Comparative Bioavailability of Vitamin C After Short-Term Consumption of Raw Fruits and Vegetables and Their Juices: A Randomized Crossover Study
et al., Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu17213331, Oct 2025
Vitamin C for COVID-19
6th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000076 from 73 studies, recognized in 22 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
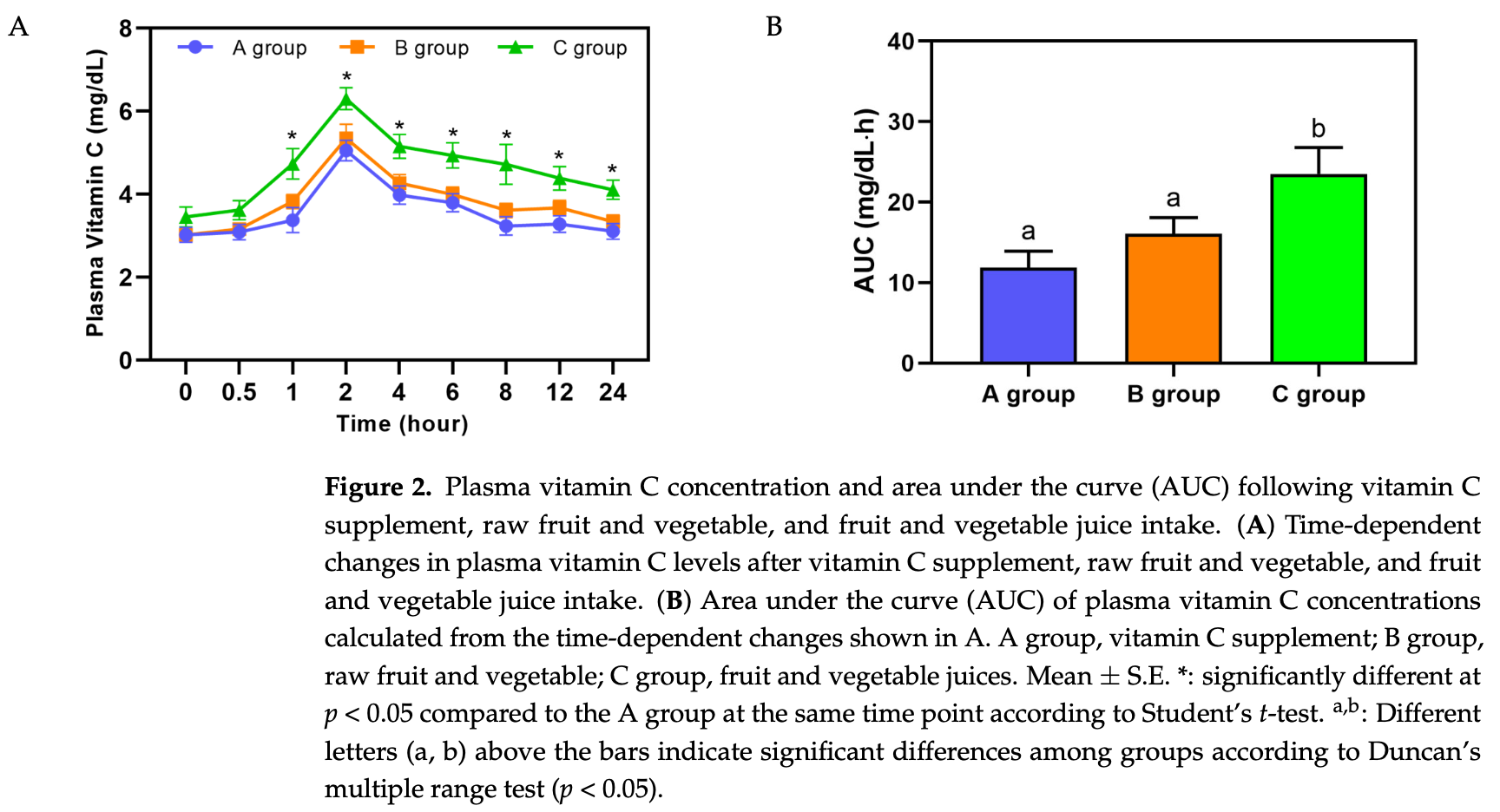
Randomized crossover trial showing vitamin C bioavailability from supplements, raw fruits and vegetables, and fruit and vegetable juices in 12 healthy adults. Authors found that fruit and vegetable juice provided the highest plasma vitamin C concentrations and area under the curve (AUC of 25.3 ± 3.2 mg/dL•h) compared to raw produce (16.1 ± 2.0) and supplements (11.9 ± 2.1). All forms reached peak plasma levels at 2 hours post-consumption.
Choi et al., 23 Oct 2025, peer-reviewed, 5 authors.
Contact: chtiger@jnu.ac.kr (corresponding author), mijjoo@kyungnam.ac.kr, kyungsoo0318@naver.com, sosung75@jnu.ac.kr, pej@kyungnam.ac.kr.
