Proton pump inhibitor use and risk for recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis
et al., Clinical Microbiology and Infection, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008, PROSPERO CRD42020203084, May 2021
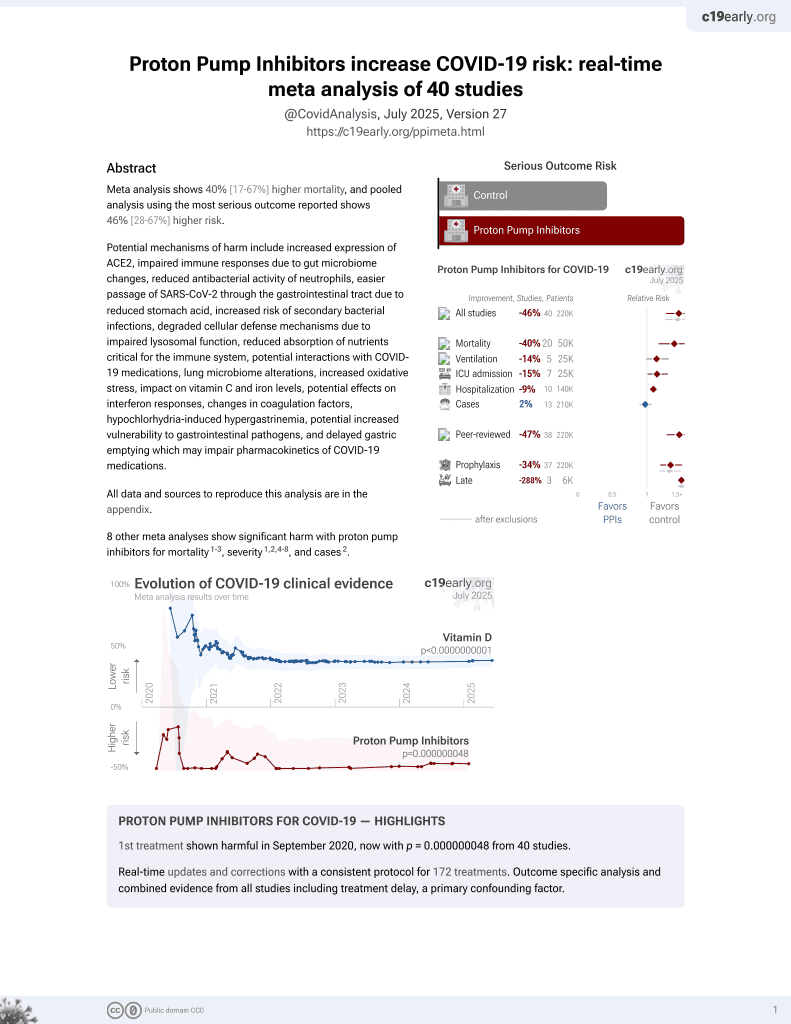
PPIs for COVID-19
1st treatment shown to increase risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000048 from 40 studies.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
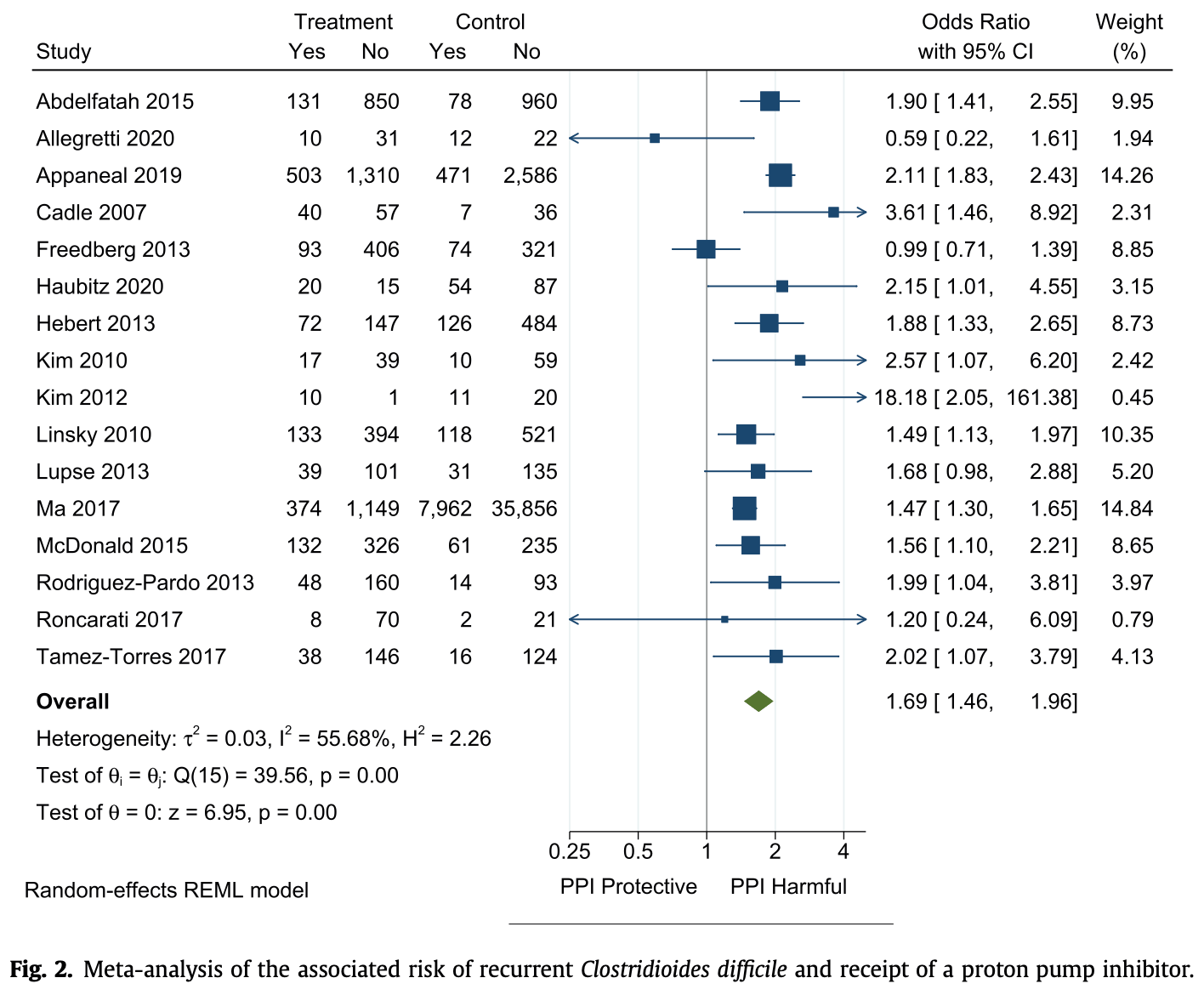
Meta-analysis of 16 studies with 57,477 patients showing significantly higher risk of recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) in patients prescribed proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) compared to those not prescribed PPIs. The association between PPI use and higher risk of CDI recurrence persisted across multiple subgroup and sensitivity analyses.
D'Silva et al., 31 May 2021, peer-reviewed, 7 authors, trial PROSPERO CRD42020203084.
Contact: emily.mcdonald@mcgill.ca.
Proton pump inhibitor use and risk for recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Clinical Microbiology and Infection, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008
Objectives: Proton pump inhibitor (PPI) therapy is a potentially modifiable risk factor for recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI). Citing an absence of clinical trials, many guidelines do not provide recommendations for addressing PPI management. Our aim was to perform an updated systematic review and meta-analysis evaluating the association between PPI use and recurrent CDI addressing prior methodological limitations. Methods: