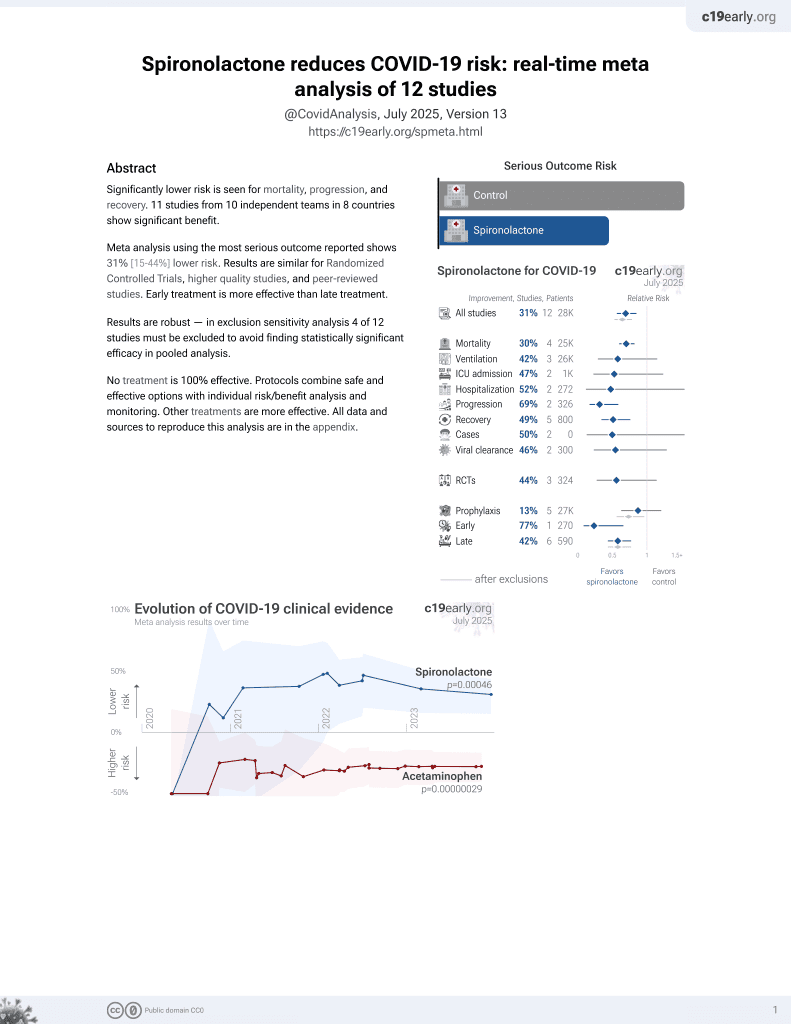
Association between spironolactone use and COVID-19 outcomes in population-scale claims data: a retrospective cohort study
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.02.28.23286515, Mar 2023
37th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2022, now with p = 0.00046 from 12 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
PSM retrospective 898,303 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in the USA, 16,324 on spironolactone, showing lower mortality and ventilation with spironolactone use.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
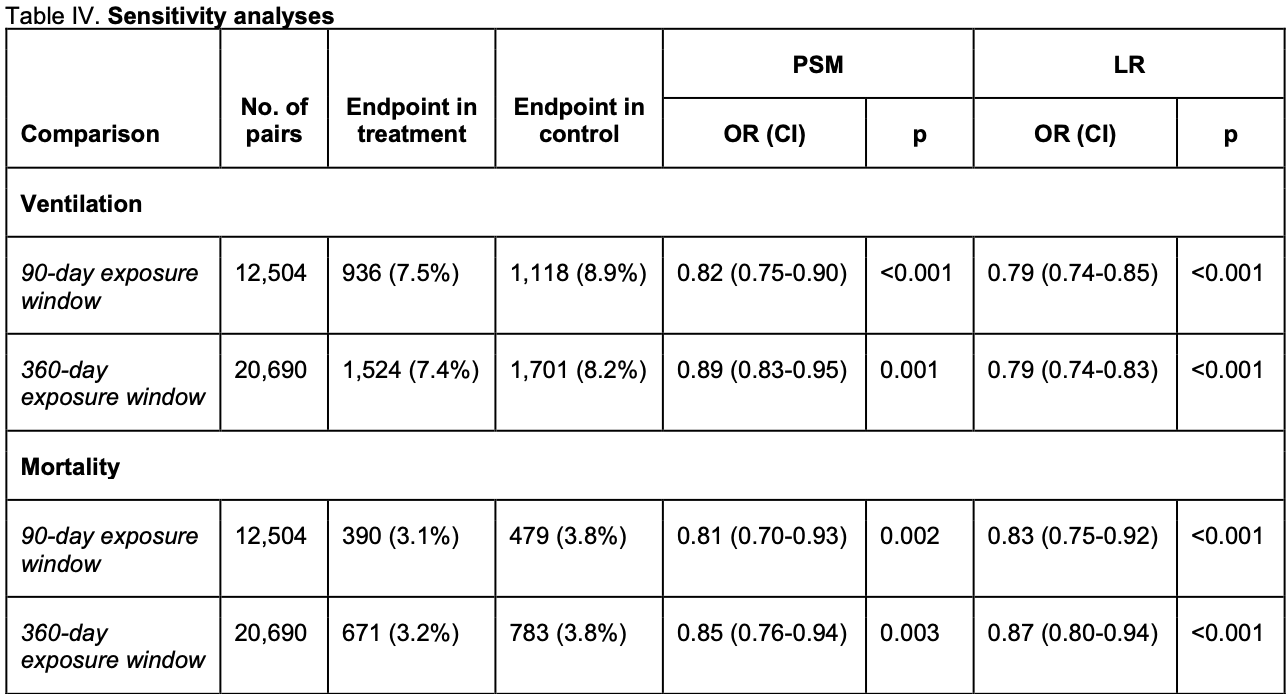
risk of death, 18.4% lower, RR 0.82, p = 0.004, treatment 390 of 12,504 (3.1%), control 479 of 12,504 (3.8%), NNT 140, odds ratio converted to relative risk, 90 day exposure window, propensity score matching.
|
|
risk of death, 11.6% lower, RR 0.88, p = 0.04, treatment 521 of 16,324 (3.2%), control 592 of 16,324 (3.6%), NNT 230, odds ratio converted to relative risk, 180 day exposure window, propensity score matching, primary outcome.
|
|
risk of death, 14.5% lower, RR 0.85, p = 0.003, treatment 671 of 20,690 (3.2%), control 783 of 20,690 (3.8%), NNT 185, odds ratio converted to relative risk, 360 day exposure window, propensity score matching.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 16.7% lower, RR 0.83, p < 0.001, treatment 936 of 12,504 (7.5%), control 1,118 of 12,504 (8.9%), NNT 69, odds ratio converted to relative risk, 90 day exposure window, propensity score matching.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 16.7% lower, RR 0.83, p < 0.001, treatment 1,212 of 16,324 (7.4%), control 1,459 of 16,324 (8.9%), NNT 66, odds ratio converted to relative risk, 180 day exposure window, propensity score matching, primary outcome.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 10.2% lower, RR 0.90, p < 0.001, treatment 1,524 of 20,690 (7.4%), control 1,701 of 20,690 (8.2%), NNT 117, odds ratio converted to relative risk, 360 day exposure window, propensity score matching.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Cousins et al., 2 Mar 2023, retrospective, propensity score matching, USA, peer-reviewed, 2 authors.
