Effects of climatic factors on COVID-19 transmission in Ethiopia
et al., Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-24024-9, Nov 2022
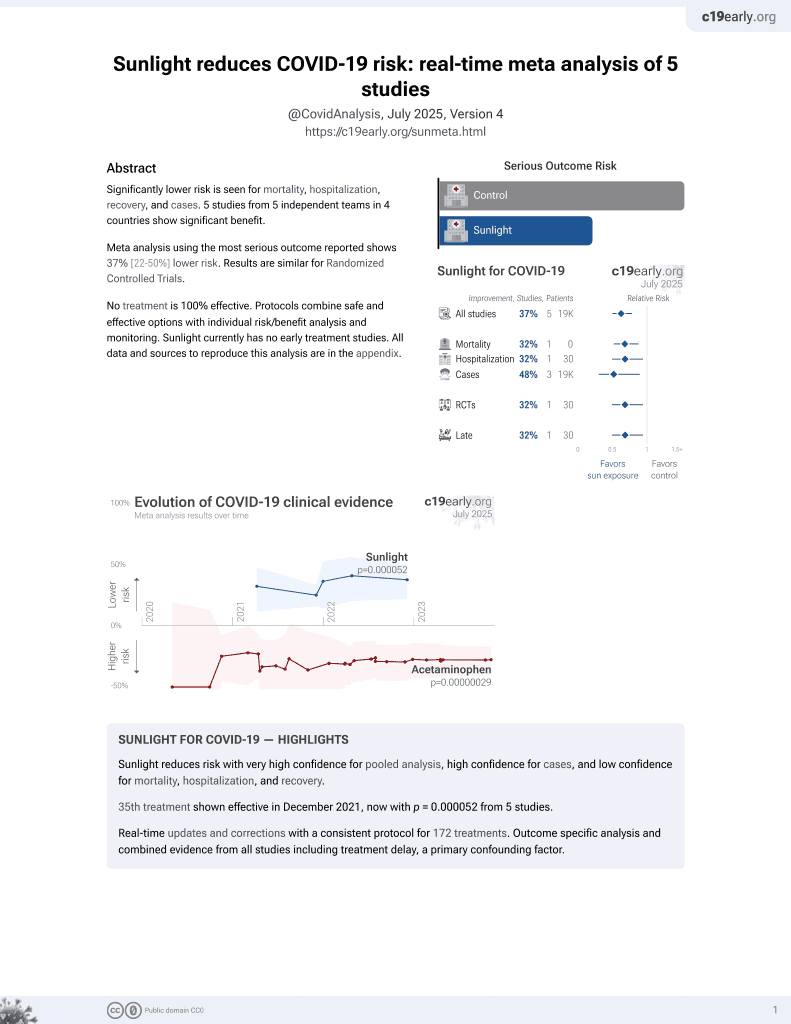
Sunlight for COVID-19
36th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2021, now with p = 0.000052 from 5 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
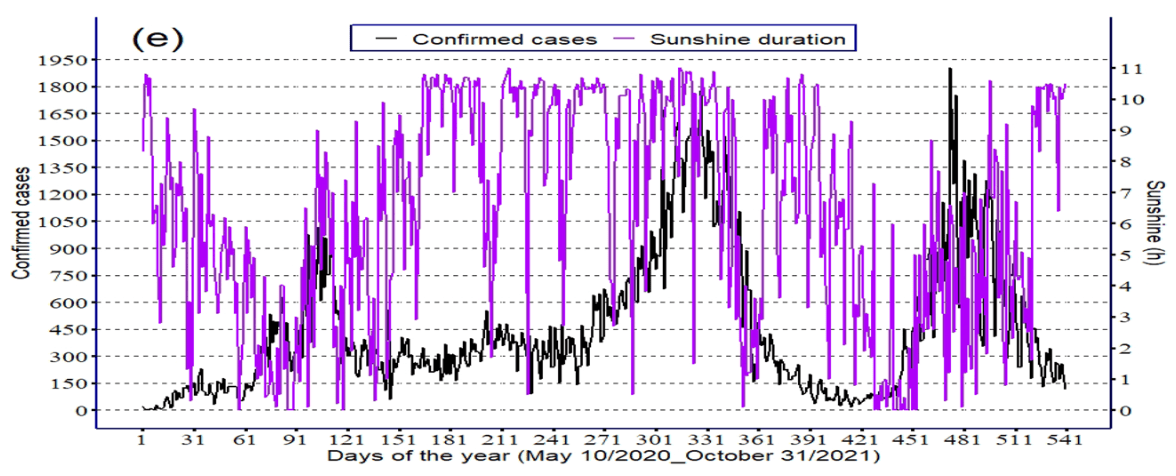
Analysis of climate and COVID-19 transmission in Ethiopia, showing no association between sunshine duration and COVID-19 risk during the study period. Authors analyze cases only and not outcomes.
