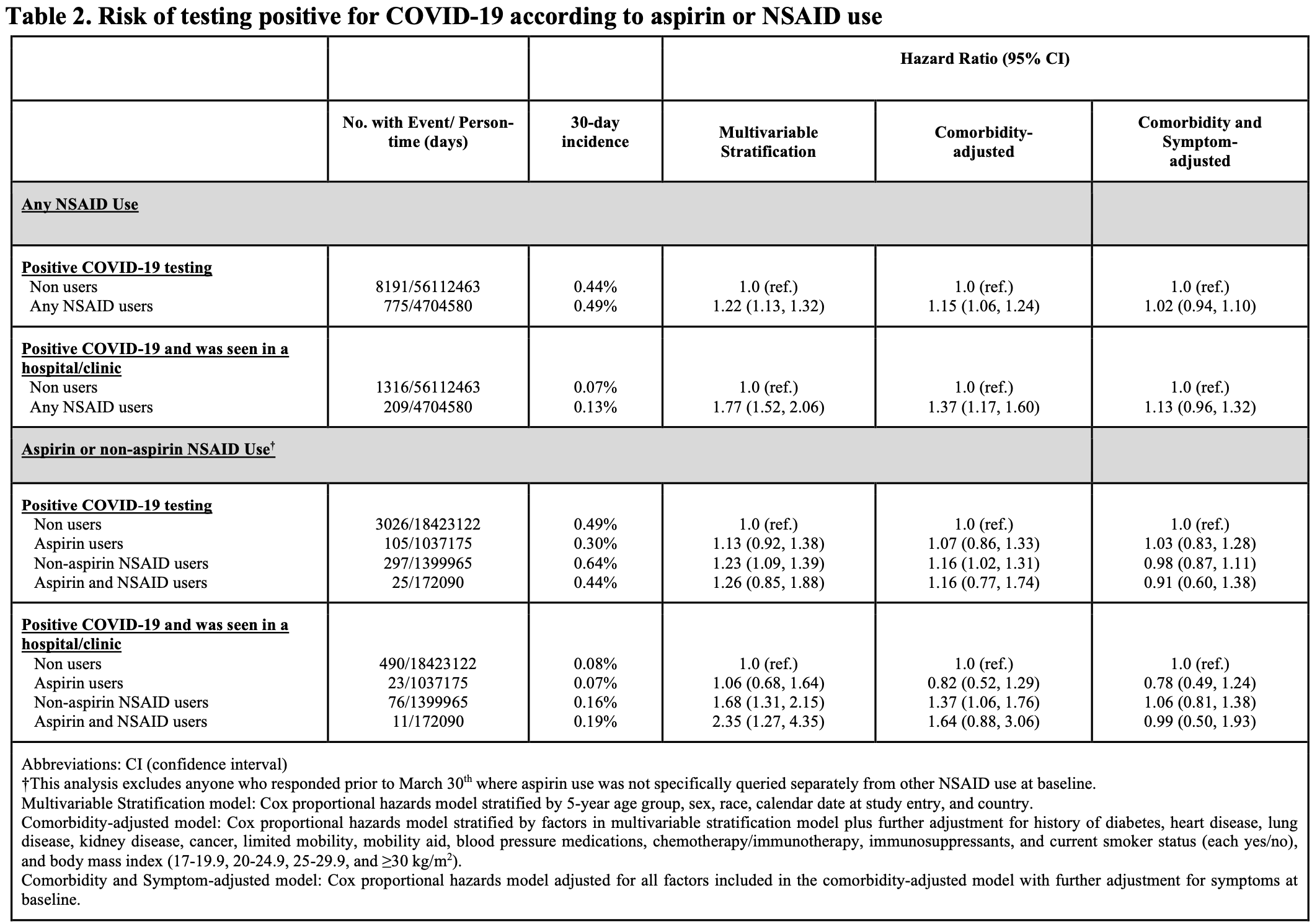
Aspirin and NSAID use and the risk of COVID-19
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.04.28.21256261, May 2021
Retrospective 2,736,091 individuals in the U.S., U.K., and Sweden, showing lower risk of hospital/clinic visits with aspirin use.
|
risk of progression, 22.0% lower, HR 0.78, p = 0.30, adjusted per study, seen in hospital/clinic, comorbidity and symptom adjusted, multivariable.
|
|
risk of case, 3.0% higher, HR 1.03, p = 0.80, adjusted per study, comorbidity and symptom adjusted, multivariable.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Drew et al., 2 May 2021, retrospective, multiple countries, preprint, 25 authors, study period 24 March, 2020 - 8 May, 2020.
Contact: achan@mgh.harvard.edu.
