Hyperthermia in Humans Enhances Interferon-γ Synthesis and Alters the Peripheral Lymphocyte Population
et al., Journal of Interferon Research, doi:10.1089/jir.1988.8.143, Apr 1988
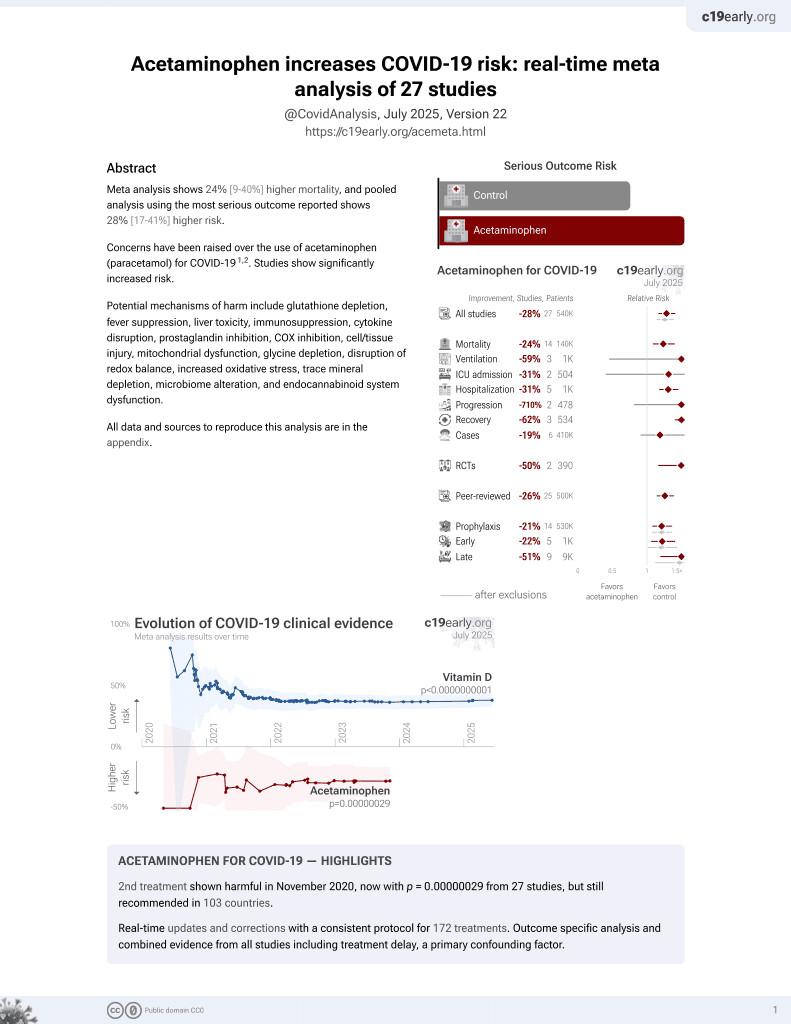
2nd treatment shown to increase risk in
November 2020, now with p = 0.00000029 from 27 studies, but still recommended in 103 countries.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
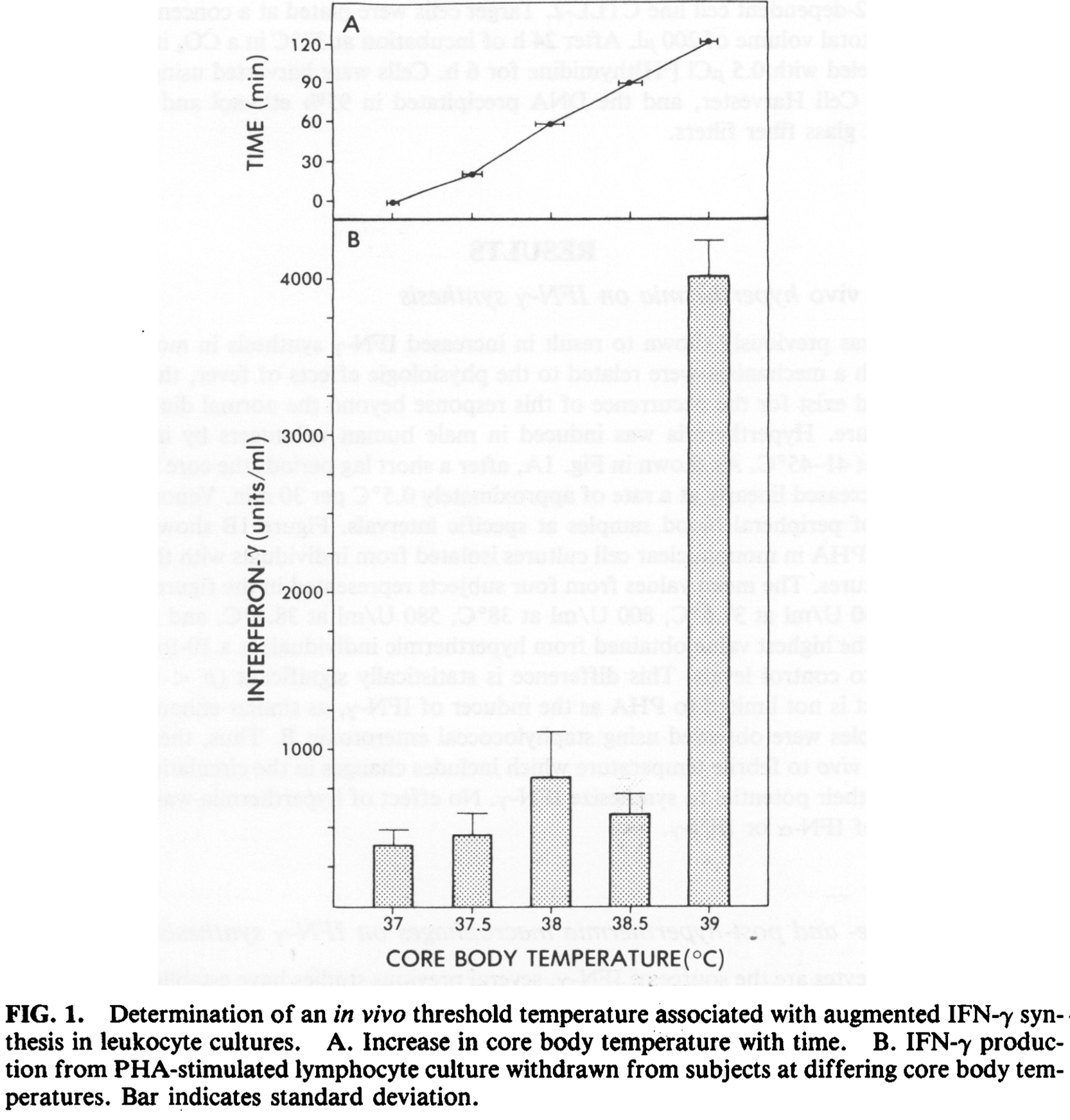
Analysis of induced hyperthermia (high body temperature) showing 10 times greater interferon gamma (IFN-γ) production and increased natural killer cells. This response was observed at a core body temperature of ~39°C, highlighting its potential relevance to fever.
Authors perfomed the analysis with healthy human volunteers by immersing them in warm water. Authors found a 10-fold increase in interferon gamma (IFN-γ) production by lymphocytes. IFN-γ has antiviral, immunomodulatory, and cell-activating functions. They also found an increase in natural killer cells, which have antitumor and antiviral activity, and increased suppressor/cytotoxic T cells and decreased helper T cells.
Authors suggest that the increased IFN-γ production and immunological changes may be relevant to fever during infections. Elevated body temperature may enhance antiviral defenses and immune cell responses.
