Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial
et al., International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949, Mar 2020 (preprint)
HCQ for COVID-19
1st treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 423 studies, used in 59 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
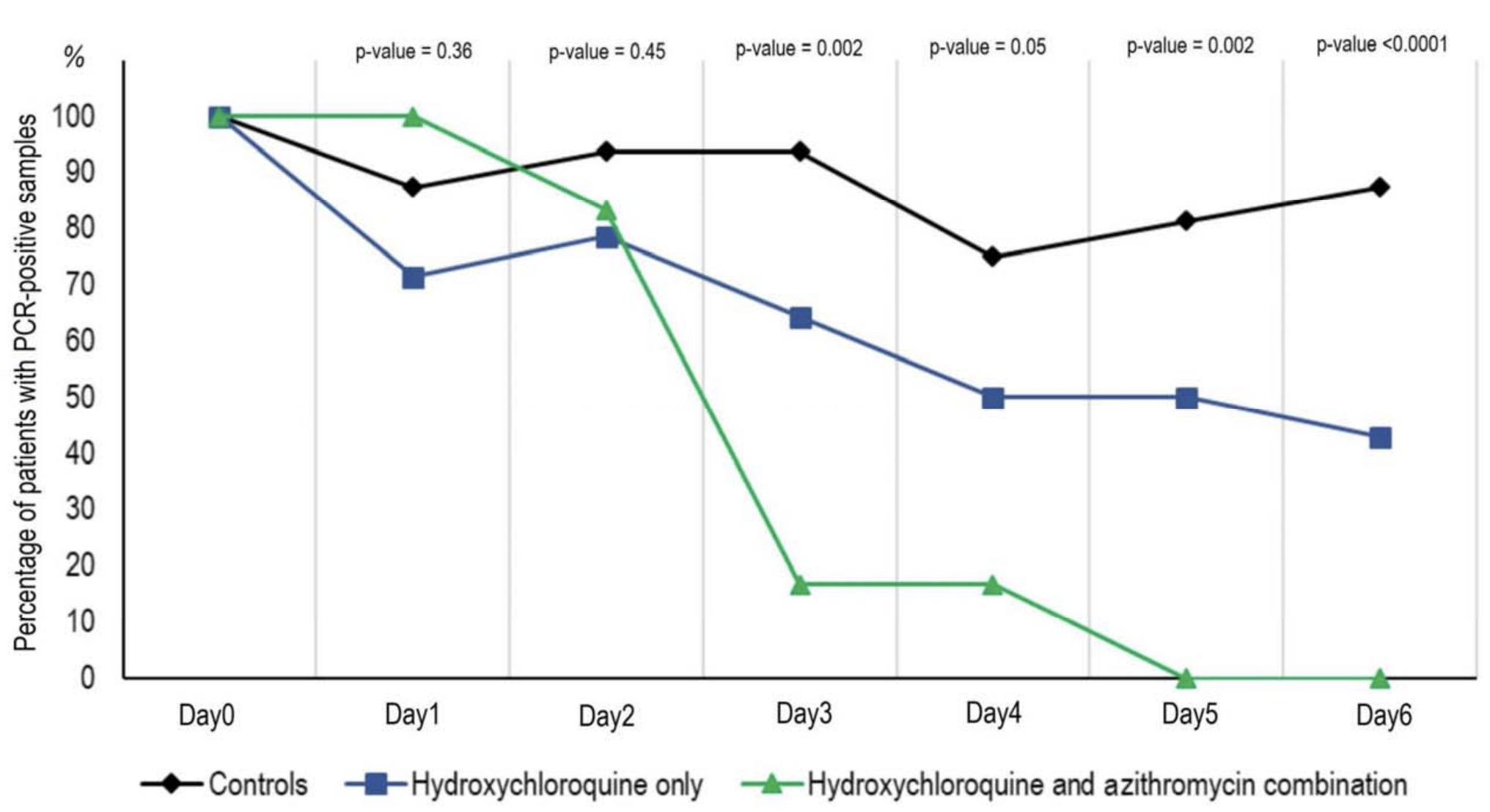
HCQ was significantly associated with reduction / elimination of viral load, which was enhanced with AZ. Responses to this paper have raised methodological issues1-3. There are unadjusted differences between groups.
