Retrospective Study of Outcomes and Hospitalization Rates of Patients in Italy with a Confirmed Diagnosis of Early COVID-19 and Treated at Home Within 3 Days or After 3 Days of Symptom Onset with Prescribed and Non-Prescribed Treatments Between November 2020 and August 2021
et al., Medical Science Monitor, doi:10.12659/MSM.935379, Dec 2021
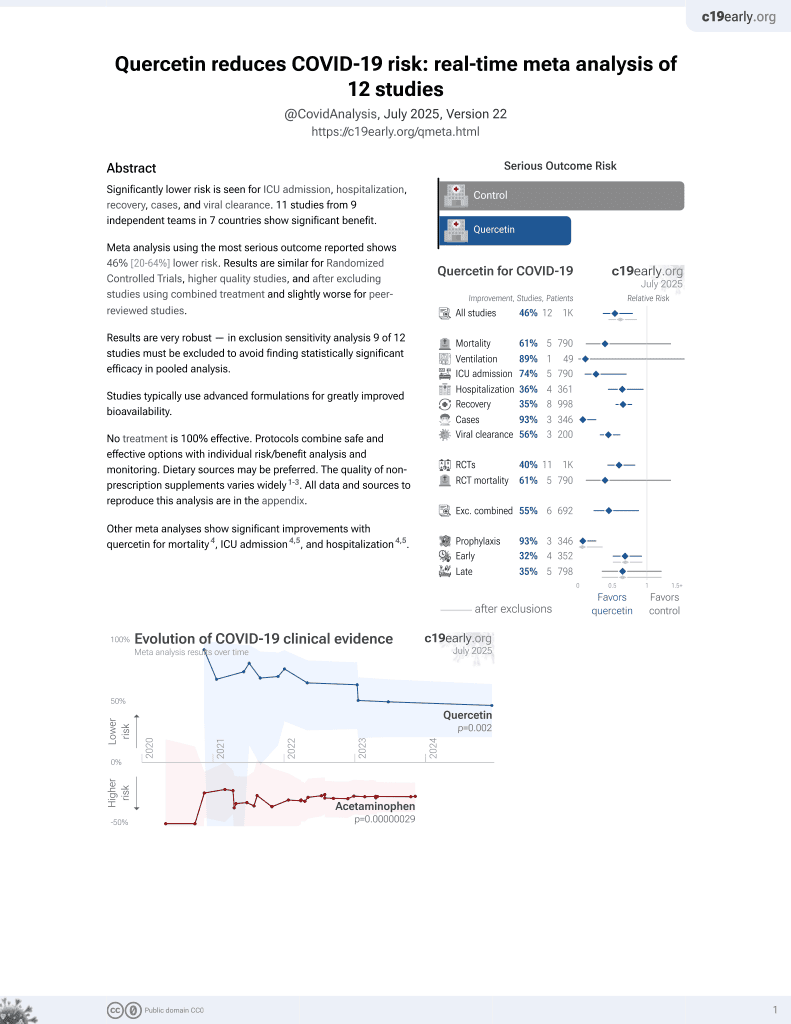
Quercetin for COVID-19
27th treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2021, now with p = 0.002 from 12 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
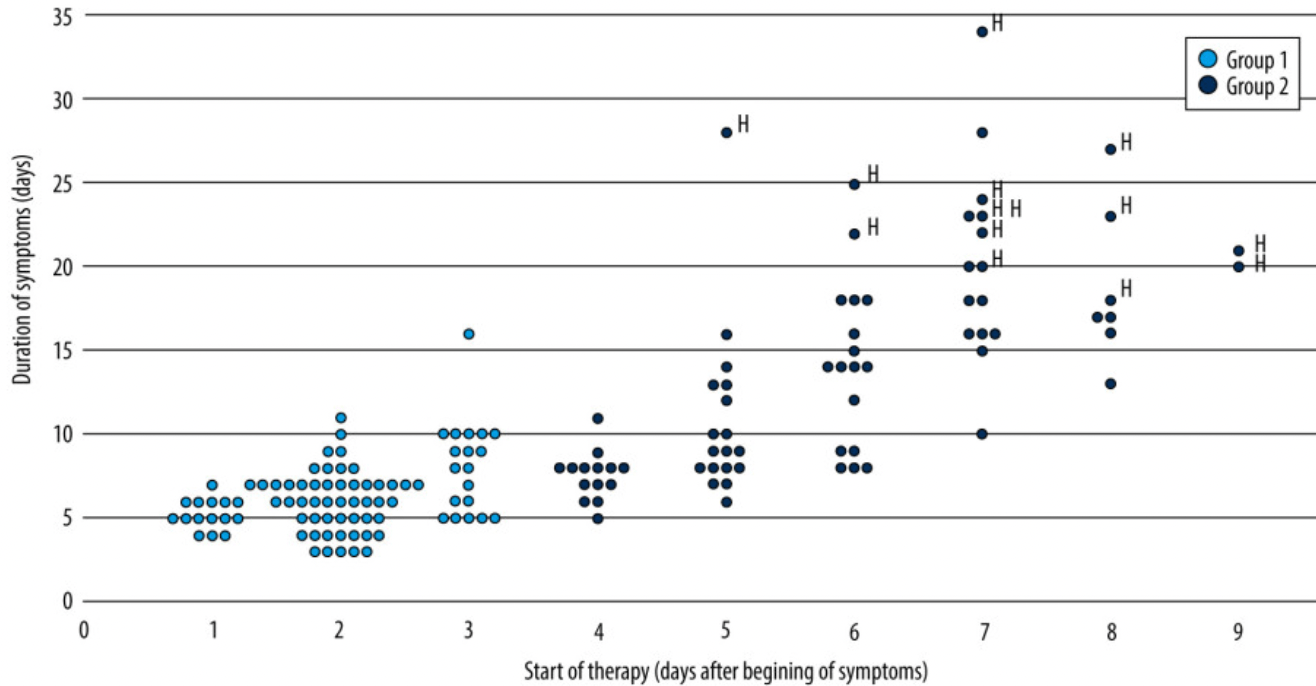
Retrospective 158 COVID-19 patients in Italy treated with hesperidin, quercetin, indomethacin, aspirin, omeprazole, azithromycin, LMWH, and betamethasone (treatment specific for each patient), showing significantly lower hospitalization and faster recovery with early treatment. Severity at baseline was similar in both groups.
Bioavailability. Quercetin has low bioavailability and studies typically use advanced formulations to improve bioavailability which may be required to reach therapeutic concentrations.
Study covers indomethacin and quercetin.
Fazio et al., 8 Dec 2021, retrospective, Italy, peer-reviewed, 6 authors, study period November 2020 - August 2021.
Contact: serafazio50@gmail.com, paolo.bellavite@gmail.com.
Retrospective Study of Outcomes and Hospitalization Rates of Patients in Italy with a Confirmed Diagnosis of Early COVID-19 and Treated at Home Within 3 Days or After 3 Days of Symptom Onset with Prescribed and Non-Prescribed Treatments Between November 2020 and August 2021
Medical Science Monitor, doi:10.12659/msm.935379
Bellavite has a consultancy agreement with Vanda s.r.l. (Frascati, Rome), but he had no role in the treatments. Other authors have no competing interests to declare
Background: This retrospective study aimed to investigate outcomes and hospitalization rates in patients with a confirmed diagnosis of early COVID-19 treated at home with prescribed and non-prescribed treatments.
Material/Methods: The medical records of a cohort of 158 Italian patients with early COVID-19 treated at home were analyzed. Treatments consisted of indomethacin, low-dose aspirin, omeprazole, and a flavonoid-based food supplement, plus azithromycin, low-molecular-weight heparin, and betamethasone as needed. The association of treatment timeliness and of clinical variables with the duration of symptoms and with the risk of hospitalization was evaluated by logistic regression.
