensuring mental health care during the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic in France: a narrative review. L’encephale 2020."
},
{
"key": "2020103005500463000_2020.10.23.20154302v2.4",
"unstructured": "New insights into the pathophysiology of allergic rhinitis. Allergy & Asthma Proceedings; 2007."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000232571",
"article-title": "Characterization of anti-inflammatory properties and evidence for no sedation liability for the novel antihistamine SUN-1334H",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "56",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "International archives of allergy and immunology",
"key": "2020103005500463000_2020.10.23.20154302v2.5",
"volume": "151",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"article-title": "NF-κB signaling in inflammation",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Signal transduction and targeted therapy",
"key": "2020103005500463000_2020.10.23.20154302v2.6",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.drudis.2020.06.022",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2020103005500463000_2020.10.23.20154302v2.7",
"unstructured": "Villoutreix BO , Beaune PH , Tamouza R , et al. Prevention of COVID-19 by drug repurposing: rationale from drugs prescribed for mental disorders. Drug Discovery Today 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s1473-3099(20)30132-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020103005500463000_2020.10.23.20154302v2.8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30232-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2020103005500463000_2020.10.23.20154302v2.9",
"unstructured": "Liu Y , Yan L-M , Wan L , et al. Viral dynamics in mild and severe cases of COVID-19. The Lancet Infectious Diseases 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.07.09.20143339",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2020103005500463000_2020.10.23.20154302v2.10",
"unstructured": "Hoertel N , Sanchez Rico M , Vernet R , et al. Association between SSRI Antidepressant Use and Reduced Risk of Intubation or Death in Hospitalized Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: a Multicenter Retrospective Observational Study. medRxiv 2020:2020.07.09.20143339."
},
{
"key": "2020103005500463000_2020.10.23.20154302v2.11",
"unstructured": "Haut Conseil de la Sant é Publique. Statement on the management at home or in a care facility of suspected or confirmed Covid-19 patients. April 8, 2020. Statement on the management at home or in a care facility of suspected or confirmed Covid-19 patients."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25819",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2020103005500463000_2020.10.23.20154302v2.12",
"unstructured": "Lagunas-Rangel FA . Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and lymphocyte-to-C-reactive protein ratio in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A meta-analysis. Journal of medical virology 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105954",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2020103005500463000_2020.10.23.20154302v2.13",
"unstructured": "Zhang C , Wu Z , Li J-W , et al. The cytokine release syndrome (CRS) of severe COVID-19 and interleukin-6 receptor (IL-6R) antagonist tocilizumab may be the key to reduce the mortality. International journal of antimicrobial agents 2020."
},
{
"key": "2020103005500463000_2020.10.23.20154302v2.14",
"unstructured": "Williamson E , Walker AJ , Bhaskaran KJ , et al. OpenSAFELY: factors associated with COVID-19-related hospital death in the linked electronic health records of 17 million adult NHS patients. MedRxiv 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2020103005500463000_2020.10.23.20154302v2.15",
"unstructured": "Zhou F , Yu T , Du R , et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. The Lancet 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-020-06028-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2020103005500463000_2020.10.23.20154302v2.16",
"unstructured": "Ruan Q , Yang K , Wang W , et al. Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China. Intensive care medicine 2020:1–3."
},
{
"key": "2020103005500463000_2020.10.23.20154302v2.17",
"unstructured": "Hur K , Price CP , Gray EL , et al. Factors Associated With Intubation and Prolonged Intubation in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19. Otolaryngology--Head and Neck Surgery."
},
{
"journal-title": "Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv preprint",
"key": "2020103005500463000_2020.10.23.20154302v2.18",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"key": "2020103005500463000_2020.10.23.20154302v2.19",
"unstructured": "Jouffroy J , Feldman SF , Lerner I , et al. MedExt: combining expert knowledge and deep learning for medication extraction from French clinical texts."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/03610910902859574",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020103005500463000_2020.10.23.20154302v2.20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00001648-200009000-00011",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2020103005500463000_2020.10.23.20154302v2.21",
"unstructured": "Robins JM , Hernan MA , Brumback B. Marginal structural models and causal inference in epidemiology: LWW, 2000."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2012410",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2020103005500463000_2020.10.23.20154302v2.22",
"unstructured": "Geleris J , Sun Y , Platt J , et al. Observational study of hydroxychloroquine in hospitalized patients with Covid-19. New England Journal of Medicine 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2307/2281868",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020103005500463000_2020.10.23.20154302v2.23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2307/3314608",
"article-title": "Nonparametric standard errors and confidence intervals",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "139",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "canadian Journal of Statistics",
"key": "2020103005500463000_2020.10.23.20154302v2.24",
"volume": "9",
"year": "1981"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/pds.1200",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020103005500463000_2020.10.23.20154302v2.25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrrheum.2015.30",
"article-title": "Active-comparator design and new-user design in observational studies",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "437",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Nature Reviews Rheumatology",
"key": "2020103005500463000_2020.10.23.20154302v2.26",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/0003-4819-147-8-200710160-00010",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020103005500463000_2020.10.23.20154302v2.27"
}
],
"reference-count": 27,
"references-count": 27,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://medrxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2020.10.23.20154302"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Association between Hydroxyzine Use and Reduced Mortality in Patients Hospitalized for Coronavirus Disease 2019: Results from a multicenter observational study",
"type": "posted-content"
}