Despite the limitations, this early observational study was an important part of the early analysis of SARS-CoV-2 treatment efficacy, including detailed daily evolution of PCR positivity. This study should be viewed in the context of the series of studies from this group. An update to this paper, including originally excluded patients, confirms the effectiveness of HCQ+AZ on viral clearance and early discharge4. Also see5 and the response from the authors6.
This paper was retracted in 2024. The retraction appears highly political. While there are some reasonable concerns, similar concerns apply to many other papers which have not been targeted. This study is not included in meta analysis. See 7 for a response to the retraction.
|
risk of no virological cure at day 6, 66.0% lower, RR 0.34, p = 0.001, treatment 6 of 20 (30.0%), control 14 of 16 (87.5%), NNT 1.7.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Gautret et al., 17 Mar 2020, prospective, France, peer-reviewed, 18 authors, average treatment delay 4.1 days, dosage 200mg tid days 1-10.
Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial
International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949
Background: Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine have been found to be efficient on SARS-CoV-2, and reported to be efficient in Chinese COV-19 patients. We evaluate the effect of hydroxychloroquine on respiratory viral loads. Patients and methods: French Confirmed COVID-19 patients were included in a single arm protocol from early March to March 16 th , to receive 600mg of hydroxychloroquine daily and their viral load in nasopharyngeal swabs was tested daily in a hospital setting. Depending on their clinical presentation, azithromycin was added to the treatment. Untreated patients from another center and cases refusing the protocol were included as negative controls. Presence and absence of virus at Day6-post inclusion was considered the end point. Results: Six patients were asymptomatic, 22 had upper respiratory tract infection symptoms and eight had lower respiratory tract infection symptoms. Twenty cases were treated in this study and showed a significant reduction of the viral carriage at D6-post inclusion compared to controls, and much lower average carrying duration than reported in the litterature for untreated patients. Azithromycin added to hydroxychloroquine was significantly more efficient for virus elimination. Conclusion: Despite its small sample size, our survey shows that hydroxychloroquine treatment is significantly associated with viral load reduction/disappearance in COVID-19 patients and its effect is reinforced by azithromycin.
Declarations
Supplementary material Supplementary material associated with this article can be found, in the online version, at doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020. 105949 .
References
Amrane, Tissot-Dupont, Doudier, Eldin, Hocquart et al., Rapid viral diagnosis and ambulatory management of suspected COVID-19 cases presenting at the infectious diseases referral hospital in Marseille, France, -January 31st to March 1st, 2020: A respiratory virus snapshot, Travel Med Infect Dis
Armstrong, Richez, Raoult, Chabriere, Simultaneous UHPLC-UV analysis of hydroxychloroquine, minocycline and doxycycline from serum samples for the therapeutic drug monitoring of Q fever and Whipple's disease, B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci
Bacharier, Guilbert, Mauger, Boehmer, Beigelman et al., Early administration of azithromycin and prevention of severe lower respiratory tract illnesses in preschool children with a history of such illnesses: A randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2015.13896
Biot, Daher, Chavain, Fandeur, Khalife et al., Design and synthesis of hydroxyferroquine derivatives with antimalarial and antiviral activities, J Med Chem
Bosseboeuf, Aubry, Nhan, De Pina, Rolain et al., Azithromycin inhibits the replication of Zika virus, J Antivirals Antiretrovirals, doi:10.4172/1948-5964.1000173
Colson, Rolain, Lagier, Brouqui, Raoult, Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine as available weapons to fight COVID-19, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Colson, Rolain, Raoult, Chloroquine for the 2019 novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, Int J Antimicrob Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105923
Gao, Tian, Yang, Breakthrough: Chloroquine phosphate has shown apparent efficacy in treatment of COVID-19 associated pneumonia in clinical studies, Biosci Trends, doi:10.5582/bst.2020.01047
Jie, He, Xi, Zhi, None, doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-0939.2020.03.009
Lagier, Raoult, Whipple's disease and Tropheryma whipplei infections: when to suspect them and how to diagnose and treat them, Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi, doi:10.1097/QCO.0000000000000489
Lai, Shih, Ko, Tang, Hsueh, Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19): The epidemic and the challenges, Int J Antimicrob Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105924
Madrid, Panchal, Warren, Shurtleff, Endsley et al., Evaluation of Ebola Virus Inhibitors for Drug Repurposing, ACS Infect Dis, doi:10.1021/acsinfecdis.5b00030
Marmor, Kellner, Lai, Melles, Mieler et al., Recommendations on Screening for Chloroquine and Hydroxychloroquine Retinopathy (2016 Revision), Ophthalmology Jun, doi:10.1016/j.ophtha.2016.01.058
Raoult, Houpikian, Dupont, Riss, Arditi-Djiane et al., Treatment of Q fever endocarditis: comparison of 2 regimens containing doxycycline and ofloxacin or hydroxychloroquine, Arch Intern Med
Retallack, Lullo, Arias, Knopp, Laurie et al., Zika virus cell tropism in the developing human brain and inhibition by azithromycin, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
Wang, Cao, Zhang, Yang, Liu et al., Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro, Cell Res
Wang, Wang, Ye, Liu, A review of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) based on current evidence, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.2648
Yao, Ye, Zhang, Cui, Huang et al., Vitro Antiviral Activity and Projection of Optimized Dosing Design of Hydroxychloroquine for the Treatment of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa237