Abstract: medRxiv preprint doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.04.28.21256261; this version posted May 2, 2021. The copyright holder for this preprint
(which was not certified by peer review) is the author/funder, who has granted medRxiv a license to display the preprint in perpetuity.
It is made available under a CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 International license .
Aspirin and NSAID use and the risk of COVID-19
David A. Drew1,2*, Chuan-Guo Guo1,2,3*, Karla A. Lee4*, Long H. Nguyen1,2,5, Amit D. Joshi1,2, Chun-Han
Lo1,2,6, Wenjie Ma1,2, Raaj S. Mehta1,2, Sohee Kwon1,2, Christina M. Astley7,8, Mingyang Song6,9, Richard
Davies10, Joan Capdevila10, Mary Ni Lochlainn4, Carole H. Sudre11, Mark S. Graham11, Thomas Varsavsky11,
Maria F. Gomez12, Beatrice Kennedy13, Hugo Fitipaldi12, Jonathan Wolf10, Tim D. Spector4, Sebastien
Ourselin11, Claire J. Steves4, Andrew T. Chan1,2,8,14,15†
Affiliations:
1
Clinical and Translational Epidemiology Unit, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School,
Boston, MA, U.S.A.
2
Division of Gastroenterology, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA,
U.S.A.
3
Department of Medicine, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
4
Department of Twin Research and Genetic Epidemiology, King’s College London, London, U.K.
5
Department of Biostatistics, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, MA, U.S.A.
6
Department of Epidemiology, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, MA, U.S.A.
7
Division of Endocrinology and Computational Epidemiology Lab, Boston Children's Hospital and Harvard
Medical School, Boston, MA, U.S.A.
8
Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Cambridge, MA, U.S.A.
9
Department of Nutrition, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, MA, U.S.A.
10
Zoe Global Ltd., London, U.K.
11
School of Biomedical Engineering & Imaging Sciences, King’s College London, London, U.K.
12
Department of Clinical Sciences, Lund University Diabetes Centre, Lund University, Malmö, Sweden
13
Department of Medical Sciences, Molecular Epidemiology and Science for Life Laboratory, Uppsala
University, Uppsala, Sweden.
14
Department of Immunology and Infectious Disease, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, MA,
U.S.A.
15
Massachusetts Consortium on Pathogen Readiness
*Contributed equally to this work
†To whom correspondence should be addressed: Andrew T. Chan, MD, MPH, Clinical & Translational
Epidemiology Unit, Massachusetts General Hospital, 100 Cambridge St. Boston, MA, 02114.
achan@mgh.harvard.edu
One Sentence Summary: NSAID use is not associated with COVID-19 risk.
NOTE: This preprint reports new research that has not been certified by peer review and should not be used to guide clinical practice.
medRxiv preprint doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.04.28.21256261; this version posted May 2, 2021. The copyright holder for this preprint
(which was not certified by peer review) is the author/funder, who has granted medRxiv a license to display the preprint in perpetuity.
It is made available under a CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 International license .
Abstract: Early reports raised concern that use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may
increase risk of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) disease (COVID-19). Users of
the COVID Symptom Study smartphone application reported use of aspirin and other NSAIDs between March
24 and May 8, 2020. Users were queried daily about symptoms, COVID-19 testing, and healthcare..
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.04.28.21256261",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/2021.04.28.21256261",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p>Early reports raised concern that use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may increase risk of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) disease (COVID-19). Users of the COVID Symptom Study smartphone application reported use of aspirin and other NSAIDs between March 24 and May 8, 2020. Users were queried daily about symptoms, COVID-19 testing, and healthcare seeking behavior. Cox proportional hazards regression was used to determine the risk of COVID-19 among according to aspirin or non-aspirin NSAID users. Among 2,736,091 individuals in the U.S., U.K., and Sweden, we documented 8,966 incident reports of a positive COVID-19 test over 60,817,043 person-days of follow-up. Compared to non-users and after stratifying by age, sex, country, day of study entry, and race/ethnicity, non-aspirin NSAID use was associated with a modest risk for testing COVID-19 positive (HR 1.23 [1.09, 1.32]), but no significant association was observed among aspirin users (HR 1.13 [0.92, 1.38]). After adjustment for lifestyle factors, comorbidities and baseline symptoms, any NSAID use was not associated with risk (HR 1.02 [0.94, 1.10]). Results were similar for those seeking healthcare for COVID-19 and were not substantially different according to lifestyle and sociodemographic factors or after accounting for propensity to receive testing. Our results do not support an association of NSAID use, including aspirin, with COVID-19 infection. Previous reports of a potential association may be due to higher rates of comorbidities or use of NSAIDs to treat symptoms associated with COVID-19.</jats:p><jats:sec><jats:title>One Sentence Summary</jats:title><jats:p>NSAID use is not associated with COVID-19 risk.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
30
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Drew",
"given": "David A.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Guo",
"given": "Chuan-Guo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Karla A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5436-4219",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Nguyen",
"given": "Long H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Joshi",
"given": "Amit D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lo",
"given": "Chun-Han",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ma",
"given": "Wenjie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mehta",
"given": "Raaj S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kwon",
"given": "Sohee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Astley",
"given": "Christina M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Song",
"given": "Mingyang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davies",
"given": "Richard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Capdevila",
