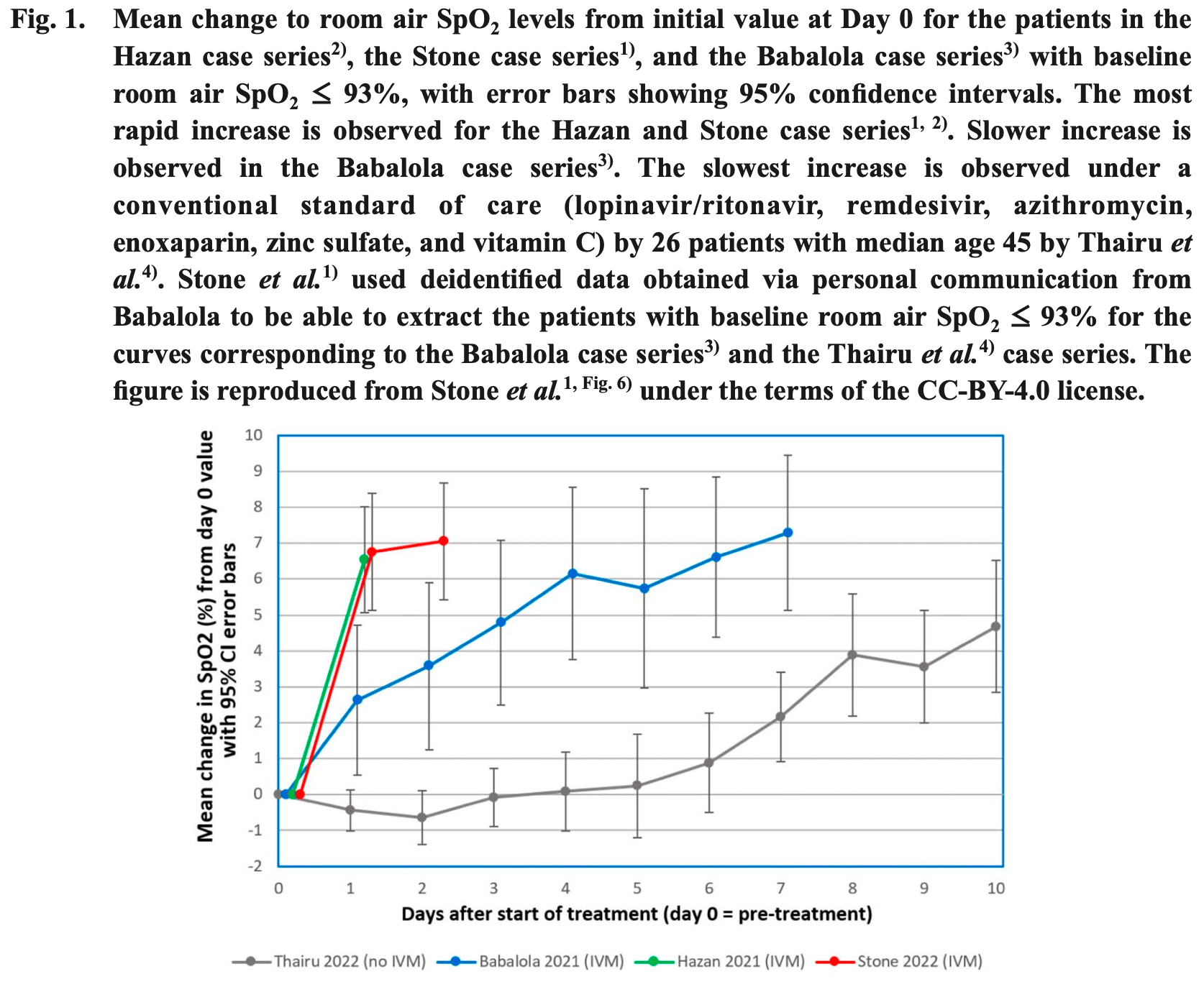
Critical appraisal of multidrug therapy in the ambulatory management of patients with COVID-19 and hypoxemia Part II: Causal inference using the Bradford Hill criteria
et al., The Japanese Journal of Antibiotics, doi:10.11553/antibiotics.78.1_35, Mar 2025
Vitamin C for COVID-19
6th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000076 from 73 studies, recognized in 22 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Critical appraisal of three case series totaling 119 COVID-19 patients with hypoxemia treated with ivermectin-based multidrug protocols in the United States, Zimbabwe, and Nigeria, showing reduced hospitalization and mortality. Authors apply Bradford Hill criteria to assess causality between treatment and outcomes. All patients survived and experienced rapid recovery of oxygen saturation within 24-48 hours of treatment initiation. Authors argue that the treatment protocols satisfy Bradford Hill criteria for temporality, strength of association, biological gradient (dose responsiveness), biological plausibility (plausible mechanism), coherence, consistency (replicability), and analogy (similarity), thus providing grounds for causal inference between the treatment and improved patient outcomes. The multidrug protocols involved combinations of ivermectin, doxycycline, zinc, vitamins C and D, and other treatments.