Association between spironolactone use and COVID-19 outcomes in population-scale claims data: a retrospective cohort study
doi:10.1101/2023.02.28.23286515
Background: Spironolactone has been proposed as a potential modulator of SARS-CoV-2 cellular entry. We aimed to measure the effect of spironolactone use on the risk of adverse outcomes following COVID-19 hospitalization.
Methods: We performed a retrospective cohort study of COVID-19 outcomes for patients with or without exposure to spironolactone, using population-scale claims data from the Komodo Healthcare Map. We identified all patients with a hospital admission for COVID-19 in the study window, defining treatment status based on spironolactone prescription orders. The primary outcomes were progression to respiratory ventilation or mortality during the hospitalization. Odds ratios (OR) were estimated following either 1:1 propensity score matching (PSM) or multivariable regression. Subgroup analysis was performed based on age, gender, body mass index (BMI), and dominant SARS-CoV-2 variant. Findings: Among 898,303 eligible patients with a COVID-19-related hospitalization, 16,324 patients (1.8%) had a spironolactone prescription prior to hospitalization. 59,937 patients (6.7%) met the ventilation endpoint, and 26,515 patients (3.0%) met the mortality endpoint. Spironolactone use was associated with a significant reduction in odds of both ventilation (OR 0.82; 95% CI: 0.75-0.88; p < 0.001) and mortality (OR 0.88; 95% CI: 0.78-0.99; p = 0.033) in the PSM analysis, supported by the regression analysis. Spironolactone use was associated with significantly reduced odds of NOTE: This preprint reports new research that has not been certified by peer review and should not be used to guide clinical practice.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS Both HCC and RBA contributed to all aspects of the manuscript (conceptualization, data acquisition, analysis, funding acquisition, investigation, methodology, project administration, resources, software, supervision, validation, visualization, drafting the manuscript, and reviewing the manuscript). Both HCC and RBA directly accessed and verified the underlying data.