Endeshaw et al., 16 Nov 2022, Ethiopia, peer-reviewed, 7 authors, study period 10 May, 2020 - 31 October, 2021.
Contact: kefyalew.alene@curtin.edu.au.
Effects of climatic factors on COVID-19 transmission in Ethiopia
Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-24024-9
Climatic conditions play a key role in the transmission and pathophysiology of respiratory tract infections, either directly or indirectly. However, their impact on the COVID-19 pandemic propagation is yet to be studied. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of climatic factors such as temperature, rainfall, relative humidity, sunshine duration, and wind speed on the number of daily COVID-19 cases in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Data on confirmed COVID-19 cases were obtained from the National Data Management Center at the Ethiopian Public Health Institute for the period 10th March 2020 to 31st October 2021. Data for climatic factors were obtained from the Ethiopia National Meteorology Agency. The correlation between daily confirmed COVID-19 cases and climatic factors was measured using the Spearman rank correlation test. The log-link negative binomial regression model was used to fit the effect of climatic factors on COVID-19 transmission, from lag 0 to lag 14 days. During the study period, a total of 245,101 COVID-19 cases were recorded in Addis Ababa, with a median of 337 new cases per day and a maximum of 1903 instances per day. A significant correlation between COVID-19 cases and humidity was observed with a 1% increase in relative humidity associated with a 1.1% [IRRs (95%CI) 0.989, 95% (0.97-0.99)] and 1.2% [IRRs (95%CI) 0.988, (0.97-0.99)] decrease in COVID-19 cases for 4 and 5 lag days prior to detection, respectively. The highest increase in the effect of wind speed and rainfall on COVID-19 was observed at 14 lag days prior to detection with IRRs of 1.85 (95%CI 1.26-2.74) and 1.078 (95%CI 1.04-1.12), respectively. The lowest IRR was 1.109 (95%CI 0.93-1.31) and 1.007 (95%CI 0.99-1.02) both in lag 0, respectively. The findings revealed that none of the climatic variables influenced the number of COVID-19 cases on the day of case detection (lag 0), and that daily average temperature and sunshine duration were not significantly linked with COVID-19 risk across the full lag period (p > 0.05). Climatic factors such as humidity, rainfall, and wind speed influence the transmission of COVID-19 in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. COVID-19 cases have shown seasonal variations with the highest number of cases reported during the rainy season and the lowest number of cases reported during the dry season. These findings suggest the need to design strategies for the prevention and control of COVID-19 before the rainy seasons. Since Corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) was officially declared by the World Health Organization (WHO) on 11 March 2020 as a global pandemic, the number of deaths and daily confirmed new cases have increased in every corner of the world. The pandemic is a serious global public health crisis affecting the physical, mental, social, and economic well-being of human beings [1] [2] [3] . Following the first reported cases of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China in late December 2019, the virus has quickly spread across the world 4 . As of 11 March 2022,..
