Regular Sports Participation as a Potential Predictor of Better Clinical Outcome in Adult Patients With COVID-19: A Large Cross-Sectional Study
et al., Journal of Physical Activity and Health, doi:10.1123/jpah.2020-0392, Dec 2020
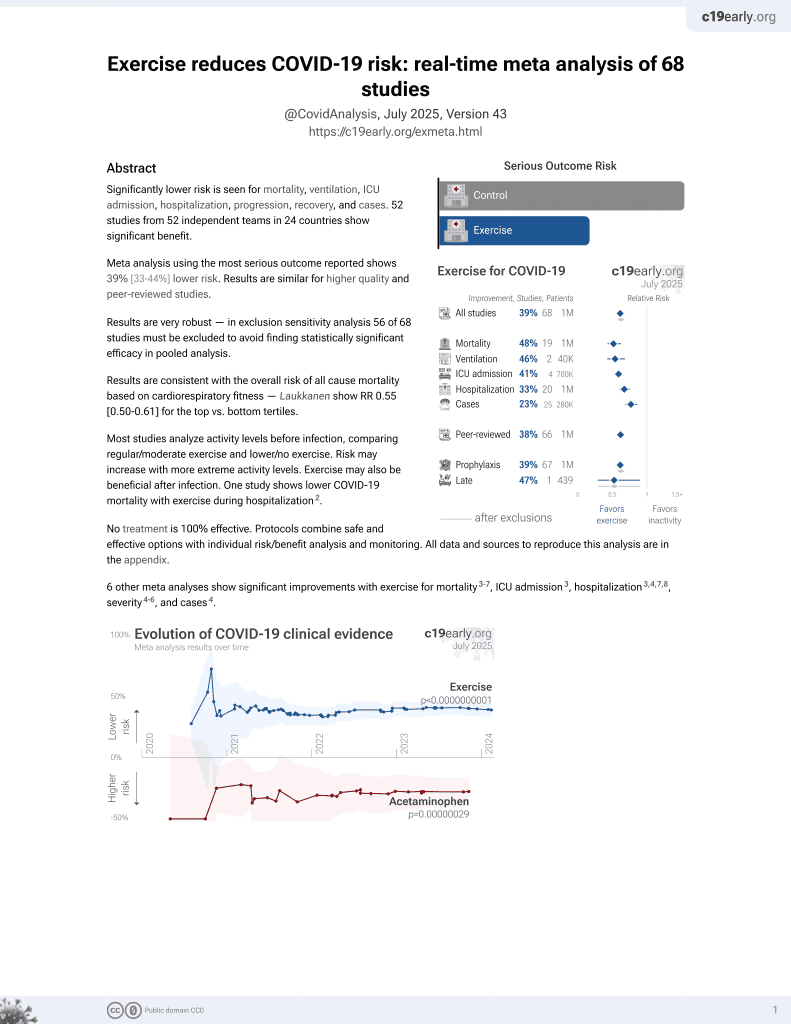
Exercise for COVID-19
9th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 68 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 4,694 COVID-19 patients in Iran, showing lower risk of hospitalization and mortality with regular sports participation.
|
risk of death, 88.8% lower, RR 0.11, p = 0.08, high activity levels 0 of 249 (0.0%), low activity levels 79 of 4,445 (1.8%), NNT 56, adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, multivariable.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 28.3% lower, RR 0.72, p = 0.04, high activity levels 30 of 249 (12.0%), low activity levels 878 of 4,445 (19.8%), adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, multivariable.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Halabchi et al., 1 Dec 2020, retrospective, Iran, peer-reviewed, 8 authors.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1123/jpah.2020-0392",
"ISSN": [
"1543-3080",
"1543-5474"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1123/jpah.2020-0392",
"abstract": "<jats:p><jats:bold>Purpose</jats:bold>: To compare the severity outcomes of COVID-19 disease between patients with and without regular sports participation. <jats:bold>Methods</jats:bold>: In a cross-sectional study, the authors investigated all patients who visited the emergency department of Imam Khomeini hospital with signs and symptoms of COVID-19 from February 20 to April 20, 2020. Then the authors assessed all patient outcomes (outpatient vs hospitalization or death). Finally, the authors compared the outcomes between athletes with regular sports participation and others, adjusting for confounding factors of age and sex. <jats:bold>Results</jats:bold>: Of all 4694 adult patients, 249 individuals (137 males and 112 females with mean [SD] age of 36.45 [9.77] y) had regular participation in different sport disciplines. Overall, 30 (12%) athletes were hospitalized or died (30 and 0, respectively) compared with 957 (21.5%) nonathletes (878 and 79, respectively). Athletes with regular sports participation were 1.49 times less likely to be hospitalized (<jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = .044). <jats:bold>Conclusions</jats:bold>: Regular sports participation may positively affect the clinical outcome, regardless of confounding factors of age and sex. The probability of hospitalization in athletes with regular sports participation was 33% lower than nonathletes. However, more longitudinal studies are needed to determine the causal effects.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Halabchi",
"given": "Farzin",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mazaheri",
"given": "Reza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sabeti",
"given": "Khashayar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yunesian",
"given": "Masoud",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alizadeh",
"given": "Zahra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmadinejad",
"given": "Zahra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aghili",
"given": "Seyed Mojtaba",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tavakol",
"given": "Zahra",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Journal of Physical Activity and Health"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2020-12-01T15:28:16Z",
"timestamp": 1606836496000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-05T07:14:31Z",
"timestamp": 1612509271000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-30T03:52:49Z",
"timestamp": 1648612369654
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 5,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "1543-3080"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "1543-5474"
}
],
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
1
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1"
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journals.humankinetics.com/view/journals/jpah/18/1/article-p8.xml",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://journals.humankinetics.com/downloadpdf/journals/jpah/18/1/article-p8.xml",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "100",
"original-title": [],
"page": "8-12",
"prefix": "10.1123",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Human Kinetics",
"reference-count": 60,
"references-count": 60,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journals.humankinetics.com/view/journals/jpah/18/1/article-p8.xml"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Orthopedics and Sports Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Regular Sports Participation as a Potential Predictor of Better Clinical Outcome in Adult Patients With COVID-19: A Large Cross-Sectional Study"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "18"
}