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS No authors declare any competing interests.
References
Abbasi, Adatorwovor, Davarpanah, A Randomized Trial of Sitagliptin and Spironolactone With Combination Therapy in Hospitalized Adults With COVID-19, J Endocr Soc
Austin, A critical appraisal of propensity-score matching in the medical literature between 1996 and 2003, Stat Med
Baker, Bolt, Smith, The Relationship of COVID-19 Vaccination with Mortality Among 86,732 Hospitalized Patients: Subpopulations, Patient Factors, and Changes over Time, J Gen Intern Med
Balachandran, Moni, Sathyapalan, A comparison of clinical outcomes between vaccinated and vaccine-naive patients of COVID-19, in four tertiary care hospitals of Kerala, South India, Clin Epidemiol Glob Heal
Cadegiani, Goren, Wambier, Spironolactone may provide protection from SARS-CoV-2: Targeting androgens, angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), Med Hypotheses, doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110112
Cadegiani, Wambier, Goren, Spironolactone: An Anti-androgenic and Anti-hypertensive Drug That May Provide Protection Against the Novel Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) in COVID-19, Front Med
Dong, Ji, Yu, Wu, Zhang, Spironolactone alleviates diabetic nephropathy through promoting autophagy in podocytes, Int Urol Nephrol
Ferreira, Rossello, Pocock, Spironolactone dose in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: findings from TOPCAT, Eur J Heart Fail
Giagulli, Kaufman, Vermeulen, Pathogenesis of the decreased androgen levels in obese men, J Clin Endocrinol Metab
Harder, Stuart, Anthony, Propensity score techniques and the assessment of measured covariate balance to test causal associations in psychological research, Psychol Methods
Jeon, Son, Choi, Effect of Spironolactone on COVID-19 in Patients With Underlying Liver Cirrhosis: A Nationwide Case-Control Study in South Korea, Front Med
Kotfis, Lechowicz, Drożdżal, COVID-19-The Potential Beneficial Therapeutic Effects of Spironolactone during SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Pharmaceuticals
Lambrou, Shirk, Steele, Genomic Surveillance for SARS-CoV-2 Variants: Predominance of the Delta, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Leach, Mohr, Giotis, The antiandrogen enzalutamide downregulates TMPRSS2 and reduces cellular entry of SARS-CoV-2 in human lung cells, Nat Commun
Mancia, Rea, Ludergnani, Apolone, Corrao, Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Blockers and the Risk of Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Mareev, Orlova, Plisyk, Results of open-label non-randomized comparative clinical trial: "Bromhexine and spironolactone for coronаvirus infection requiring hospitalization (BISCUIT), Kardiologiya
Marzolini, Kuritzkes, Marra, Prescribing Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir: How to Recognize and Manage Drug-Drug Interactions, Ann Intern Med
Meng, Abdullahi, Ferreira, Altered TMPRSS2 usage by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron impacts infectivity and fusogenicity, Nature
Meng, Ge, Li, Protective trend of anti-androgen therapy during the COVID-19 pandemic: A meta-analysis, J Infect
Montopoli, Zumerle, Vettor, Androgen-deprivation therapies for prostate cancer and risk of infection by SARS-CoV-2: a population-based study (N = 4532), Ann Oncol
Murakami, Hayden, Hills, Therapeutic advances in COVID-19, Nat Rev Nephrol
Pottegård, Hallas, Assigning exposure duration to single prescriptions by use of the waiting time distribution, Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf
Qiao, Wang, Mannan, Targeting transcriptional regulation of SARS-CoV-2 entry factors ACE2 and TMPRSS2, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
Quan, Sundararajan, Halfon, Coding algorithms for defining comorbidities in ICD-9-CM and ICD-10 administrative data, Med Care
Ranganath, Horo, Challener, Rebound Phenomenon after Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir Treatment of Coronavirus Disease-2019 in High-Risk Persons, Clin Infect Dis
Samuel, Majd, Richter, Androgen Signaling Regulates SARS-CoV-2 Receptor Levels and Is Associated with Severe COVID-19 Symptoms in Men, Cell Stem Cell
Sica, Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Mineralocorticoid Blocking Agents and their Effects on Potassium Homeostasis, Heart Fail Rev
Southren, Tochimoto, Carmody, Isurugi, Plasma production rates of testosterone in normal adult men and women and in patients with the syndrome of feminizing testes, J Clin Endocrinol Metab
Tanskanen, Taipale, Koponen, Drug exposure in register-based research-An expert-opinion based evaluation of methods, PLoS One
Travison, Vesper, Orwoll, Harmonized Reference Ranges for Circulating Testosterone Levels in Men of Four Cohort Studies in the United States and Europe, J Clin Endocrinol Metab
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2023.02.28.23286515",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/2023.02.28.23286515",