www.nature.com/scientificreports/ Seasonal and daily variation of climate factors against daily confirmed new cases. As can be seen from Fig. 2 , on average, the highest and lowest rainfall record in Addis Ababa were from June to September and October to November, respectively. However, the maximum (May) and minimum (December) temperatures recorded in Addis Ababa were during the second small rainy season (February to May) and October to January period (Fig. 3 ). As Fig. 4a illustrates, Addis Ababa experienced 3 COVID-19 peak periods since community-level transmission occurred. The two highest numbers of COVID-19 cases per day were registered in the second rainy season (March to May) and the main rainy season (June to September) with a magnitude of 1775 and 1903 cases, respectively. The number of COVID-19 cases declined following the main rainy season, from October to January. The decline in COVID-19 cases between October and January links to the lowest amount of rainfall, while the increased number of COVID-19 cases between March-May and June-September links to increased seasonal rainfall (Fig. 4b ). The average temperature shows a decreasing trend during the peak outbreak period (Fig. 4a ). Taking into account the lag effects of climatic factors, wind and relative humidity increased prior to the day of detection of COVID-19 cases (Fig. 4c,d ). The increased number of COVID-19 cases between March and September of the study period corresponded with decreased sunshine..
References
Adekunle, Tella, Oyesiku, Oseni, Spatio-temporal analysis of meteorological factors in abating the spread of COVID-19 in Africa, Heliyon
Ahmadi, Sharifi, Dorosti, Ghoushchi, Ghanbari, Investigation of effective climatology parameters on COVID-19 outbreak in Iran, Sci. Total Environ
Aidoo, Adebanji, Awashie, Appiah, The effects of weather on the spread of COVID-19: Evidence from Ghana, Bull. Natl. Res. Centre
Alene, COVID-19 in Ethiopia: A geospatial analysis of vulnerability to infection, case severity and death, BMJ Open
Araujo, Naimi, Spread of SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus likely to be constrained by climate
Awasthi, Sharma, Kaur, Gugamsetty, Kumar, Statistical interpretation of environmental influencing parameters on COVID-19 during the lockdown in Delhi, India, Environ Dev Sustain
Bahl, Airborne or droplet precautions for health workers treating coronavirus disease 2019, J Infect Dis
Bashir, Correlation between climate indicators and COVID-19 pandemic in New York, USA. Sci Total Environ
Bashir, Ma, Shahzad, A brief review of socio-economic and environmental impact of Covid-19, Air Qual Atmos Health
Chetty, Adeleye, Ilori, The impact of climate temperature on counts, recovery, and death rates due to SARS-CoV-2 in South Africa
Chien, Chen, Lin, Lagged meteorological impacts on COVID-19 incidence among high-risk counties in the United States-a spatiotemporal analysis, J. Exposure Sci. Environ. Epidemiol
Chien, Chen, Meteorological impacts on the incidence of COVID-19 in the US, Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess
Gissila, Black, Grimes, Slingo, Seasonal forecasting of the Ethiopian summer rains, Int. J. Climatol. J. R. Meteorol. Soc
Gupta, Pradhan, Impact of daily weather on COVID-19 outbreak in India
Hridoy, Impact of meteorological parameters on COVID-19 transmission in Bangladesh: A spatiotemporal approach, Theor. Appl. Climatol
Huang, Global prediction system for COVID-19 pandemic, Sci. Bull
Huang, Optimal temperature zone for the dispersal of COVID-19, Sci. Total Environ
Huang, The oscillation-outbreaks characteristic of the COVID-19 pandemic, Natl. Sci. Rev
Iddrisu, Appiahene, Kessie, Effects of weather and policy intervention on COVID-19 infection in Ghana
Li, Wang, Zheng, Impact of weather factors on influenza hospitalization across different age groups in subtropical Hong Kong, Int. J. Biometeorol
Lian, Impact of city lockdown on the air quality of COVID-19-hit of Wuhan city, Sci. Total Environ
Mansouri Daneshvar, Ebrahimi, Sadeghi, Mahmoudzadeh, Climate effects on the COVID-19 outbreak: A comparative analysis between the UAE and Switzerland, Model. Earth Syst. Environ
Meo, Impact of weather conditions on incidence and mortality of COVID-19 pandemic in Africa, Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci
Onder, Rezza, Brusaferro, Characteristics of patients dying in relation to COVID-19 in Italy, JAMA
Rajgor, Lee, Archuleta, Bagdasarian, Quek, The many estimates of the COVID-19 case fatality rate, Lancet Infect. Dis
Ratnesar-Shumate, Simulated sunlight rapidly inactivates SARS-CoV-2 on surfaces, J Infect Dis
Rehman, Rehman, Association of climatic factors with COVID-19 in Pakistan, AIMS Public Health
Riddell, Goldie, Hill, Eagles, Drew, The effect of temperature on persistence of SARS-CoV-2 on common surfaces, Virol J
Rosario, Mutz, Bernardes, Conte-Junior, Relationship between COVID-19 and weather: Case study in a tropical country, Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health
Singh, Bhardwaj, Kumar, Association between climatic variables and COVID-19 pandemic in National Capital Territory of Delhi, India. Environ. Dev. Sustain