Acetaminophen is also known as paracetamol, Tylenol, Panadol, Calpol, Tempra, Calprofen, Doliprane, Efferalgan, Grippostad C, Dolo, Acamol, Fevadol, Crocin, and Perfalgan.
Downing et al., 30 Apr 1988, Canada, peer-reviewed, 5 authors.
Hyperthermia in Humans Enhances Interferon-7 Synthesis and Alters the Peripheral Lymphocyte Population
Induction of hyperthermia (39°C) in human volunteers by immersion in warm water (41-45°C) rapidly alters the cell populations in the peripheral blood. In addition to granulocytosis, there is an alteration of the normal ratios among T-lymphocyte subsets. Follow¬ ing in vitro mitogen stimulation, lymphocytes from hyperthermic individuals produce as much as 10-fold more interferon-(IFN-) than cells withdrawn at basal core tempera¬ tures from the same individuals. A temperature threshold of 39°C for this response sug¬ gests potential relevance to fever. No change was noted in the activity of the macrophage population. The possible involvement of interleukin-2 (IL-2) in this enhanced production is discussed. No changes were noted in the circulating levels of IFN-.
References
Beisel, Alterations in hormone production and utilization during infection, in: Infection: The Physiologic and Metabolic Responses of the Host
Boyum, Separation of leukocytes from blood and bone marrow, Scand. J. Clin. Lab
Brahmi, Thomas, Park, Park, Dowdeswell, The effect of acute exercise on natural killer-cell activity of trained and sedentary human subjects, J. Clin. Immunol
Cohen, A study of the leukocytosis produced in man by artificial fever, J. Clin. Invest
Crary, Hauser, Borysenko, Kutz, Hoban et al., Epinephrine-induced changes in the distribution of lymphocyte subsets in peripheral blood of humans, J. Immunol
Dinarello, Conti, Mier, Effects of human interleukin-1 on natural killer cell activity: Is fever a host defense mechanism for tumor killing?, Yale J. Biol. Med
Downing, Taylor, Wei, Elizondo, In vivo hyperthermia en¬ hances plasma antiviral activity and stimulates peripheral lymphocytes for increased synthesis of inter¬ feron, J. Interferon Res
Downing, The effect of in vivo hyperthermia on selected lympho¬ kines in man, Lymphokine Res
Epstein, Cline, Merigan, The interaction of human macrophages and lymphocytes in the phytohemagglutinin-stimulated production of interferon, J. Clin. Invest
Farrar, Johnson, Farrar, Regulation of the production of im¬ mune interferon and cytotoxic lymphocytes by interleukin 2, J. Immunol
Herberman, Interferon and cytotoxic effector cells
Jampel, Duff, Gershon, Atkins, Fever and immunoregulation. III. Hyperthermia augments the primary in vitro humoral immune response, J. Exp. Med
Nahas, Tannieres, Lennon, Direct measurement of leukocyte motility: Effect of pH and temperature, Soc. Exp. Biol. Med
Palacios, Martinez-, Deley, Determination of human leukocyte populations involved in production of interferons alpha and gamma, Eur. J. Immunol
Roberts, Jr, Sandberg, Hyperthermia and human leukocyte functions. II. Enhanced production of and response to leukocyte migration inhibition factor (LIF), J. Immunol
Roberts, Temperature and host defense, Microbiol. Rev
Sariran, Nickerson, Enhancement of murine in vitro antibody formation by hyperthermia, Cell Immunol
Schultz, Kleinschmidt, Functional identity between murine -interferon and macrophage activating factor, Nature
Sidman, Marshall, Schultz, Gray, -Interferon is one of several direct cell-maturing lymphokines, Nature
Vaughn, Kluger, Fever and survival in bacterially infected rabbits, Proc. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol
Wallach, Fellous, Revel, Preferential effect of -interferon on the syn¬ thesis of HLA antigens and their mRNAs in human cells, Nature
Wallach, The HLA proteins and a related protein of 28 KDa are preferentially induced by interferon-in human WISH cells, Eur. J. Immunol
Wiranowska-Stewart, Ii, Determination of human leukocyte populations involved in production of interferons alpha and gamma, J. Interferon Res
Wong, Clark-Lewis, Mckimm-Breschjkin, Harris, Schrader, Interferoninduces enhanced expression of la and H-2 antigens on B-lymphoid, macrophage, and myeloid cell lines, J. Immunol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1089/jir.1988.8.143",
"ISSN": [
"0197-8357"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/jir.1988.8.143",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1089/jir.1988.8.143"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "DOWNING",
"given": "J.F.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "MARTINEZ-VALDEZ",
"given": "H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "ELIZONDO",
"given": "R.S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "WALKER",
"given": "E.B.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "TAYLOR",