Data sources were MEDLINE and EMBASE. Eligible studies were cohort and caseecontrol studies; there were no restrictions on study setting or duration of follow-up. Participants were adults with prior CDI who did or did not receive PPI therapy and were assessed for recurrent CDI. Summary (unadjusted) odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated using a random effects model. Prespecified subgroup analyses were performed to explore heterogeneity including study design, study quality, duration of follow-up, adjustment for confounders, and outcome definition. Results: Sixteen studies were included in the meta-analysis, comprising 57 477 patients with CDI, of whom 6870 (12%) received PPIs. The rate of recurrent CDI was 24% in patients treated with PPIs versus 18% in those who were not. A meta-analysis that pooled unadjusted odds ratios demonstrated higher odds of recurrent CDI in patients who received PPIs (OR 1.69, 95%CI 1.46e1.96) versus those who did not. There was moderate heterogeneity between studies (I 2 56%); however, a sensitivity analysis restricted to studies with 56 days of follow-up substantially reduced the heterogeneity (OR 1.59, 95%CI 1.36e1.85; I 2 12%). An analysis restricted to multivariate studies that combined adjusted ORs also demonstrated higher odds of recurrent CDI in patients who received PPIs (OR 1.49, 95%CI 1.12e2.00). No publication bias was identified. Conclusions: We found significantly higher odds of recurrent CDI among users of PPIs that persisted across multiple sensitivity analyses. These results support stronger recommendations for PPI stewardship at CDI diagnosis.