Results: Patients were divided into 2 groups: group 1 (n=85) was treated at the earliest possible time (<72 h from onset of symptoms), and group 2 (n=73) was treated >72 h after the onset of symptoms. Clinical severity at the beginning of treatment was similar in the 2 groups. In group 1, symptom duration was shorter than in group 2 (median 6.0 days vs 13.0 days, P<0.001) and no hospitalizations occurred, compared with 19.18% hospitalizations in group 2. One patient in group 1 developed chest X-ray alterations and 2 patients experienced an increase in D-dimer levels, compared with 30 and 22 patients, respectively, in group 2. The main factor determining the duration of symptoms and the risk of hospitalization was the delay in starting therapy (P<0.001).
Conclusions: This real-world study of patients in the community showed that early diagnosis and early supportive patient management reduced the severity of COVID-19 and reduced the rate of hospitalization.
Declaration of Figures' Authenticity All figures submitted have been created by the authors, who confirm that the images are original with no duplication and have not been previously published in whole or in part.
References
Abian, Ortega-Alarcon, Jimenez-Alesanco, Structural stability of SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro and identification of quercetin as an inhibitor by experimental screening, Int J Biol Macromol
Alexander, Armstrong, Fareed, Early multidrug treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19) and reduced mortality among nursing home (or outpatient/ambulatory) residents, Med Hypotheses
Alkotaji, Al-Zidan, Indomethacin: Can it counteract bradykinin effects in COVID-19 patients?, Curr Pharmacol Rep
Amici, Di, Ciucci, Indomethacin has a potent antiviral activity against SARS coronavirus, Antivir Ther
Aviram, Dornfeld, Rosenblat, Pomegranate juice consumption reduces oxidative stress atherogenic modifications to LDL and platelet aggregation: Studies in humans and in atherosclerotic apolipoprotein E-deficient mice, Am J Clin Nutr
Bahrami, Daryani, Haghpanah, Effects of indomethacin on viral replication markers in asymptomatic carriers of hepatitis B: A randomized placebo-controlled trial, Am J Gastroenterol
Balmeh, Mahmoudi, Mohammadi, Karabedianhajiabadi, Predicted therapeutic targets for COVID-19 disease by inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 and its related receptors, Inform Med Unlocked
Bellavite, Donzelli, Hesperidin and SARS-CoV-2: New light on the healthy function of citrus fruits, Antioxidants
Bellavite, Reappraisal of dietary phytochemicals for coronavirus infection: Focus on hesperidin and quercetin
Biancatelli, Berrill, Catravas, Marik, Quercetin and vitamin C: An experimental synergistic therapy for the prevention and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 related disease (COVID-19), Front Immunol
Bianchi Porro, Lazzaroni, Petrillo, Prevention of gastroduodenal damage with omeprazole in patients receiving continuous NSAIDs treatment. A double blind placebo controlled study, Ital J Gastroenterol Hepatol
Bonaventura, Vecchie, Dagna, Endothelial dysfunction and immunothrombosis as key pathogenic mechanisms in COVID-19, Nat Rev Immunol
Cabbab, Manalo, Anti-inflammatory drugs and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system: Current knowledge and potential effects on early SARS-CoV-2 infection, Virus Res
Checconi, De, Marcocci, Redox-modulating agents in the treatment of viral infections, Int J Mol Sci
Consolaro, Rubis, Pedroni, A home-treatment algorithm based on anti-inflammatory drugs to prevent hospitalization of patients with early COVID-19: A matched-cohort study (Cover 2), MedRxiv
Delgado-Roche, Mesta, Oxidative stress as key player in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) infection, Arch Med Res
Derosa, Maffioli, Angelo, Pierro, A role for quercetin in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Phytother Res
Derwand, Scholz, Zelenko, COVID-19 outpatients: Early risk-stratified treatment with zinc plus low-dose hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin: A retrospective case series study, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Di Vetta, Morrone, Fazio, COVID-19: Off-label therapies based on mechanism of action while waiting for evidence-based medicine recommendations, World J Meta-Anal
Ding, Sun, Zhu, Hesperidin attenuates influenza A virus (H1N1) induced lung injury in rats through its anti-inflammatory effect, Antivir Ther
Elmaaty, Hamed, Ismail, Computational insights on the potential of some NSAIDs for treating COVID-19: Priority set and lead optimization, Molecules