Gkioulekas et al., 25 Mar 2025, peer-reviewed, 3 authors.
Contact: eleftherios.gkioulekas@utrgv.edu.
Critical appraisal of multidrug therapy in the ambulatory management of patients with COVID-19 and hypoxemia Part II: Causal inference using the Bradford Hill criteria
doi:10.11553/antibiotics.78.1_35
We continue the critical appraisal of three published case series of 119 COVID-19 patients with hypoxemia, treated in the United States, Zimbabwe, and Nigeria with similar ivermectin-based multidrug treatments, to assess the available evidence supporting a causal relationship between treatment and reduction in hospitalizations and mortality. A narrative review was conducted to assess the Bradford Hill criteria for a causal association. We used a previously proposed refinement of the Bradford Hill criteria that reorganized them into three categories of direct, mechanistic, and parallel evidence. The efficacy of the two most aggressive ivermectin-based multidrug protocols is supported by the Bradford Hill criteria for temporality, strength of association, biological gradient, biological plausibility, coherence, consistency, and analogy. The causal relation between the treatment of hypoxemic COVID-19 patients using these protocols and the reduction in hospitalizations and mortality is supported as an inference to the best explanation.
Abbreviations ACE2, Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2; AgNP, silver nanoparticles; CFR, Case Fatality Rate; CD147/EMMPRIN, Cluster of differentiation 147 / extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer; COVID-19, Coronavirus Disease 2019; DPP4/CD26, Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 / cluster of differentiation 26; IL-6, Interleukin 6; IMP, importin; MERS, Middle Eastern Respiratory Syndrome; MMP-9, matrix metalloproteinase-9; NF-κB, Nuclear factor kappa B; RDRP, RNA Dependent RNA Polymerase; S1-NTD, S1-N-Terminal Domain; S1-RBD, S1 Receptor Binding Domain; PVP, poly (N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone); ROS, Reactive Oxygen Species; RAS, Renin Angiotensis System; SARS, Sudden Acute Respiratory Syndrome; SARS-CoV-2, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2; SpO 2 , Peripheral oxygen saturation; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha.
Ethics approval and consent to participate Not applicable. The study is an analysis of previously published data.
Conflict of interest Peter McCullough is the part-time Chief Scientific Officer for the Wellness Company, Boca Raton, Florida, United States of America, which had no role in the study or the writing of the manuscript. Eleftherios Gkioulekas is affiliated with the School of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences at The University of Texas Rio Grande Valley, which regularly invites visiting scholars from other academic institutions and directly receives donations to fund scholarships, however he has not himself hosted any visiting scholars or received a..