"abstract": "<jats:title>ABSTRACT</jats:title><jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>Spironolactone has been proposed as a potential modulator of SARS-CoV-2 cellular entry. We aimed to measure the effect of spironolactone use on the risk of adverse outcomes following COVID-19 hospitalization.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>We performed a retrospective cohort study of COVID-19 outcomes for patients with or without exposure to spironolactone, using population-scale claims data from the Komodo Healthcare Map. We identified all patients with a hospital admission for COVID-19 in the study window, defining treatment status based on spironolactone prescription orders. The primary outcomes were progression to respiratory ventilation or mortality during the hospitalization. Odds ratios (OR) were estimated following either 1:1 propensity score matching (PSM) or multivariable regression. Subgroup analysis was performed based on age, gender, body mass index (BMI), and dominant SARS-CoV-2 variant.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Findings</jats:title><jats:p>Among 898,303 eligible patients with a COVID-19-related hospitalization, 16,324 patients (1.8%) had a spironolactone prescription prior to hospitalization. 59,937 patients (6.7%) met the ventilation endpoint, and 26,515 patients (3.0%) met the mortality endpoint. Spironolactone use was associated with a significant reduction in odds of both ventilation (OR 0.82; 95% CI: 0.75-0.88; p < 0.001) and mortality (OR 0.88; 95% CI: 0.78-0.99; p = 0.033) in the PSM analysis, supported by the regression analysis. Spironolactone use was associated with significantly reduced odds of ventilation for all age groups, men, women, and non-obese patients, with the greatest protective effects in younger patients, men, and non-obese patients.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Interpretation</jats:title><jats:p>Spironolactone use was associated with a protective effect against ventilation and mortality following COVID-19 infection, amounting to up to 64% of the protective effect of vaccination against ventilation and consistent with an androgen-dependent mechanism. The findings warrant initiation of large-scale randomized controlled trials to establish a potential therapeutic role for spironolactone in COVID-19 patients.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
2
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8694-0604",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Cousins",
"given": "Henry C.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3859-2905",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Altman",
"given": "Russ B.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-04T18:40:31Z",
"timestamp": 1677955231000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-08T16:36:39Z",
"timestamp": 1678293399000
},
"group-title": "Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS)",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-18T06:40:16Z",
"timestamp": 1700289616274
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "medRxiv"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
2
]
]
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1101/2023.02.28.23286515",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "246",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
2
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.1101",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "Therapeutic advances in COVID-19",
"first-page": "38",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Nephrol",
"key": "2023030808351443000_2023.02.28.23286515v1.1",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Rebound Phenomenon after Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir Treatment of Coronavirus Disease-2019 in High-Risk Persons",
"first-page": "e537",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "2023030808351443000_2023.02.28.23286515v1.2",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M22-0281",
"article-title": "Prescribing Nirmatrelvir–Ritonavir: How to Recognize and Manage Drug–Drug Interactions",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "744",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "2023030808351443000_2023.02.28.23286515v1.3",
"volume": "175",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110112",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023030808351443000_2023.02.28.23286515v1.4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10741-005-2345-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023030808351443000_2023.02.28.23286515v1.5"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19-The Potential Beneficial Therapeutic Effects of Spironolactone during SARS-CoV-2 Infection",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Pharmaceuticals (Basel)",
"key": "2023030808351443000_2023.02.28.23286515v1.6",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11255-019-02074-9",
"article-title": "Spironolactone alleviates diabetic nephropathy through promoting autophagy in podocytes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "755",
"journal-title": "Int Urol Nephrol",
"key": "2023030808351443000_2023.02.28.23286515v1.7",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2020.00453",
"article-title": "Spironolactone: An Anti-androgenic and Anti-hypertensive Drug That May Provide Protection Against the Novel Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) in COVID-19",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "453",
"journal-title": "Front Med",
"key": "2023030808351443000_2023.02.28.23286515v1.8",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.stem.2020.11.009",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023030808351443000_2023.02.28.23286515v1.9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2021.629176",