To, Correlation of ambient temperature and COVID-19 incidence in Canada, Sci. Total Environ
Tosepu, Correlation between weather and Covid-19 pandemic in Jakarta, Indonesia, Sci. Total Environ
Wang, Tang, Feng, Lv, High temperature and high humidity reduce the transmission of COVID-19
Ward, Xiao, Zhang, The role of climate during the COVID-19 epidemic in New South Wales, Australia, Transbound. Emerg. Dis
Who, None, WHO Health Emergency Dashboard
Şahin, Impact of weather on COVID-19 pandemic in Turkey, Sci. Total Environ
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-022-24024-9",
"ISSN": [
"2045-2322"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-24024-9",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p>Climatic conditions play a key role in the transmission and pathophysiology of respiratory tract infections, either directly or indirectly. However, their impact on the COVID-19 pandemic propagation is yet to be studied. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of climatic factors such as temperature, rainfall, relative humidity, sunshine duration, and wind speed on the number of daily COVID-19 cases in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Data on confirmed COVID-19 cases were obtained from the National Data Management Center at the Ethiopian Public Health Institute for the period 10th March 2020 to 31st October 2021. Data for climatic factors were obtained from the Ethiopia National Meteorology Agency. The correlation between daily confirmed COVID-19 cases and climatic factors was measured using the Spearman rank correlation test. The log-link negative binomial regression model was used to fit the effect of climatic factors on COVID-19 transmission, from lag 0 to lag 14 days. During the study period, a total of 245,101 COVID-19 cases were recorded in Addis Ababa, with a median of 337 new cases per day and a maximum of 1903 instances per day. A significant correlation between COVID-19 cases and humidity was observed with a 1% increase in relative humidity associated with a 1.1% [IRRs (95%CI) 0.989, 95% (0.97–0.99)] and 1.2% [IRRs (95%CI) 0.988, (0.97–0.99)] decrease in COVID-19 cases for 4 and 5 lag days prior to detection, respectively. The highest increase in the effect of wind speed and rainfall on COVID-19 was observed at 14 lag days prior to detection with IRRs of 1.85 (95%CI 1.26–2.74) and 1.078 (95%CI 1.04–1.12), respectively. The lowest IRR was 1.109 (95%CI 0.93–1.31) and 1.007 (95%CI 0.99–1.02) both in lag 0, respectively. The findings revealed that none of the climatic variables influenced the number of COVID-19 cases on the day of case detection (lag 0), and that daily average temperature and sunshine duration were not significantly linked with COVID-19 risk across the full lag period (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> > 0.05). Climatic factors such as humidity, rainfall, and wind speed influence the transmission of COVID-19 in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. COVID-19 cases have shown seasonal variations with the highest number of cases reported during the rainy season and the lowest number of cases reported during the dry season. These findings suggest the need to design strategies for the prevention and control of COVID-19 before the rainy seasons.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"24024"
],
"article-number": "19722",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "2 June 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "9 November 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "16 November 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1,
"value": "The authors declare no competing interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Endeshaw",
"given": "Fitsum Bekele",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Getnet",
"given": "Fentabil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Temesgen",
"given": "Awoke Misganaw",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mirkuzie",
"given": "Alemnesh H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Olana",
"given": "Latera Tesfaye",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alene",
"given": "Kefyalew Addis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Birhanie",
"given": "Solomon Kibret",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Scientific Reports",
"container-title-short": "Sci Rep",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-16T18:02:44Z",
"timestamp": 1668621764000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-16T18:12:16Z",
"timestamp": 1668622336000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100000925",
"award": [
"APP1196549"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Health and Medical Research Council"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-17T06:04:13Z",
"timestamp": 1668665053031
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
16