References
Adjei, Hong, Molinari, Mortality risk among patients hospitalized primarily for COVID-19 during the Omicron and Delta variant pandemic periods-United States, April 2020-June 2022, MMWR
Akinbolagbe, Otrofanowei, Akase, Predictors and outcomes of COVID-19 patients with hypoxemia in Lagos, Nigeria, J Pan Afr Thorac Soc
Aldous, Dancis, Dancis, Oldfield, Wheel replacing pyramid: Better paradigm representing totality of Evidence-Based Medicine, Ann Glob Health
Aldous, Gkioulekas, Oldfield, Ivermectin, Varon et al., None
Almanza-Reyes, Moreno, Plascencia-Lopez, Evaluation of silver nanoparticles for the prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infection in health workers: in vitro and in vivo, PLoS ONE
Aminpour, Cannariato, Safaeeardebili, In silico analysis of the multi-targeted mode of action of ivermectin and related compounds, Computation
Anglemyer, Horvath, Bero, Healthcare outcomes assessed with observational study designs compared with those assessed in randomized trials, Cochrane Database Syst Rev
Annunziata, Coppola, Carannante, Home management of patients with moderate or severe respiratory failure secondary to COVID-19, using remote monitoring and oxygen with or without HFNC, Pathogens
Arakawa, Neault, Tajmir-Riahi, Silver(i) complexes with DNA and RNA studied by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and capillary electrophoresis, Biophys J
Arefin, Povidone iodine (PVP-I) oro-nasal spray: An effective shield for COVID-19 protection for Health Care Worker (HCW), for all, Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg
Asghar, Yousuf, Shoaib, Asghar, Antibacterial, anticoagulant and cytotoxic evaluation of biocompatible nanocomposite of chitosan loaded green synthesized bioinspired silver nanoparticles, Int J Biol Macromol
Babalola, Ajayi, The place of ivermectin in the management of Covid-19: State of the evidence, Med Res Arch, doi:10.18103/mra.v11i4.3778
Babalola, Ajayi, Yunusa, Ndanusa, Ogedengbe et al., Ivermectin is associated with increase in SpO 2 in hypoxemic SARS-CoV-2 patients: pharmacodynamic profile and correlates, J Clin Chem and Lab Med
Babalola, Ndanusa, Ajayi, Ogedengbe, Thairu et al., A randomized controlled trial of ivermectin monotherapy versus hydroxychloroquine, ivermectin, and azithromycin combination therapy in COVID-19 patients in Nigeria, J Infect Dis Epidemiol
Babalola, None
Balmforth, Swales, Silpa, Evaluating the efficacy and safety of a novel prophylactic nasal spray in the prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infection: a multi-centre, double blind, placebocontrolled, randomised trial, J Clin Virol
Basu, Khawaja, Rizvi, Sanchez-Gonzalez, Ferrer, Evaluation of patient experience for a computationally-guided intranasal spray protocol to augment therapeutic penetration: implications for effective treatments for COVID-19, rhinitis, and sinusitis, Med Res Arch, doi:10.18103/mra.v10i4.2774
Benson, Hartz, A comparison of observational studies and randomized, controlled trials, NEJM
Biancatelli, Berrill, Marik, The antiviral properties of vitamin C, Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther
Boretti, Banik, More widespread use of ivermectin for the treatment of COVID-19 infection could have saved many, Curr Organocatal
Borody, Clancy, Combination therapy for COVID-19 based on ivermectin in an Australian population
Borsche, Glauner, Mendel, COVID-19 Mortality risk correlates inversely with vitamin D3 status, and a mortality rate close to zero could theoretically be achieved at 50 ng/mL 25(OH) D3: results of a systematic review and meta-analysis, Nutrients
Boschi, Scheim, Bancod, SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induces hemagglutination: implications for COVID-19 morbidities and therapeutics and for vaccine adverse effects, Int J Mol Sci
Bramante, Huling, Tignanelli, Randomized trial of metformin, ivermectin, and fluvoxamine for COVID-19, NEJM
Bryant, Lawrie, Dowswell, Ivermectin for prevention and treatment of COVID-19 infection: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and trial sequential analysis to inform clinical guidelines, Am J Ther
Buonfrate, Chesini, Martini, High dose ivermectin for the early treatment of COVID-19 (COVER study): a randomised, double-blind, multicentre, phase II, dose-finding, proof of concept clinical trial, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Caly, Druce, Catton, Jans, Wagstaff, The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, Antiviral Res