Comparative Bioavailability of Vitamin C After Short-Term Consumption of Raw Fruits and Vegetables and Their Juices: A Randomized Crossover Study
Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu17213331
Background/Objectives: Vitamin C plays a vital role in human health, functioning as a powerful antioxidant and enzymatic cofactor. Although vitamin C bioavailability from food versus supplements has been debated, few studies have examined how intake form affects absorption and physiological markers. Methods: This randomized, controlled, crossover trial aimed to compare the bioavailability of vitamin C consumed as a supplement, through raw fruits and vegetables, or through fruit and vegetable juice. Twelve healthy adults underwent three 1-day crossover trials, each separated by a 2-week washout. Participants consumed 101.7 mg of vitamin C via powder, raw fruits and vegetables (186.8 g), or juice (200 mL). Plasma and urinary vitamin C concentrations, urinary metabolites ( 1 H NMR), and antioxidant activity (ORAC and TRAP) were assessed over 24 h. Results: All interventions elevated plasma vitamin C levels, with juice yielding the highest AUC (25.3 ± 3.2 mg/dL•h). Urinary vitamin C increased in all groups. Metabolomics revealed increased urinary excretion of mannitol, glycine, taurine, dimethylglycine (DMG), and asparagine, and decreased choline and dimethylamine (DMA). Notably, urinary mannitol increased only in the morning. Choline significantly decreased after powder intake (p = 0.001), with similar trends observed in the other groups. DMG and glycine increased following raw and juiced vegetable intake. Antioxidant activity showed transient ORAC elevation post-powder but no sustained improvements. Conclusions: Vitamin C is bioavailable from all intake forms, with juice providing the most efficient absorption. Urinary metabolite changes suggest microbiota-related modulation, while antioxidant activity improvements were limited.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
Buettner, The Pecking Order of Free Radicals and Antioxidants: Lipid Peroxidation, α-Tocopherol, and Ascorbate, Arch. Biochem. Biophys, doi:10.1006/abbi.1993.1074
Carr, Bozonet, Pullar, Simcock, Vissers, A Randomized Steady-State Bioavailability Study of Synthetic versus Natural (Kiwifruit-Derived) Vitamin C, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu5114451
Carr, Frei, Toward a New Recommended Dietary Allowance for Vitamin C Based on Antioxidant and Health Effects in Humans, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/69.6.1086
Carr, Vissers, Synthetic or Food-Derived Vitamin C-Are They Equally Bioavailable?, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu5114284
Chambial, Dwivedi, Shukla, John, Sharma, Vitamin C in Disease Prevention and Cure: An Overview, Indian J. Clin. Biochem, doi:10.1007/s12291-013-0375-3
Cloarec, Dumas, Craig, Barton, Trygg et al., Statistical Total Correlation Spectroscopy: An Exploratory Approach for Latent Biomarker Identification from Metabolic 1H NMR Data Sets, Anal. Chem, doi:10.1021/ac048630x
Frei, England, Ames, Ascorbate Is an Outstanding Antioxidant in Human Blood Plasma, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.86.16.6377
Graumlich, Ludden, Conry-Cantilena, Cantilena, Wang et al., Pharmacokinetic Model of Ascorbic Acid in Healthy Male Volunteers during Depletion and Repletion, Pharm. Res, doi:10.1023/A:1012186203165
Guzior, Quinn, Review: Microbial Transformations of Human Bile Acids, Microbiome
Hazan, Dave, Papoutsis, Deshpande, Howell et al., Vitamin C Improves Gut Bifidobacteria in Humans, Future Microbiol, doi:10.2217/fmb-2022-0209
Jacob, Sotoudeh, Vitamin C Function and Status in Chronic Disease, Nutr. Clin. Care, doi:10.1046/j.1523-5408.2002.00005.x
Jung, Lee, Kim, Park, Bae et al., Metagenomic Analysis of Kimchi, a Traditional Korean Fermented Food, Appl. Environ. Microbiol, doi:10.1128/AEM.02157-10
Koeth, Wang, Levison, Buffa, Org et al., Intestinal Microbiota Metabolism of L-Carnitine, a Nutrient in Red Meat, Promotes Atherosclerosis, Nat. Med, doi:10.1038/nm.3145
Kurihara, Fukama, Asami, Totoda, Nakai et al., Effects of Oolong Tea on Plasma Antioxidative Capacity in Mice Loaded with Restraint Stress Assessed Using the Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity (ORAC) Assay, Biol. Pharm. Bull, doi:10.1248/bpb.27.1093
Levine, Conry-Cantilena, Wang, Welch, Washko et al., Vitamin C Pharmacokinetics in Healthy Volunteers: Evidence for a Recommended Dietary Allowance, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.93.8.3704
Li, Schellhorn, New Developments and Novel Therapeutic Perspectives for Vitamin C, J. Nutr, doi:10.1093/jn/137.10.2171
Louis, Flint, Formation of Propionate and Butyrate by the Human Colonic Microbiota, Environ. Microbiol, doi:10.1111/1462-2920.13589
Moolenaar, Poggi-Bach, Engelke, Corstiaensen, Heerschap et al., Defect in Dimethylglycine Dehydrogenase, a New Inborn Error of Metabolism: NMR Spectroscopy Study, Clin. Chem, doi:10.1093/clinchem/45.4.459