"given": "Joan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lochlainn",
"given": "Mary Ni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5753-428X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sudre",
"given": "Carole H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4170-1095",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Graham",
"given": "Mark S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Varsavsky",
"given": "Thomas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gomez",
"given": "Maria F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kennedy",
"given": "Beatrice",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fitipaldi",
"given": "Hugo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wolf",
"given": "Jonathan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Spector",
"given": "Tim D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5694-5340",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ourselin",
"given": "Sebastien",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Steves",
"given": "Claire J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chan",
"given": "Andrew T.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2021-05-02T19:15:12Z",
"timestamp": 1619982912000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2021-05-04T13:50:57Z",
"timestamp": 1620136257000
},
"group-title": "Epidemiology",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-21T02:28:29Z",
"timestamp": 1663727309988
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "medRxiv"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
2
]
]
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1101/2021.04.28.21256261",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "246",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
2
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.1101",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb8034",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021050406501407000_2021.04.28.21256261v1.1"
},
{
"key": "2021050406501407000_2021.04.28.21256261v1.2",
"unstructured": "U. National Health Service. (NHS UK, nhs.uk, 2020)."
},
{
"key": "2021050406501407000_2021.04.28.21256261v1.3",
"unstructured": "USFDA. (2020), vol. 2020."
},
{
"key": "2021050406501407000_2021.04.28.21256261v1.4",
"unstructured": "G. Kolata , in The New York Times. (nytimes.com, nytimes.com, 2020), vol. 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30116-8",
"article-title": "Are patients with hypertension and diabetes mellitus at increased risk for COVID-19 infection?",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e21",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "2021050406501407000_2021.04.28.21256261v1.5",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2002032",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021050406501407000_2021.04.28.21256261v1.6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/all.14238",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021050406501407000_2021.04.28.21256261v1.7",
"unstructured": "J. J. Zhang et al., Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China. Allergy, (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30079-5",
"article-title": "Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "475",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "2021050406501407000_2021.04.28.21256261v1.8",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021050406501407000_2021.04.28.21256261v1.9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2006923",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021050406501407000_2021.04.28.21256261v1.10",
"unstructured": "G. Mancia , F. Rea , M. Ludergnani , G. Apolone , G. Corrao , Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Blockers and the Risk of Covid-19. N Engl J Med, (2020)."
},
{
"key": "2021050406501407000_2021.04.28.21256261v1.11",
"unstructured": "H. R. Reynolds et al., Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitors and Risk of Covid-19. N Engl J Med, (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m606",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021050406501407000_2021.04.28.21256261v1.12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021050406501407000_2021.04.28.21256261v1.13",
"unstructured": "C. Wu et al., Risk Factors Associated With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Death in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA Intern Med, (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrc.2016.4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021050406501407000_2021.04.28.21256261v1.14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.294.5548.1871",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021050406501407000_2021.04.28.21256261v1.15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrclinonc.2011.199",
"article-title": "The role of aspirin in cancer prevention",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "259",
"journal-title": "Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology",
"key": "2021050406501407000_2021.04.28.21256261v1.16",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M16-0577",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021050406501407000_2021.04.28.21256261v1.17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.10478",
"article-title": "Venous Thrombosis Among Critically Ill Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2010478",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "2021050406501407000_2021.04.28.21256261v1.18",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "2021050406501407000_2021.04.28.21256261v1.19",
"unstructured": "P. Horby et al., Effect of Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: Preliminary Report. medRxiv, 2020.2006.2022.20137273 (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.04.02.20051334",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2021050406501407000_2021.04.28.21256261v1.20",
"unstructured": "D. A. Drew et al., Rapid implementation of mobile technology for real-time epidemiology of COVID-19. Science, (2020)."
},
{
"key": "2021050406501407000_2021.04.28.21256261v1.21",
"unstructured": "W. M. van der Wal , R. B. Geskus , ipw: An R Package for Inverse Probability Weighting. Journal of Statistical Software; Vol 1, Issue 13 (2011), (2011)."
}
],
"reference-count": 21,
"references-count": 21,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://medrxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2021.04.28.21256261"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Aspirin and NSAID use and the risk of COVID-19",
"type": "posted-content"
}