Carvallo, Hirsch, Ivermectin and herd immunity in SARS COV2 pandemic from local experience to broader possibility, Clin Immunol Res
Carvallo, Hirsch, Safety and efficacy of the combined use of ivermectin, dexamethasone, enoxaparin and aspirina against COVID-19. the I.D.E.A. protocol, J Clin Trials
Castillo, Costa, Barrios, Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: a pilot randomized clinical study, J Steroid Biochem Molec Biol
Chaccour, Casellas, Matteo, The effect of early treatment with ivermectin on viral load, symptoms and humoral response in patients with non-severe COVID-19: a pilot, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial, EClinicalMedicine
Chamie, Hibberd, Scheim, COVID-19 excess deaths in Peruʼs 25 states in 2020: nationwide trends, confounding factors, and correlations with the extent of ivermectin treatment by state, Cureus
Chen, Wu, Guo, Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019, J Clin Invest
Chetty, Elucidating the pathogenesis and Rx of COVID reveals a missing element, Mod Med
Choudhury, Shabnam, Ahsan, Kabir, Khan et al., Effect of 1% povidone iodine mouthwash/gargle, nasal and eye drop in COVID-19 patient, Bioresearch Comm
Dayyab, Bashir, Sulaiman, Determinants of mortality among hospitalized patients with COVID-19 during first and second waves of the pandemic: a retrospective cohort study from an isolation center in Kano, Nigeria, PLoS ONE
Deaton, Cartwright, Understanding and misunderstanding randomized controlled trials, Soc Sci Med
Derouiche, Chetehouna, Djouadi, Boulaares, Guemari, The possible mechanisms of silver nanoparticles against Sars-CoV 2, Front Biomed Technol
Derwand, Scholz, Does zinc supplementation enhance the clinical efficacy of chloroquine/ hydroxychloroquine to win todayʼs battle against COVID-19?, Med Hypotheses
Derwand, Scholz, Zelenko, COVID-19 outpatients-Early risk-stratified treatment with zinc plus low dose hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin: a retrospective case series study, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Fazio, Bellavite, Zanolin, Mccullough, Pandolfi et al., Retrospective study of outcomes and hospitalization rates of patients in Italy with a confirmed diagnosis of early COVID-19 and treated at home within 3 days or after 3 days of symptom onset with prescribed and non-prescribed treatments between November 2020 and August 2021, Med Sci Monit
Gautret, Lagier, Parola, Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Gkioulekas, Data and materials: critical appraisal of multi-drug therapy in the ambulatory management of patients with COVID-19 and hypoxemia, doi:10.6084/m9.figshare.24329611
Gkioulekas, Mccullough, Aldous, Critical appraisal of multi-drug therapy in the ambulatory management of patients with COVID-19 and hypoxemia. Part 1. Evidence supporting the strength of association, Jpn J Antibiot
Gkioulekas, Mccullough, Use of hydroxychloroquine in multidrug protocols for SARS-CoV-2, Tasman Med J
Gkioulekas, Mccullough, Zelenko, Statistical analysis methods applied to early outpatient COVID-19 treatment case series data, COVID
Gkioulekas, Rendell, Risch, Stricker, An open letter to the American Board of Medical Specialties and the Federation of State Medical Boards: the destruction of member Boardsʼ credibility, J Am Phys Surg
Gonzalez, Gamez, Enciso, Efficacy and safety of ivermectin and hydroxychloroquine in patients with severe COVID-19: a randomized controlled trial, Infect Dis Rep
Harman, The inference to the best explanation, Philos Rev
Hashim, Maulood, Ali, Controlled randomized clinical trial on using ivermectin with doxycycline for treating COVID-19 patients in Baghdad, Iraq J Med Sci
Hayward, Yu, Little, Ivermectin for COVID-19 in adults in the community (PRINCI-PLE): an open, randomised, controlled, adaptive platform trial of short-and longer-term outcomes, J Infect
Hazan, Gunaratne, Effectiveness of ivermectin-based multidrug therapy in severely hypoxic, ambulatory COVID-19 patients, Future Microbiol
Hazan, Vidal, Gkioulekas, Rapid recovery of peripheral oxygen saturation in hypoxic COVID-19 patients with ivermectin/doxycycline/zinc multidrug therapy, doi:10.6084/m9.figshare.28592639
Hill, The environment and disease: Association or causation?, Proc R Soc Med
