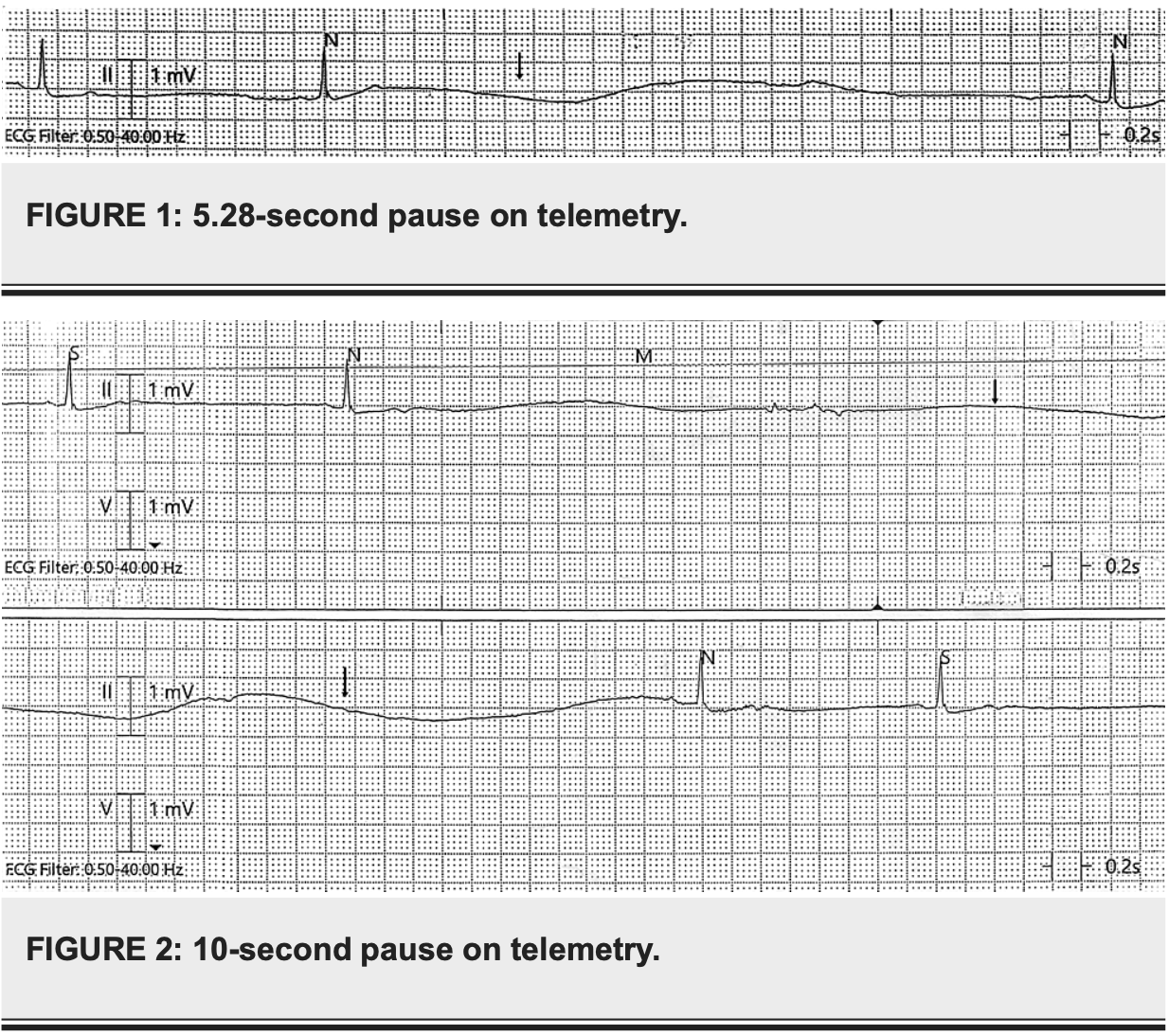
Paxlovid-Induced Symptomatic Bradycardia and Syncope
et al., Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.33831, Jan 2023
Case report of a 71-year-old female who developed symptomatic bradycardia, syncopal episodes, and sinus pause after taking paxlovid (nirmatrelvir/ritonavir) for mild COVID-19 infection.
Ganipisetti et al., 16 Jan 2023, USA, peer-reviewed, 3 authors.
Contact: venuganipisetti5@gmail.com.
Paxlovid-Induced Symptomatic Bradycardia and Syncope
Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.33831
Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir/ritonavir) is a game changer in the fight against COVID-19 due to its ease of administration and significant benefits of reducing progression to severe COVID-19, hospitalization, and death. Cardiac adverse events such as bradycardia and syncope are not known with this medication. We report a case of a 71-year-old patient who developed symptomatic bradycardia, syncopal episodes, and sinus pause after taking Paxlovid. Discontinuing medication and intravenous atropine helped to reverse the bradycardia and symptoms promptly. She did not require a pacemaker. We would like to report this possible association between Paxlovid and bradycardia. Until further information or studies are available, it is advised to promptly discontinue Paxlovid after any evidence of bradycardia and closely monitor for at least 40 hours in a hospital setting. The reported half-life (t 1/2) of the medication is 6.05 ± 1.79 hours and using 8 hours as a reference for the upper limit of t 1/2, around 97 % of the medication should be cleared off in about 40 hours (five half-lives).