Fazio, Tufano, De Simone, Sustained high D-dimer in outpatients who have recovered from mild to moderate coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Semin Thromb Hemost
Ghareeb, Saleh, Nofal, Potential therapeutic and pharmacological strategies for SARS-CoV2, J Pharm Investig
Gomeni, Xu, Gao, Bressolle-Gomeni, Model based approach for estimating the dosage regimen of indomethacin a potential antiviral treatment of patients infected with SARS CoV-2, J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn
Haggag, El-Ashmawy, Okasha, Is hesperidin essential for prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19 Infection?, Med Hypotheses
Ho, Zheng, Wu, Perspective adjunctive therapies for COVID-19: Beyond antiviral therapy, Int J Med Sci
Iddir, Brito, Dingeo, Strengthening the immune system and reducing inflammation and oxidative stress through diet and nutrition: Considerations during the COVID-19 crisis, Nutrients
Khezri, Zolbanin, Ghasemnejad-Berenji, Jafari, Azithromycin: Immunomodulatory and antiviral properties for SARS-CoV-2 infection, Eur J Pharmacol
Kiani, Scholey, Dahl, Mcmann, Iversen et al., In vitro assessment of the antiviral activity of ketotifen indomethacin and naproxen alone and in combination against SARS-CoV-2, Viruses
Li, Wei, Suo, Low-dose aspirin prevents kidney damage in LPSinduced preeclampsia by inhibiting the WNT5A and NF-kappaB signaling pathways, Front Endocrinol
Liu, Huang, Li, Effect of low-dose aspirin on mortality and viral duration of the hospitalized adults with COVID-19, Medicine
Lucas, The pharmacology of indomethacin, Headache
Marinella, Indomethacin and resveratrol as potential treatment adjuncts for SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19, Int J Clin Pract
Mccullough, Favipiravir and the need for early ambulatory treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19), Antimicrob Agents Chemother
Mccullough, Kelly, Ruocco, Pathophysiological basis and rationale for early outpatient treatment of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infection, Am J Med
Mccullough, Vijay, SARS-CoV-2 infection and the COVID-19 pandemic: a call to action for therapy and interventions to resolve the crisis of hospitalization death and handle the aftermath, Rev Cardiovasc Med
Mironova, Belosludtseva, Ananyan, Prospects for the use of regulators of oxidative stress in the comprehensive treatment of the novel Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) and its complications, Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci
Mrityunjaya, Pavithra, Neelam, Immune-boosting antioxidant and anti-inflammatory food supplements targeting pathogenesis of COVID-19, Front Immunol
Oh, Adnan, Cho, Network pharmacology approach to decipher signaling pathways associated with target proteins of NSAIDs against COVID-19, Sci Rep
Pandolfi, Simonetti, Ricevuti, Chirumbolo, Paracetamol in the home treatment of early COVID-19 symptoms: A possible foe rather than a friend for elderly patients?, J Med Virol
Parhiz, Roohbakhsh, Soltani, Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of the citrus flavonoids hesperidin and hesperetin: An updated review of their molecular mechanisms and experimental models, Phytother Res
Pierro, Derosa, Maffioli, Possible therapeutic effects of adjuvant quercetin supplementation against early-stage COVID-19 infection: A prospective randomized controlled and open-label study, Int J Gen Med
Pierro, Iqtadar, Khan, Potential clinical benefits of quercetin in the early stage of COVID-19: Results of a second pilot randomized controlled and open-label clinical trial, Int J Gen Med
Polonikov, Endogenous deficiency of glutathione as the most likely cause of serious manifestations and death in COVID-19 patients, ACS Infect Dis
Potus, Mai, Lebret, Novel insights on the pulmonary vascular consequences of COVID-19, Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol
Prasher, Sharma, Gunupuru, Targeting cyclooxygenase enzyme for the adjuvant COVID-19 therapy
Qiao, Arthur, Gardiner, Regulation of platelet activation and thrombus formation by reactive oxygen species, Redox Biol
Ravichandran, Mohan, Sukumaran, Use of indomethacin for mild and moderate COVID-19 patients. A randomized controlled trial
Reynolds, Enquist, Biological interactions between herpesviruses and cyclooxygenase enzymes, Rev Med Virol
Russell, Moss, George, Associations between immune-suppressive and stimulating drugs and novel COVID-19-a systematic review of current evidence, Ecancermedicalscience