Howick, Glasziou, Aronson, The evolution of evidence hierarchies: what can Bradford Hillʼs ʼguidelines for causationʼ contribute?, JRSM
Huijghebaert, Parviz, Rabago, Saline nasal irrigation and gargling in COVID-19: a multidisciplinary review of effects on viral load, mucosal dynamics, and patient outcomes, Front Public Health
Jassat, Mudara, Ozougwu, Difference in mortality among individuals admitted to hospital with COVID-19 during the first and second waves in South Africa: a cohort study, Lancet Glob Health
Jeremiah, Miyakawa, Morita, Yamaoka, Ryo, Potent antiviral effect of silver nanoparti-cles on SARS-CoV-2, Biochem and Biophys Res Commun
Jothimani, Kailasam, Danielraj, COVID-19: poor outcomes in patients with zinc deficiency, Int J Infect Dis
Kerr, Baldi, Lobo, Regular use of ivermectin as prophylaxis for COVID-19 led up to a 92% reduction in COVID-19 mortality rate in a dose-response manner: results of a prospective observational study of a strictly controlled population of 88,012 subjects, Cureus
Kerr, Cadegiani, Baldi, Ivermectin prophylaxis used for COVID-19 reduces COVID-19 infection and mortality rates: a 220,517-subject, populational-level retrospective citywide, Cureus
Kow, Hasan, Ramachandram, The effect of vitamin C on the risk of mortality in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Inflammopharmacology
Krolewiecki, Lifschitz, Moragas, Antiviral effect of high-dose ivermectin in adults with COVID-19: a proof-of-concept randomized trial, EClinicalMedicine
Lehrer, Rheinstein, Ivermectin docks to the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain attached to ACE2, Vivo
Lesgards, Cerdan, Perronne, Toxicity of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein from the virus and produced from COVID-19 mRNA or adenoviral DNA vaccines, Arch Microbiol Immunol
Lim, Hor, Tay, Efficacy of ivermectin treatment on disease progression among adults with mild to moderate COVID-19 and comorbidities: the I-TECH randomized clinical trial, JAMA Intern Med
Lopez-Medina, Lopez, Hurtado, Effect of ivermectin on time to resolution of symptoms among adults with mild COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Luceri, Francese, Lembo, Ferraris, Balagna, Silver nanoparticles: review of antiviral properties, mechanism of action and applications, Microorganisms
Madamombe, Shambira, Masoja, Factors associated with COVID-19 fatality among patients admitted in Mashonaland West Province, Zimbabwe 2020-2022: A secondary data analysis, Pan Afr Med J
Mahmud, Rahman, Alam, Ivermectin in combination with doxycycline for treating COVID-19 symptoms: a randomized trial, J Int Med Res
Malek, Granwehr, Kontoyiannis, Doxycycline as a potential partner of COVID-19 therapies, IDCases
Mathieu, Ritchie, Rodes-Guirao, Coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19). Our World in Data
Mccullough, Alexander, Armstrong, Multifaceted highly targeted sequential multi-78-1 Mar. 2025 drug treatment of early ambulatory high-risk SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19), Rev Cardiovasc Med
Mccullough, Innovative early sequenced multidrug therapy for SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infection to reduce hospitalization and death, Int J Med Sci Clin Invent
Mccullough, Kelly, Ruocco, Pathophysiological basis and rationale for early outpatient treatment of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infection, Am J Med
Mccullough, Oskoui, Early multidrug regimens in new potentially fatal medical problems, Rev Cardiovasc Med
Mcgonagle, Bridgewood, Meaney, A tricompartmental model of lung oxygenation disruption to explain pulmonary and systemic pathology in severe COVID-19, Lancet Respir Med
Mercola, Grant, Wagner, Evidence regarding vitamin D and risk of COVID-19 and its severity, Nutrients
Million, Lagier, Tissot-Dupont, Early treatment with hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin in 10,429 COVID-19 outpatients: a monocentric retrospective cohort study, Rev Cardiovasc Med
Mohan, Tiwari, Suri, Single-dose oral ivermectin in mild and moderate COVID-19 (RIVET-COV): a single-centre randomized, placebo-controlled trial, J Infect Chemother
Naggie, Boulware, Lindsell, Effect of higher-dose ivermectin for 6 days vs. placebo on time to sustained recovery in outpatients with COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Naggie, Boulware, Lindsell, Effect of ivermectin vs. placebo on time to sustained recovery in outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Nishihara, Eguchi, Zhou, Silver ion (Ag + ) formulations with virucidal efficacy against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)