Additional Information Disclosures Human subjects: Consent was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
References
Gottlieb, Vaca, Paredes, Early remdesivir to prevent progression to severe COVID-19 in outpatients, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2116846?utm_medium=email&utm_source=transaction
Hallare, Gerriets, Half Life . StatPearls
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with COVID-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2118542?utm_medium=email&utm_source=transaction
Mali, Eerike, Raj, Efficacy and safety of molnupiravir in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review, Ir J Med Sci, doi:10.1007/s11845-022-03139-y?utm_medium=email&utm_source=transaction
Najjar-Debbiny, Gronich, Weber, Effectiveness of Paxlovid in reducing severe COVID-19 and mortality in high risk patients, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac443?utm_medium=email&utm_source=transaction
Vangeel, Chiu, Jonghe, Remdesivir, molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir remain active against SARS-CoV-2 omicron and other variants of concern, Antiviral Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105252?utm_medium=email&utm_source=transaction
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.7759/cureus.33831",
"ISSN": [
"2168-8184"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.7759/cureus.33831",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ganipisetti",
"given": "Venu M",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bollimunta",
"given": "Pratyusha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maringanti",
"given": "Sriram",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Cureus",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-16T16:31:21Z",
"timestamp": 1673886681000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-09T19:48:37Z",
"timestamp": 1707508117000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-17T02:11:32Z",
"timestamp": 1715911892985
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
16
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.cureus.com/articles/132780-paxlovid-induced-symptomatic-bradycardia-and-syncope",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.7759",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
16
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
16
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"key": "ref1",
"unstructured": "WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. (2023). Accessed. January 6, 2023: https://covid19.who.int."
},
{
"key": "ref2",
"unstructured": "Covid 19 Clinical Presentation. Center for Disease Control and Prevention . (2023). Accessed. January 6, 2023: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/clinical-care/clinical-considerations-presentation.html."
},
{
"key": "ref3",
"unstructured": "Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Underlying Medical Conditions Associated with High Risk for Severe COVID- 19. Information for Healthcare Providers. (2023). Accessed: January 6, 2023: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/clinical-care/underlyingconditions.html."
},
{
"key": "ref4",
"unstructured": "COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines. National Institutes of Health. (2023). Accessed. January 6, 2023: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/.."
},
{
"key": "ref5",
"unstructured": "US Food and Drug Administration. Fact Sheet for Healthcare Providers. Emergency Use Authorization for Paxlovid. (2023). Accessed: January 6, 2023: https://www.fda.gov/media/155050/download."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"article-title": "Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with COVID-19",
"author": "Hammond J",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "ref6",
"unstructured": "Hammond J, Leister-Tebbe H, Gardner A, et al.. Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with COVID-19. N Engl J Med. 2022, 386:1397-408. 10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105252",
"article-title": "Remdesivir, molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir remain active against SARS-CoV-2 omicron and other variants of concern",
"author": "Vangeel L",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res",
"key": "ref7",
"unstructured": "Vangeel L, Chiu W, De Jonghe S, et al.. Remdesivir, molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir remain active against SARS-CoV-2 omicron and other variants of concern. Antiviral Res. 2022, 198:105252. 10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105252",
"volume": "198",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac443",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of Paxlovid in reducing severe COVID-19 and mortality in high risk patients",
"author": "Najjar-Debbiny R",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "ref8",
"unstructured": "Najjar-Debbiny R, Gronich N, Weber G, et al.. Effectiveness of Paxlovid in reducing severe COVID-19 and mortality in high risk patients. Clin Infect Dis. 2022, ciac443. 10.1093/cid/ciac443",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116846",
"article-title": "Early remdesivir to prevent progression to severe COVID-19 in outpatients",
"author": "Gottlieb RL",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "ref9",
"unstructured": "Gottlieb RL, Vaca CE, Paredes R, et al.. Early remdesivir to prevent progression to severe COVID-19 in outpatients. N Engl J Med. 2022, 386:305-15. 10.1056/NEJMoa2116846",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11845-022-03139-y",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of molnupiravir in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review",
"author": "Mali KR",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Ir J Med Sci",
"key": "ref10",
"unstructured": "Mali KR, Eerike M, Raj GM, et al.. Efficacy and safety of molnupiravir in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review. Ir J Med Sci. 2022, 10.1007/s11845-022-03139-y",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Half Life",
"author": "Hallare J",
"key": "ref11",
"unstructured": "Hallare J, Gerriets V. Half Life. StatPearls (ed): StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island, FL; 2022.",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 11,
"references-count": 11,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.cureus.com/articles/132780-paxlovid-induced-symptomatic-bradycardia-and-syncope"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Paxlovid-Induced Symptomatic Bradycardia and Syncope",
"type": "journal-article"
}