Zhou, Yu, Du, Fan, Liu et al., Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949",
"ISSN": [
"0924-8579"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949",
"alternative-id": [
"S0924857920300996"
],
"article-number": "105949",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2020 Published by Elsevier B.V."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gautret",
"given": "Philippe",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lagier",
"given": "Jean-Christophe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parola",
"given": "Philippe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hoang",
"given": "Van Thuan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Meddeb",
"given": "Line",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mailhe",
"given": "Morgane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Doudier",
"given": "Barbara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Courjon",
"given": "Johan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Giordanengo",
"given": "Valérie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vieira",
"given": "Vera Esteves",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tissot Dupont",
"given": "Hervé",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Honoré",
"given": "Stéphane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Colson",
"given": "Philippe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chabrière",
"given": "Eric",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "La Scola",
"given": "Bernard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rolain",
"given": "Jean-Marc",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brouqui",
"given": "Philippe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Raoult",
"given": "Didier",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents",
"container-title-short": "International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
3,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2020-03-20T16:28:15Z",
"timestamp": 1584721695000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-03T15:56:06Z",
"timestamp": 1656863766000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-08T08:29:42Z",
"timestamp": 1712564982928
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 3245,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2020-07-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1593561600000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://www.elsevier.com/open-access/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "am",
"delay-in-days": 388,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-24T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1627084800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0924857920300996?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0924857920300996?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "105949",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105924",
"article-title": "Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19): The epidemic and the challenges",
"author": "Lai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Int J Antimicrob Agents",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949_bib0001",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "A review of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) based on current evidence”",
"author": "Wang",
"journal-title": "Int J Antimicrob Agents",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949_bib0002",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949_bib0003",
"unstructured": "WHO Director-General's opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 - 11 March 2020. [https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-media-briefing-on-covid-19---11-march-2020]"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"article-title": "Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949_bib0004",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949_bib0005",
"unstructured": "Santé Publique France. Infection au nouveau Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2), COVID-19, France et Monde [https://www.santepubliquefrance.fr/maladies-et-traumatismes/maladies-et-infections-respiratoires/infection-a-coronavirus/articles/infection-au-nouveau-coronavirus-sars-cov-2-covid-19-france-et-monde]"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105923",
"article-title": "Chloroquine for the 2019 novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Colson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Int J Antimicrob Agents",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949_bib0006",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105932",
"article-title": "Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine as available weapons to fight COVID-19",
"author": "Colson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Int J Antimicrob Agents",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949_bib0007",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro",
"author": "Wang",
"first-page": "10",
"journal-title": "Cell Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949_bib0008",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5582/bst.2020.01047",
"article-title": "Breakthrough: Chloroquine phosphate has shown apparent efficacy in treatment of COVID-19 associated pneumonia in clinical studies",
"author": "Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Biosci Trends",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949_bib0009",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949_bib0010",
"unstructured": "Chinese Clinical Trial Registry. http://www.chictr.org.cn/searchproj.aspx?title=%E6%B0%AF%E5%96%B9&officialname=&subjectid=&secondaryid=&applier=&studyleader=ðicalcommitteesanction=&sponsor=&studyailment=&studyailmentcode=&studytype=0&studystage=0&studydesign=0&minstudyexecutetime=&maxstudyexecutetime=&recruitmentstatus=0&gender=0&agreetosign=&secsponsor=®no=®status=0&country=&province=&city=&institution=&institutionlevel=&measure=&intercode=&sourceofspends=&createyear=0&isuploadrf=&whetherpublic=&btngo=btn&verifycode=&page=1."