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-16T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1668556800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-16T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1668556800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-24024-9.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-24024-9",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-24024-9.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1038",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
16
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
16
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30244-9",
"author": "DD Rajgor",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "776",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect. Dis.",
"key": "24024_CR1",
"unstructured": "Rajgor, D. D., Lee, M. H., Archuleta, S., Bagdasarian, N. & Quek, S. C. The many estimates of the COVID-19 case fatality rate. Lancet Infect. Dis. 20, 776–777 (2020).",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "G Onder",
"first-page": "1775",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "24024_CR2",
"unstructured": "Onder, G., Rezza, G. & Brusaferro, S. Characteristics of patients dying in relation to COVID-19 in Italy. JAMA 323, 1775–1776 (2020).",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "24024_CR3",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) SITUATION Report-51 (2020a)."
},
{
"key": "24024_CR4",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report-41 (2020b)."
},
{
"key": "24024_CR5",
"unstructured": "WHO. WHO Health Emergency Dashboard (2022)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12985-020-01418-7",
"author": "S Riddell",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Virol J",
"key": "24024_CR6",
"unstructured": "Riddell, S., Goldie, S., Hill, A., Eagles, D. & Drew, T. W. The effect of temperature on persistence of SARS-CoV-2 on common surfaces. Virol J 17, 1–7 (2020).",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiaa274",
"author": "S Ratnesar-Shumate",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "214",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis",
"key": "24024_CR7",
"unstructured": "Ratnesar-Shumate, S. et al. Simulated sunlight rapidly inactivates SARS-CoV-2 on surfaces. J Infect Dis 222, 214–222 (2020).",
"volume": "222",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiaa189",
"author": "P Bahl",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1561",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis",
"key": "24024_CR8",
"unstructured": "Bahl, P. et al. Airborne or droplet precautions for health workers treating coronavirus disease 2019. J Infect Dis 225, 1561–1568 (2022).",
"volume": "225",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138835",
"author": "MF Bashir",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "138835",
"journal-title": "Sci Total Environ",
"key": "24024_CR9",
"unstructured": "Bashir, M. F. et al. Correlation between climate indicators and COVID-19 pandemic in New York, USA. Sci Total Environ 728, 138835 (2020).",
"volume": "728",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11869-020-00894-8",
"author": "MF Bashir",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1403",
"journal-title": "Air Qual Atmos Health",
"key": "24024_CR10",
"unstructured": "Bashir, M. F., Ma, B. & Shahzad, L. A brief review of socio-economic and environmental impact of Covid-19. Air Qual Atmos Health 13, 1403–1409 (2020C).",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "S Meo",
"first-page": "9753",
"journal-title": "Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci",
"key": "24024_CR11",
"unstructured": "Meo, S. et al. Impact of weather conditions on incidence and mortality of COVID-19 pandemic in Africa. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24, 9753–9759 (2020).",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10668-020-01000-9",
"author": "A Awasthi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "8147",
"journal-title": "Environ Dev Sustain",
"key": "24024_CR12",
"unstructured": "Awasthi, A., Sharma, A., Kaur, P., Gugamsetty, B. & Kumar, A. Statistical interpretation of environmental influencing parameters on COVID-19 during the lockdown in Delhi, India. Environ Dev Sustain 23, 8147–8160 (2021).",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "24024_CR13",
"unstructured": "Iddrisu, W. A., Appiahene, P. & Kessie, J. A. Effects of weather and policy intervention on COVID-19 infection in Ghana. arXiv preprint https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.00106 (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.07.16.20155523",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "24024_CR14",
"unstructured": "Chetty, N., Adeleye, B. & Ilori, A. O. The impact of climate temperature on counts, recovery, and death rates due to SARS-CoV-2 in South Africa. medRxiv (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.03.12.20034728",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "24024_CR15",
"unstructured": "Araujo, M. B. & Naimi, B. Spread of SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus likely to be constrained by climate (2020)."