Appendix A. Supplementary data Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008 .
References
Abdelfatah, Nayfe, Nijim, Enriquez, Ali et al., Factors predicting recurrence of Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) in hospitalized patients, J Investig Med
Allegretti, Marcus, Storm, Sitko, Kennedy et al., Clinical predictors of recurrence after primary Clostridioides difficile infection: a prospective cohort study, Dig Dis Sci
Appaneal, Caffrey, Beganovic, Avramovic, Laplante, Predictors of Clostridioides difficile recurrence across a national cohort of veterans in outpatient, acute, and long-term care settings, Am J Health Syst Pharm
Azab, Doo, Doo, Elmofti, Ahmed et al., Comparison of the hospital-acquired Clostridium difficile infection risk of using proton pump inhibitors versus histamine-2 receptor antagonists for prophylaxis and treatment of stress ulcers: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Gut Liver
Cadle, Mansouri, Logan, Kudva, Musher, Association of proton-pump inhibitors with outcomes in Clostridium difficile colitis, Am J Health Syst Pharm
Choudhry, Soran, Ziglam, Overuse and inappropriate prescribing of proton pump inhibitors in patients with Clostridium difficile-associated disease, Q J Med
Cohen, Gerding, Johnson, Kelly, Loo et al., Clinical practice guidelines for Clostridium difficile infection in adults: 2010 update by the society for healthcare epidemiology of America (SHEA) and the infectious Diseases society of America (IDSA), Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol
Freedberg, Salmasian, Friedman, Abrams, Proton pump inhibitors and risk for recurrent Clostridium difficile infection among inpatients, Am J Gastroenterol
Guery, Galperine, Barbut, Clostridioides difficile: diagnosis and treatments, BMJ
Guyatt, Oxman, Vist, Kunz, Falck-Ytter et al., GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations, BMJ
Hafiz, Wong, Paynter, David, Peeters, The risk of community-acquired enteric infection in proton pump inhibitor therapy: systematic review and meta-analysis, Ann Pharmacother
Haubitz, Bartlom, Laffer, Spelters, Fankhauser et al., Outcome of Clostridioides difficile infections treated in a Swiss tertiary care hospital: an observational study, Swiss Med Weekly
Hebert, Du, Peterson, Robicsek, Electronic health record-based detection of risk factors for Clostridium difficile infection relapse, Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol
Hopkins, Wilson, Treatment of recurrent Clostridium difficile colitis: a narrative review, Gastroenterol Rep
Kim, Graham, Jang, Proton pump inhibitor use and recurrent Clostridium difficile-associated disease, J Clin Gastroenterol
Kim, Lee, Jeong, Kim, Shin et al., Proton pump inhibitors as a risk factor for recurrence of Clostridium-difficile-associated diarrhea, World J Gastroenterol
Kimura, Snijder, Sugitani, Characterization and risk factors for recurrence of Clostridioides (Clostridium) difficile infection in Japan: a nationwide real-world analysis using a large hospital-based administrative dataset, J Infect Chemother
Linsky, Gupta, Lawler, Fonda, Hermos, Proton pump inhibitors and risk for recurrent Clostridium difficile infection, Arch Intern Med
Loo, Davis, Embil, Evans, Hota et al., Association of medical microbiology and infectious disease Canada treatment practice guideline for Clostridium difficile infection, Off J Assoc Med Microbiol Infect Dis Can
Lupse, Flonta, Cioara, Filipescu, Todor, Predictors of first recurrence in Clostridium difficile-associated disease. A study of 306 patients hospitalized in a Romanian tertiary referral center, J Gastrointest Liver Dis
Ma, Brensinger, Wu, Lewis, Increasing incidence of multiply recurrent Clostridium difficile infection in the United States: a cohort study, Ann Intern Med
Maier, Pruteanu, Kuhn, Zeller, Telzerow et al., Extensive impact of non-antibiotic drugs on human gut bacteria, Nature
Mcdonald, Gerding, Johnson, Bakken, Carroll et al., Clinical practice guidelines for Clostridium difficile infection in adults and children: 2017 update by the infectious Diseases society of America (IDSA) and society for healthcare epidemiology of America (SHEA), Clin Infect Dis
Mcdonald, Jones, Green, Jayaraman, Lee, Reduction of inappropriate exit prescriptions for proton pump inhibitors: a before-after study using education paired with a web-based quality-improvement tool, J Hosp Med
Mcdonald, Milligan, Frenette, Lee, Continuous proton pump inhibitor therapy and the associated risk of recurrent Clostridium difficile infection, JAMA Intern Med
Mcdonald, Wu, Rashidi, Forster, Huang et al., The MedSafer Study: a controlled trial of an electronic decision support tool for deprescribing in acute care, J Am Geriatr Soc
Mehta, Nahass, Brunetti, Acid suppression medications during hospitalization as a risk factor for recurrence of Clostridioides difficile infection: systematic review and meta-analysis, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa545
Moher, Liberati, Tetzlaff, Altman, Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement, BMJ
Oshima, Wu, Li, Fukui, Watari et al., Magnitude and direction of the association between Clostridium difficile infection and proton pump inhibitors in adults and pediatric patients: a systematic review and metaanalysis, J Gastroenterol
Rodriguez-Pardo, Almirante, Bartolome, Pomar, Mirelis et al., Epidemiology of Clostridium difficile infection and risk factors for unfavorable clinical outcomes: results of a hospital-based study in Barcelona, Spain, J Clin Microbiol
Roncarati, Dallolio, Leoni, Panico, Zanni et al., Surveillance of Clostridium difficile infections: results from a six-year retrospective study in nine hospitals of a North Italian Local Health Authority, Int J Environ Res Public Health
Rotramel, Poritz, Messaris, Berg, Stewart, PPI therapy and albumin are better predictors of recurrent Clostridium difficile colitis than choice of antibiotics, J Gastrointest Surg
Santos-Schaller, Boisset, Seigneurin, Epaulard, Recurrence and death after Clostridium difficile infection: gender-dependant influence of proton pump inhibitor therapy, Springerplus