Osman, Farouk, Osman, Abdrabou, Longitudinal assessment of chest computerized tomography and oxygen saturation for patients with COVID-19, Egypt J Radiol Nucl Med
Palazzuoli, Beltrami, Mccullough, Acute COVID-19 management in heart failure patients: a specific setting requiring detailed inpatient and outpatient hospital care, Biomedicines
Parry, Lefringhausen, Turni, ʼSpikeopathyʼ: COVID-19 spike protein is pathogenic, from both virus and vaccine mRNA, Biomedicines
Phillips, Goodman, The missed lessons of Sir Austin Bradford Hill, Epidemiol Perspect & Innov
Pilaquinga, Morey, Torres, Seqqat, Pina, Silver nanoparticles as a potential treatment against SARS-CoV-2: a review, Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol
Popp, Reis, Schieber, Ivermectin for preventing and treating COVID-19, Cochrane Database Syst Rev
Prabhakaran, Singh, Kondal, Cardiovascular risk factors and clinical outcomes among patients hospitalized with COVID-19: findings from the World Heart Federation COVID-19 study, Glob Heart
Procter, Ross, Pickard, Smith, Hanson et al., Clinical outcomes after early ambulatory multidrug therapy for high-risk SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infection, Rev Cardiovasc Med
Procter, Ross, Pickard, Smith, Hanson et al., Early ambulatory multidrug therapy reduces hospitalization and death in high-risk patients with SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19), Int J Innov Res Med Sci
Qin, Xu, Chen, Effects of vitamin C supplements on clinical outcomes and hospitalization duration for patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): a systematic review and meta-analysis, Nutr Rev
Rajter, Sherman, Fatteh, Vogel, Sacks et al., Use of ivermectin is associated with lower mortality in hospitalized patients with Coronavirus Disease, CHEST
Ravikirti, Pattadar, Evaluation of ivermectin as a potential treatment for mild to moderate COVID-19: a double-blind randomized placebo controlled trial in Eastern India, J Pharm Pharm Sci
Reina, Peng, Jacquemin, Andrade, Bianco, Hard nanomaterials in time of viral pandemics, ACS Nano
Reis, Silva, Silva, Effect of early treatment with ivermectin among patients with COVID-19, NEJM
Rheingold, Raval, Gordon, Hardigan, Zinc supplementation associated with a decrease in mortality in COVID-19 patients: a meta-analysis, Cureus
Risch, Early outpatient treatment of symptomatic, high-risk COVID-19 patients that should be ramped-up immediately as key to the pandemic crisis, Am J Epidemiol
Risch, Plausibility, not science, has dominated public discussions of the COVID pandemic, Am J Econ Sociol
Rizzo, Ivermectin, antiviral properties and COVID-19: a possible new mechanism of action, Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol
Robba, Battaglini, Ball, Distinct phenotypes require distinct respiratory management strategies in severe COVID-19, Respir Physiol Neurobiol
Santin, Scheim, Mccullough, Yagisawa, Borody, Ivermectin: a multifaceted drug of Nobel prize-honoured distinction with indicated efficacy against a new global scourge, COVID-19, New Microbes New Infect
Scheim, A deadly embrace: Hemagglutination mediated by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein at its 22 N-glycosylation sites, red blood cell surface sialoglycoproteins, and antibody, Int J Mol Sci
Scheim, Aldous, Osimani, Fordham, Hoy, When characteristics of clinical trials require Per-Protocol as well as Intention-To-Treat outcomes to draw reliable conclusions: three examples, J Clin Med
Scheim, Hibberd, Chamie-Quintero, ; -Medina, switched ivermectin (IVM) and placebo doses, failure of blinding, widespread IVM sales OTC in Cali, and nearly identical AEs for the IVM and control groups, doi:10.31219/osf.io/u7ewz
Scheim, Parry, Rabbolini, Back to the basics of SARS-CoV-2 biochemistry: microvascular occlusive glycan bindings govern its morbidities and inform therapeutic responses, Viruses
Scheim, Vottero, Santin, Hirsh, Sialylated glycan bindings from SARS-CoV-2 spike protein to blood and endothelial cells govern the severe morbidities of COVID-19, Int J Mol Sci
Skalny, Rink, Ajsuvakova, Zinc and respiratory tract infections: perspectives for COVID-19 (Review), Int J Mol Med