},
{
"article-title": "Expert consensus on chloroquine phosphate for the treatment of novel coronavirus pneumonia]",
"first-page": "185",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949_bib0011",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/jm0601856",
"article-title": "Design and synthesis of hydroxyferroquine derivatives with antimalarial and antiviral activities",
"author": "Biot",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2845",
"journal-title": "J Med Chem",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949_bib0012",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ophtha.2016.01.058",
"article-title": "Recommendations on Screening for Chloroquine and Hydroxychloroquine Retinopathy (2016 Revision)",
"author": "Marmor",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1386",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Ophthalmology",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949_bib0013",
"volume": "123",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa237",
"article-title": "In Vitro Antiviral Activity and Projection of Optimized Dosing Design of Hydroxychloroquine for the Treatment of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)",
"author": "Yao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949_bib0014",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/archinte.159.2.167",
"article-title": "Treatment of Q fever endocarditis: comparison of 2 regimens containing doxycycline and ofloxacin or hydroxychloroquine",
"author": "Raoult",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "167",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Arch Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949_bib0015",
"volume": "159",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/QCO.0000000000000489",
"article-title": "Whipple's disease and Tropheryma whipplei infections: when to suspect them and how to diagnose and treat them",
"author": "Lagier",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "463",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Curr Opin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949_bib0016",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101632",
"article-title": "Rapid viral diagnosis and ambulatory management of suspected COVID-19 cases presenting at the infectious diseases referral hospital in Marseille, France, - January 31st to March 1st, 2020: A respiratory virus snapshot",
"author": "Amrane",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Travel Med Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949_bib0017",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jchromb.2017.06.011",
"article-title": "Simultaneous UHPLC-UV analysis of hydroxychloroquine, minocycline and doxycycline from serum samples for the therapeutic drug monitoring of Q fever and Whipple's disease",
"author": "Armstrong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "166",
"journal-title": "J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949_bib0018",
"volume": "1060",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949_bib0019",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1618029113",
"article-title": "Zika virus cell tropism in the developing human brain and inhibition by azithromycin",
"author": "Retallack",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "14408",
"issue": "50",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949_bib0020",
"volume": "113",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsinfecdis.5b00030",
"article-title": "Evaluation of Ebola Virus Inhibitors for Drug Repurposing",
"author": "Madrid",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "317",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "ACS Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949_bib0021",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4172/1948-5964.1000173",
"article-title": "Azithromycin inhibits the replication of Zika virus",
"author": "Bosseboeuf",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Antivirals Antiretrovirals",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949_bib0022",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2015.13896",
"article-title": "Early administration of azithromycin and prevention of severe lower respiratory tract illnesses in preschool children with a history of such illnesses: A randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Bacharier",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2034",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949_bib0023",
"volume": "314",
"year": "2015"
}
],
"reference-count": 23,
"references-count": 23,
"relation": {
"has-preprint": [
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.1101/2020.03.16.20037135",
"id-type": "doi"
}
],
"has-review": [
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.3410/f.737589198.793573012",
"id-type": "doi"
},
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.3410/f.737589198.793575483",
"id-type": "doi"
},
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.3410/f.737589198.793575078",
"id-type": "doi"
},
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.3410/f.737589198.793575992",
"id-type": "doi"
}
]
},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0924857920300996"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pharmacology (medical)",
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)",
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "56"
}