Stroup, Berlin, Morton, Olkin, Williamson et al., Metaanalysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting, JAMA
Tamez-Torres, Torres-Gonz Alez, Leal-Vega, Garcia-Alderete, Garcia et al., Impact of Clostridium difficile infection caused by the NAP1/RT027 strain on severity and recurrence during an outbreak and transition to endemicity in a Mexican tertiary care center, Int J Infect Dis
Tariq, Singh, Gupta, Pardi, Khanna, Association of gastric acid suppression with recurrent Clostridium difficile infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis, JAMA Intern Med
Vilcu, Sabatte, Blanchon, Souty, Maravic et al., Association between acute gastroenteritis and continuous use of proton pump inhibitors during winter periods of highest circulation of enteric viruses, JAMA Netw Open
Wells, Shea, Connell, The NewcastleeOttawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of non-randomized studies in meta-analyses
Willems, Van Dijk, Ket, Vandenbroucke-Grauls, Evaluation of the association between gastric acid suppression and risk of intestinal colonization with multidrug-resistant microorganisms, JAMA Intern Med
Zhang, Palazuelos-Munoz, Balsells, Nair, Chit et al., Cost of hospital management of Clostridium difficile infection in United Statesda meta-analysis and modelling study, BMC Infect Dis
Zimmermann, Zimmermann-Kogadeeva, Wegmann, Goodman, Mapping human microbiome drug metabolism by gut bacteria and their genes, Nature
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008",
"ISSN": [
"1198-743X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008",
"alternative-id": [
"S1198743X21000355"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "D'Silva",
"given": "Kristin M.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mehta",
"given": "Raaj",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mitchell",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Todd C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Singhal",
"given": "Vibha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilson",
"given": "Marnie Goodwin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McDonald",
"given": "Emily G.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Clinical Microbiology and Infection",
"container-title-short": "Clinical Microbiology and Infection",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-18T06:57:04Z",
"timestamp": 1610953024000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-04T00:55:48Z",
"timestamp": 1635987348000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100000156",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/501100000156",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Fonds de Recherche du Québec - Santé"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000002",
"award": [
"T32-AR-007258"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100000002",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "National Institutes of Health"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-01T22:49:17Z",
"timestamp": 1722552557074
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 34,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-05-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1619827200000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-14T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1610582400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1198743X21000355?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1198743X21000355?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "697-703",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-016-1786-6",
"article-title": "Cost of hospital management of Clostridium difficile infection in United States—a meta-analysis and modelling study",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib1",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/gastro/gox041",
"article-title": "Treatment of recurrent Clostridium difficile colitis: a narrative review",
"author": "Hopkins",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "21",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterol Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib2",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.42",
"article-title": "Continuous proton pump inhibitor therapy and the associated risk of recurrent Clostridium difficile infection",
"author": "McDonald",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "784",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib3",
"volume": "175",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5009/gnl16568",
"article-title": "Comparison of the hospital-acquired Clostridium difficile infection risk of using proton pump inhibitors versus histamine-2 receptor antagonists for prophylaxis and treatment of stress ulcers: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Azab",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "781",
"journal-title": "Gut Liver",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib4",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2017.0212",
"article-title": "Association of gastric acid suppression with recurrent Clostridium difficile infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Tariq",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "784",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib5",
"volume": "177",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "Overuse and inappropriate prescribing of proton pump inhibitors in patients with Clostridium difficile-associated disease",
"author": "Choudhry",
"first-page": "445",
"journal-title": "Q J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib6",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jhm.2330",
"article-title": "Reduction of inappropriate exit prescriptions for proton pump inhibitors: a before-after study using education paired with a web-based quality-improvement tool",
"author": "McDonald",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "281",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J Hosp Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib7",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00535-017-1369-3",