Saeedi-Boroujeni, Mr, Anti-inflammatory potential of Quercetin in COVID-19 treatment, J Inflamm (Lond)
Saha, Takahashi, Suzuki, Glucosyl hesperidin prevents influenza a virus replication in vitro by inhibition of viral sialidase, Biol Pharm Bull
Saleh, Peyssonnaux, Singh, Edeas, Mitochondria and microbiota dysfunction in COVID-19 pathogenesis, Mitochondrion
Schroer, Shenk, Inhibition of cyclooxygenase activity blocks cellto-cell spread of human cytomegalovirus, Proc Natl Acad Sci
Shovlin, Vizcaychipi, Vascular inflammation and endothelial injury in SARS-CoV-2 infection: The overlooked regulatory cascades implicated by the ACE2 gene cluster, QJM
Siemieniuk, Bartoszko, Ge, Drug treatments for COVID-19: Living systematic review and network meta-analysis, BMJ
Solnier, Fladerer, Flavonoids: A complementary approach to conventional therapy of COVID-19?, Phytochem Rev
Soto, Guarner-Lans, Soria-Castro, Is antioxidant therapy a useful complementary measure for COVID-19 treatment? An algorithm for its application, Medicina (Kaunas)
Suhail, Zajac, Fossum, Role of oxidative stress on SARS-CoV (SARS) and SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infection: A review, Protein J
Suter, Consolaro, Pedroni, A simple home-therapy algorithm to prevent hospitalisation for COVID-19 patients: A retrospective observational matched-cohort study, EClinical Medicine
Thachil, The versatile heparin in COVID-19, J Thromb Haemost
Violi, Oliva, Cangemi, Nox2 activation in COVID-19, Redox Biol
Wu, Liu, Yang, Analysis of therapeutic targets for SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of potential drugs by computational methods, Acta Pharm Sin B
Xu, Gao, Wu, Indomethacin has a potent antiviral activity against SARS-COV-2 in vitro and canine coronavirus in vivo, BioRxiv
Yao, Cao, Wang, D-dimer as a biomarker for disease severity and mortality in COVID-19 patients: A case control study, J Intensive Care
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.12659/msm.935379",
"ISSN": [
"1643-3750"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.12659/msm.935379",
"alternative-id": [
"935379"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Retired Professor of Internal Medicine, Medical School University Federico II, Naples, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Fazio",
"given": "Serafino",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Physiopathology Chair, Homeopathic Medical School of Verona, Verona, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Bellavite",
"given": "Paolo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Unit of Epidemiology and Medical Statistics, Department of Diagnostics and Public Health, University of Verona, Verona, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Zanolin",
"given": "Elisabetta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Cardiology, Truth for Health Foundation, Tucson, USA, AZ"
}
],
"family": "McCullough",
"given": "Peter A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Neurosurgery, Villa Mafalda Clinics, Rome, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Pandolfi",
"given": "Sergio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Independent Researcher, Gallipoli, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Affuso",
"given": "Flora",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Medical Science Monitor"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-15T15:10:06Z",
"timestamp": 1639581006000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-15T15:10:07Z",
"timestamp": 1639581007000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-16T06:44:52Z",
"timestamp": 1639637092325
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "1643-3750"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
8
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.medscimonit.com/download/index/idArt/935379",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "4947",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.12659",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
8
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
8
]
]
},
"publisher": "International Scientific Information, Inc.",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Med Sci Monit"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Retrospective Study of Outcomes and Hospitalization Rates of Patients in Italy with a Confirmed Diagnosis of Early COVID-19 and Treated at Home Within 3 Days or After 3 Days of Symptom Onset with Prescribed and Non-Prescribed Treatments Between November 2020 and August 2021"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "28"
}