"given": "M.W.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Interferon Research",
"container-title-short": "Journal of Interferon Research",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2011,
3,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2011-03-10T06:46:41Z",
"timestamp": 1299739601000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2020-06-17T07:06:38Z",
"timestamp": 1592377598000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-28T05:29:08Z",
"timestamp": 1703741348446
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 54,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
1988,
4
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
1988,
4
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://www.liebertpub.com/nv/resources-tools/text-and-data-mining-policy/121/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
1988,
4,
1
]
],
"date-time": "1988-04-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 575856000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://www.liebertpub.com/doi/pdf/10.1089/jir.1988.8.143",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "278",
"original-title": [],
"page": "143-150",
"prefix": "10.1089",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
1988,
4
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
1988,
4
]
]
},
"publisher": "Mary Ann Liebert Inc",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1128/MMBR.43.2.241-259.1979",
"author": "ROBERTS N.J.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "241",
"journal-title": "Microbiol. Rev.",
"key": "p_26",
"volume": "43",
"year": "1979"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI100693",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "p_27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3181/00379727-138-35894",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "p_28"
},
{
"author": "ROBERTS N.J.",
"first-page": "1990",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "p_29",
"volume": "122",
"year": "1979"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1084/jem.157.4.1229",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "p_30"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0008-8749(82)90031-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "p_31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/305239a0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "p_32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/299833a0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "p_33"
},
{
"author": "WONG G.H.",
"first-page": "788",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "p_34",
"volume": "131",
"year": "1983"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/eji.1830131003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "p_35"
},
{
"author": "FARRAR W.L.",
"first-page": "1120",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "p_37",
"volume": "126",
"year": "1981"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/309801a0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "p_38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/jir.1987.7.185",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "p_39"
},
{
"author": "BOYUM A.",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Scand. J. Clin. Lab. (Suppl.)",
"key": "p_40",
"volume": "97",
"year": "1968"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI106545",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "p_41"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/jir.1981.1.233",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "p_42"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/eji.1830130308",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "p_43"
},
{
"author": "DOWNING J.F.",
"first-page": "103",
"journal-title": "Lymphokine Res.",
"key": "p_44",
"volume": "6",
"year": "1987"
},
{
"author": "DINARELLO CA.",
"first-page": "97",
"journal-title": "Yale J. Biol. Med.",
"key": "p_45",
"volume": "59",
"year": "1986"
},
{
"author": "VAUGHN L.K.",
"first-page": "511",
"journal-title": "Proc. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol.",
"key": "p_46",
"volume": "36",
"year": "1977"
},
{
"author": "CRARY B.",
"first-page": "1178",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "p_47",
"volume": "131",
"year": "1983"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/BF00918251",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "p_48"
}
],
"reference-count": 22,
"references-count": 22,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://www.liebertpub.com/doi/10.1089/jir.1988.8.143"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Virology",
"Immunology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Hyperthermia in Humans Enhances Interferon-γ Synthesis and Alters the Peripheral Lymphocyte Population",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "8"
}