},
{
"author": "M Mansouri Daneshvar",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Model. Earth Syst. Environ.",
"key": "24024_CR16",
"unstructured": "Mansouri Daneshvar, M., Ebrahimi, M., Sadeghi, A. & Mahmoudzadeh, A. Climate effects on the COVID-19 outbreak: A comparative analysis between the UAE and Switzerland. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 8, 1–14 (2021).",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2139/ssrn.3551767",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "24024_CR17",
"unstructured": "Wang, J., Tang, K., Feng, K. & Lv, W. High temperature and high humidity reduce the transmission of COVID-19. Available at SSRN 3551767, 2020b (2020)"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/joc.1078",
"author": "T Gissila",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1345",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Climatol. J. R. Meteorol. Soc.",
"key": "24024_CR18",
"unstructured": "Gissila, T., Black, E., Grimes, D. & Slingo, J. Seasonal forecasting of the Ethiopian summer rains. Int. J. Climatol. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 24, 1345–1358 (2004).",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"key": "24024_CR19",
"unstructured": "Ethiopian Statistics Service. Census-Population Projection."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138436",
"author": "R Tosepu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Sci. Total Environ.",
"key": "24024_CR20",
"unstructured": "Tosepu, R. et al. Correlation between weather and Covid-19 pandemic in Jakarta, Indonesia. Sci. Total Environ. 725, 138436 (2020).",
"volume": "725",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00484-018-1561-z",
"author": "Y Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1615",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Biometeorol.",
"key": "24024_CR21",
"unstructured": "Li, Y., Wang, X.-L. & Zheng, X. Impact of weather factors on influenza hospitalization across different age groups in subtropical Hong Kong. Int. J. Biometeorol. 62, 1615–1624 (2018).",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"key": "24024_CR22",
"unstructured": "RFfS Computing. (2021)."
},
{
"author": "L-C Chien",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Exposure Sci. Environ. Epidemiol.",
"key": "24024_CR23",
"unstructured": "Chien, L.-C., Chen, L.-W.A. & Lin, R.-T. Lagged meteorological impacts on COVID-19 incidence among high-risk counties in the United States—a spatiotemporal analysis. J. Exposure Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 32, 1–8 (2021).",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141484",
"author": "T To",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "141484",
"journal-title": "Sci. Total Environ.",
"key": "24024_CR24",
"unstructured": "To, T. et al. Correlation of ambient temperature and COVID-19 incidence in Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 750, 141484 (2021).",
"volume": "750",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/tbed.13631",
"author": "MP Ward",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2313",
"journal-title": "Transbound. Emerg. Dis.",
"key": "24024_CR25",
"unstructured": "Ward, M. P., Xiao, S. & Zhang, Z. The role of climate during the COVID-19 epidemic in New South Wales, Australia. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 67, 2313–2317 (2020).",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3934/publichealth.2020066",
"author": "Y Rehman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "854",
"journal-title": "AIMS Public Health",
"key": "24024_CR26",
"unstructured": "Rehman, Y. & Rehman, N. Association of climatic factors with COVID-19 in Pakistan. AIMS Public Health 7, 854 (2020).",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00704-021-03535-x",
"author": "A-EE Hridoy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "273",
"journal-title": "Theor. Appl. Climatol.",
"key": "24024_CR27",
"unstructured": "Hridoy, A.-E.E. et al. Impact of meteorological parameters on COVID-19 transmission in Bangladesh: A spatiotemporal approach. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 144, 273–285 (2021).",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04749",
"author": "IA Adekunle",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e04749",
"journal-title": "Heliyon",
"key": "24024_CR28",
"unstructured": "Adekunle, I. A., Tella, S. A., Oyesiku, K. O. & Oseni, I. O. Spatio-temporal analysis of meteorological factors in abating the spread of COVID-19 in Africa. Heliyon 6, e04749 (2020).",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s42269-021-00484-3",
"author": "EN Aidoo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Bull. Natl. Res. Centre",