Soler, De Mendoza, Cuello, Intranasal xylitol for the treatment of COVID-19 in the outpatient setting: a pilot study, Cureus
Stone, Aldous, An ethical clinical, and regulatory analysis: Ivermectin and COVID-19 treatment in Zimbabwe
Stone, Gill, Zimbabwe rollout of Silver and Ivermectin Protocol
Stone, Gkioulekas, The Stone/Gill SID treatment protocol for COVID-19
Stone, Ndarukwa, Scheim, Changes in SpO 2 on room air for 34 severe COVID-19 patients after ivermectin-based combination treatment: 62% normalization within 24 hours, Biologics
Stone, Ndarukwa, Scheim, Rapid increase of SpO 2 on room air for 34 severe COVID-19 patients after ivermectin-based combination treatment: 55-62% normalization within 12-24 hours, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-1048271/v1
Stone, None
Tabatabaeizadeh, Zinc supplementation and COVID-19 mortality: a meta-analysis, Eur J Med Res
Thairu, Babalola, Ajayi, Ndanusa, Ogedengbe et al., A comparison of ivermectin and non ivermectin based regimen for COVID-19 in Abuja: effects on virus clearance, days-todischarge and mortality, J Pharm Res Int
Tran, Pham, Nguyen, Therapeutic efficacy of AFree oral spray on the symptoms and course of moderate and severe COVID-19 in the field hospital, Vivo
Trejo, Castaneda, Rodriguez, Hydrogen peroxide as an adjuvant therapy for COVID-19: a case series of patients and caregivers in the Mexico City metropolitan area, Evid Based Complement Alternat Med
Vallejos, Zoni, Bangher, Ivermectin to prevent hospitalizations in patients with COVID-19 (IVERCOR-COVID19) a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, BMC Infect Dis
Velthuis, Van Den Worm, Sims, Baric, Snijder et al., Zn 2+ inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture, PLoS Pathog
Wang, Liu, Ma, Silver nanoparticles induced RNA polymerase-silver binding and RNA transcription inhibition in erythroid progenitor cells, ACS Nano
Ward, The role of causal criteria in causal inferences: Bradford Hillʼs ʻaspects of associationʼ, Epidemiol Perspect & Innov
Wessels, Rolles, Rink, The potential impact of zinc supplementation on COVID-19 pathogenesis, Front Immunol
Wieler, Vittos, Mukherjee, Sarkar, Reduction in the COVID-19 pneumonia case fatality rate by silver nanoparticles: a randomized case study, Heliyon
Wong, Viswanathan, Wang, Sun, Clark et al., Current and future developments in the treatment of virus-induced hypercytokinemia, Future Med Chem
Xu, Tang, Liu, Wang, Liu, Evaluation of the adjuvant effect of silver nanoparticles both in vitro and in vivo, Toxicol Lett
Yagisawa, Foster, Hanaki, Omura, Global trends in clinical studies of ivermectin in COVID-19 -Part 2, Jpn J Antibiot
Yagisawa, Foster, Hanaki, Omura, Global trends in clinical studies of ivermectin in COVID-19, Jpn J Antibiot
Yates, Newman, Oshry, Glassman, Leone et al., Doxycycline treatment of highrisk COVID-19-positive patients with comorbid pulmonary disease, Ther Adv Respir Dis
Zachar, Nanomedicine formulations for respiratory infections by inhalation delivery: covid-19 and beyond, Med Hypotheses
Zaidi, Dehgani-Mobaraki, The mechanisms of action of ivermectin against SARS-CoV-2. An extensive review, J Antibiot
Zbarsky, Thomas, Greenfield, Bioactivity of a peptide derived from acetylcholinesterase: involvement of an ivermectin-sensitive site on the alpha 7 nicotinic receptor, Neurobiol Dis
Zelenko, Correspondence from Dr Vladimir Zelenko on Treatment of COVID-19
Zelenko, Hamachek, Zelenko: How To Decapitate The Serpent
Zelenko, To all medical professionals around the world
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.11553/antibiotics.78.1_35",
"ISSN": [
"03682781",
"03682781",
"21865477"
],
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.11553/antibiotics.78.1_35",
"author": [
{
"family": "Gkioulekas, Ph.D.",
"given": "Eleftherios"
},
{
"family": "McCullough, M.D., M.P.H.",
"given": "Peter A."
},
{
"family": "Aldous, Ph.D.",
"given": "Colleen"
}
],
"container-title": "The Japanese Journal of Antibiotics",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
25
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"number": "1",
"page": "35-68",
"publisher": "Japan Antibiotics Research Association",
"title": "Critical appraisal of multidrug therapy in the ambulatory management of patients with COVID-19 and hypoxemia Part II: Causal inference using the Bradford Hill criteria",
"volume": "78"
}
gkioulekas5