"article-title": "Effect of Spironolactone on COVID-19 in Patients With Underlying Liver Cirrhosis: A Nationwide Case-Control Study in South Korea",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "629176",
"journal-title": "Front Med",
"key": "2023030808351443000_2023.02.28.23286515v1.10",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18087/cardio.2020.11.n1440",
"article-title": "Results of open-label non-randomized comparative clinical trial: “Bromhexine and spironolactone for coron?virus infection requiring hospitalization (BISCUIT)",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4",
"journal-title": "Kardiologiya",
"key": "2023030808351443000_2023.02.28.23286515v1.11",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "A Randomized Trial of Sitagliptin and Spironolactone With Combination Therapy in Hospitalized Adults With COVID-19",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J Endocr Soc",
"key": "2023030808351443000_2023.02.28.23286515v1.12",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/pds.3459",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023030808351443000_2023.02.28.23286515v1.13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0184070",
"article-title": "Drug exposure in register-based research—An expert-opinion based evaluation of methods",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0184070",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "2023030808351443000_2023.02.28.23286515v1.14",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/01.mlr.0000182534.19832.83",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023030808351443000_2023.02.28.23286515v1.15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/sim.3150",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023030808351443000_2023.02.28.23286515v1.16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1037/a0019623",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023030808351443000_2023.02.28.23286515v1.17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7106a4externalicon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023030808351443000_2023.02.28.23286515v1.18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11606-022-08007-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2023030808351443000_2023.02.28.23286515v1.19",
"unstructured": "Baker TB , Bolt DM , Smith SS , et al. The Relationship of COVID-19 Vaccination with Mortality Among 86,732 Hospitalized Patients: Subpopulations, Patient Factors, and Changes over Time. J Gen Intern Med 2023; : 1."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cegh.2022.100971",
"article-title": "A comparison of clinical outcomes between vaccinated and vaccine-naive patients of COVID-19, in four tertiary care hospitals of Kerala, South India",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100971",
"journal-title": "Clin Epidemiol Glob Heal",
"key": "2023030808351443000_2023.02.28.23286515v1.20",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2006923",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023030808351443000_2023.02.28.23286515v1.21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.annonc.2020.04.479",
"article-title": "Androgen-deprivation therapies for prostate cancer and risk of infection by SARS-CoV-2: a population-based study (N = 4532)",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1040",
"journal-title": "Ann Oncol",
"key": "2023030808351443000_2023.02.28.23286515v1.22",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2021450118",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023030808351443000_2023.02.28.23286515v1.23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2022.03.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023030808351443000_2023.02.28.23286515v1.24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-20241-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023030808351443000_2023.02.28.23286515v1.25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jcem-25-11-1441",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023030808351443000_2023.02.28.23286515v1.26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.79.4.997",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023030808351443000_2023.02.28.23286515v1.27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2016-2935",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2023030808351443000_2023.02.28.23286515v1.28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04474-x",
"article-title": "Altered TMPRSS2 usage by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron impacts infectivity and fusogenicity",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "706",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "2023030808351443000_2023.02.28.23286515v1.29",
"volume": "603",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ejhf.1909",
"article-title": "Spironolactone dose in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: findings from TOPCAT",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1615",
"journal-title": "Eur J Heart Fail",
"key": "2023030808351443000_2023.02.28.23286515v1.30",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 30,
"references-count": 30,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://medrxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2023.02.28.23286515"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Association between spironolactone use and COVID-19 outcomes in population-scale claims data: a retrospective cohort study",
"type": "posted-content"
}
cousins2