"article-title": "Magnitude and direction of the association between Clostridium difficile infection and proton pump inhibitors in adults and pediatric patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Oshima",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "84",
"journal-title": "J Gastroenterol",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib8",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"article-title": "Acid suppression medications during hospitalization as a risk factor for recurrence of Clostridioides difficile infection: systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Mehta",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/cix1085",
"article-title": "Clinical practice guidelines for Clostridium difficile infection in adults and children: 2017 update by the infectious Diseases society of America (IDSA) and society for healthcare epidemiology of America (SHEA)",
"author": "McDonald",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib10",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.283.15.2008",
"article-title": "Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting",
"author": "Stroup",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2008",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib11",
"volume": "283",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.b2535",
"article-title": "Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement",
"author": "Moher",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib12",
"volume": "339",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"author": "Wells",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib13",
"series-title": "The Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of non-randomized studies in meta-analyses",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1086/651706",
"article-title": "Clinical practice guidelines for Clostridium difficile infection in adults: 2010 update by the society for healthcare epidemiology of America (SHEA) and the infectious Diseases society of America (IDSA)",
"author": "Cohen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "431",
"journal-title": "Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib14",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/JIM.0000000000000188",
"article-title": "Factors predicting recurrence of Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) in hospitalized patients",
"author": "Abdelfatah",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "747",
"journal-title": "J Investig Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib15",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajhp/zxz032",
"article-title": "Predictors of Clostridioides difficile recurrence across a national cohort of veterans in outpatient, acute, and long-term care settings",
"author": "Appaneal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "581",
"journal-title": "Am J Health Syst Pharm",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib16",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2146/ajhp060629",
"article-title": "Association of proton-pump inhibitors with outcomes in Clostridium difficile colitis",
"author": "Cadle",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2359",
"journal-title": "Am J Health Syst Pharm",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib17",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"article-title": "Outcome of Clostridioides difficile infections treated in a Swiss tertiary care hospital: an observational study",
"author": "Haubitz",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Swiss Med Weekly",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib18",
"volume": "150",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3748/wjg.v16.i28.3573",
"article-title": "Proton pump inhibitors as a risk factor for recurrence of Clostridium-difficile-associated diarrhea",
"author": "Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3573",
"journal-title": "World J Gastroenterol",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib19",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MCG.0b013e3182431d78",
"article-title": "Proton pump inhibitor use and recurrent Clostridium difficile-associated disease",
"author": "Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "397",
"journal-title": "J Clin Gastroenterol",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib20",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiac.2019.03.011",
"article-title": "Characterization and risk factors for recurrence of Clostridioides (Clostridium) difficile infection in Japan: a nationwide real-world analysis using a large hospital-based administrative dataset",
"author": "Kimura",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "615",
"journal-title": "J Infect Chemother",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib21",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "Predictors of first recurrence in Clostridium difficile-associated disease. A study of 306 patients hospitalized in a Romanian tertiary referral center",
"author": "Lupse",
"first-page": "397",
"journal-title": "J Gastrointest Liver Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib22",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M16-2733",
"article-title": "Increasing incidence of multiply recurrent Clostridium difficile infection in the United States: a cohort study",
"author": "Ma",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "152",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib23",
"volume": "167",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph14010061",
"article-title": "Surveillance of Clostridium difficile infections: results from a six-year retrospective study in nine hospitals of a North Italian Local Health Authority",
"author": "Roncarati",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Int J Environ Res Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib24",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2017.09.022",