"key": "24024_CR29",
"unstructured": "Aidoo, E. N., Adebanji, A. O., Awashie, G. E. & Appiah, S. K. The effects of weather on the spread of COVID-19: Evidence from Ghana. Bull. Natl. Res. Centre 45, 1–6 (2021).",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138810",
"author": "M Şahin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "138810",
"journal-title": "Sci. Total Environ.",
"key": "24024_CR30",
"unstructured": "Şahin, M. Impact of weather on COVID-19 pandemic in Turkey. Sci. Total Environ. 728, 138810 (2020).",
"volume": "728",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10668-020-01003-6",
"author": "O Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "9514",
"journal-title": "Environ. Dev. Sustain.",
"key": "24024_CR31",
"unstructured": "Singh, O., Bhardwaj, P. & Kumar, D. Association between climatic variables and COVID-19 pandemic in National Capital Territory of Delhi, India. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 23, 9514–9528 (2021).",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138705",
"author": "M Ahmadi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "138705",
"journal-title": "Sci. Total Environ.",
"key": "24024_CR32",
"unstructured": "Ahmadi, M., Sharifi, A., Dorosti, S., Ghoushchi, S. J. & Ghanbari, N. Investigation of effective climatology parameters on COVID-19 outbreak in Iran. Sci. Total Environ. 729, 138705 (2020).",
"volume": "729",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijheh.2020.113587",
"author": "DK Rosario",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "113587",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health",
"key": "24024_CR33",
"unstructured": "Rosario, D. K., Mutz, Y. S., Bernardes, P. C. & Conte-Junior, C. A. Relationship between COVID-19 and weather: Case study in a tropical country. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 229, 113587 (2020).",
"volume": "229",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00477-020-01835-8",
"author": "L-C Chien",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1675",
"journal-title": "Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess.",
"key": "24024_CR34",
"unstructured": "Chien, L.-C. & Chen, L.-W. Meteorological impacts on the incidence of COVID-19 in the US. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 34, 1675–1680 (2020).",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.06.15.20131490",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "24024_CR35",
"unstructured": "Gupta, A. & Pradhan, B. Impact of daily weather on COVID-19 outbreak in India. (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2020-044606",
"author": "KA Alene",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e044606",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open",
"key": "24024_CR36",
"unstructured": "Alene, K. A. et al. COVID-19 in Ethiopia: A geospatial analysis of vulnerability to infection, case severity and death. BMJ Open 11, e044606 (2021).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140556",
"author": "X Lian",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "140556",
"journal-title": "Sci. Total Environ.",
"key": "24024_CR37",
"unstructured": "Lian, X. et al. Impact of city lockdown on the air quality of COVID-19-hit of Wuhan city. Sci. Total Environ. 742, 140556 (2020).",
"volume": "742",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nsr/nwab100",
"author": "J Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "nwab100",
"journal-title": "Natl. Sci. Rev.",
"key": "24024_CR38",
"unstructured": "Huang, J. et al. The oscillation-outbreaks characteristic of the COVID-19 pandemic. Natl. Sci. Rev. 8, nwab100 (2021).",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139487",
"author": "Z Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "139487",
"journal-title": "Sci. Total Environ.",
"key": "24024_CR39",
"unstructured": "Huang, Z. et al. Optimal temperature zone for the dispersal of COVID-19. Sci. Total Environ. 736, 139487 (2020).",
"volume": "736",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scib.2020.08.002",
"author": "J Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1884",
"journal-title": "Sci. Bull.",
"key": "24024_CR40",
"unstructured": "Huang, J. et al. Global prediction system for COVID-19 pandemic. Sci. Bull. 65, 1884 (2020).",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 40,
"references-count": 40,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-24024-9"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Multidisciplinary"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effects of climatic factors on COVID-19 transmission in Ethiopia",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "12"
}