"article-title": "Impact of Clostridium difficile infection caused by the NAP1/RT027 strain on severity and recurrence during an outbreak and transition to endemicity in a Mexican tertiary care center",
"author": "Tamez-Torres",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "44",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib25",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10620-019-05900-3",
"article-title": "Clinical predictors of recurrence after primary Clostridioides difficile infection: a prospective cohort study",
"author": "Allegretti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1761",
"journal-title": "Dig Dis Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib26",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ajg.2013.333",
"article-title": "Proton pump inhibitors and risk for recurrent Clostridium difficile infection among inpatients",
"author": "Freedberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1794",
"journal-title": "Am J Gastroenterol",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib27",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1086/669864",
"article-title": "Electronic health record-based detection of risk factors for Clostridium difficile infection relapse",
"author": "Hebert",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "407",
"journal-title": "Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib28",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/archinternmed.2010.73",
"article-title": "Proton pump inhibitors and risk for recurrent Clostridium difficile infection",
"author": "Linsky",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "772",
"journal-title": "Arch Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib29",
"volume": "170",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JCM.03352-12",
"article-title": "Epidemiology of Clostridium difficile infection and risk factors for unfavorable clinical outcomes: results of a hospital-based study in Barcelona, Spain",
"author": "Rodriguez-Pardo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1465",
"journal-title": "J Clin Microbiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib30",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40064-016-2058-z",
"article-title": "Recurrence and death after Clostridium difficile infection: gender-dependant influence of proton pump inhibitor therapy",
"author": "Dos Santos-Schaller",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Springerplus",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib31",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11605-012-2037-9",
"article-title": "PPI therapy and albumin are better predictors of recurrent Clostridium difficile colitis than choice of antibiotics",
"author": "Rotramel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2267",
"journal-title": "J Gastrointest Surg",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib32",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-019-1291-3",
"article-title": "Mapping human microbiome drug metabolism by gut bacteria and their genes",
"author": "Zimmermann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "462",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib33",
"volume": "570",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature25979",
"article-title": "Extensive impact of non-antibiotic drugs on human gut bacteria",
"author": "Maier",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "623",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib34",
"volume": "555",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0009",
"article-title": "Evaluation of the association between gastric acid suppression and risk of intestinal colonization with multidrug-resistant microorganisms",
"author": "Willems",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "561",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib35",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.16205",
"article-title": "Association between acute gastroenteritis and continuous use of proton pump inhibitors during winter periods of highest circulation of enteric viruses",
"author": "Vilcu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib36",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1060028018760569",
"article-title": "The risk of community-acquired enteric infection in proton pump inhibitor therapy: systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Hafiz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "613",
"journal-title": "Ann Pharmacother",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib37",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jgs.16040",
"article-title": "The MedSafer Study: a controlled trial of an electronic decision support tool for deprescribing in acute care",
"author": "McDonald",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1843",
"journal-title": "J Am Geriatr Soc",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib38",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "Clostridioides difficile: diagnosis and treatments",
"author": "Guery",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib39",
"volume": "366",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "Association of medical microbiology and infectious disease Canada treatment practice guideline for Clostridium difficile infection",
"author": "Loo",
"first-page": "71",
"journal-title": "Off J Assoc Med Microbiol Infect Dis Can",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib40",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.39489.470347.AD",
"article-title": "GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations",
"author": "Guyatt",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "924",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.008_bib41",
"volume": "336",
"year": "2008"
}
],
"reference-count": 41,
"references-count": 41,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1198743X21000355"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Proton pump inhibitor use and risk for recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "27"
}