Nishikimi, Koshizaka, Ozawa, Yagi, Occurrence in Humans and Guinea Pigs of the Gene Related to Their Missing Enzyme L-Gulono-γ-Lactone Oxidase, Arch. Biochem. Biophys, doi:10.1016/0003-9861(88)90093-8
Otten, Bourgonje, Harmsen, Alizadeh, Dijkstra et al., Vitamin C Supplementation in Healthy Individuals Leads to Shifts of Bacterial Populations in the Gut-A Pilot Study, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox10081278
Ou, Hampsch-Woodill, Prior, Development and Validation of an Improved Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity Assay Using Fluorescein as the Fluorescent Probe, J. Agric. Food Chem, doi:10.1021/jf010586o
Padayatty, Sun, Wang, Riordan, Hewitt et al., Vitamin C Pharmacokinetics: Implications for Oral and Intravenous Use, Ann. Intern. Med, doi:10.7326/0003-4819-140-7-200404060-00010
Qian, Li, Yu, Tian, Zhao et al., Effects of Taurine on Gut Microbiota Homeostasis: An Evaluation Based on Two Models of Gut Dysbiosis, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines11041048
Rice-Evans, Miller, Total Antioxidant Status in Plasma and Body Fluids, Methods Enzymol, doi:10.1016/0076-6879(94)34095-1
Rozman, Gašperlin, Stability of Vitamins C and E in Topical Microemulsions for Combined Antioxidant Therapy, Drug Deliv, doi:10.1080/10717540601067786
Santos, Mendiola, Oliveira, Ibáñez, Herrero, Sequential Determination of Fat-and Water-Soluble Vitamins in Green Leafy Vegetables during Storage, J. Chromatogr. A, doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2012.04.067
Savini, Rossi, Pierro, Avigliano, Catani, SVCT1 and SVCT2: Key Proteins for Vitamin C Uptake, Amino Acids, doi:10.1007/s00726-007-0555-7
Shimpo, Akamatsu, Kojima, Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Food and Drink Consumption and Related Factors: A Scoping Review, Nutr. Health, doi:10.1177/02601060221078161
Vera, Rivas, Velásquez, Zhang, Concha et al., Resolution of the Facilitated Transport of Dehydroascorbic Acid from Its Intracellular Accumulation as Ascorbic Acid, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.270.40.23706
Vinson, Bose, Comparative Bioavailability to Humans of Ascorbic Acid Alone or in a Citrus Extract, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/48.3.601
Walsh, Brennan, Pujos-Guillot, Sébédio, Scalbert et al., Influence of Acute Phytochemical Intake on Human Urinary Metabolomic Profiles, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/86.5.1687
Wang, Klipfell, Bennett, Koeth, Levison et al., Gut Flora Metabolism of Phosphatidylcholine Promotes Cardiovascular Disease, Nature, doi:10.1038/nature09922
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu17213331",
"ISSN": [
"2072-6643"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/nu17213331",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background/Objectives: Vitamin C plays a vital role in human health, functioning as a powerful antioxidant and enzymatic cofactor. Although vitamin C bioavailability from food versus supplements has been debated, few studies have examined how intake form affects absorption and physiological markers. Methods: This randomized, controlled, crossover trial aimed to compare the bioavailability of vitamin C consumed as a supplement, through raw fruits and vegetables, or through fruit and vegetable juice. Twelve healthy adults underwent three 1-day crossover trials, each separated by a 2-week washout. Participants consumed 101.7 mg of vitamin C via powder, raw fruits and vegetables (186.8 g), or juice (200 mL). Plasma and urinary vitamin C concentrations, urinary metabolites (1H NMR), and antioxidant activity (ORAC and TRAP) were assessed over 24 h. Results: All interventions elevated plasma vitamin C levels, with juice yielding the highest AUC (25.3 ± 3.2 mg/dL·h). Urinary vitamin C increased in all groups. Metabolomics revealed increased urinary excretion of mannitol, glycine, taurine, dimethylglycine (DMG), and asparagine, and decreased choline and dimethylamine (DMA). Notably, urinary mannitol increased only in the morning. Choline significantly decreased after powder intake (p = 0.001), with similar trends observed in the other groups. DMG and glycine increased following raw and juiced vegetable intake. Antioxidant activity showed transient ORAC elevation post-powder but no sustained improvements. Conclusions: Vitamin C is bioavailable from all intake forms, with juice providing the most efficient absorption. Urinary metabolite changes suggest microbiota-related modulation, while antioxidant activity improvements were limited.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"nu17213331"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4527-2475",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "RISE Bio-Center, Kyungnam University, Changwon 51767, Republic of Korea"
},
{
"name": "Department of Food and Nutrition, Kyungnam University, Changwon 51767, Republic of Korea"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Choi",
"given": "Mijoo",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Food and Nutrition, Kyungnam University, Changwon 51767, Republic of Korea"
}
],
"family": "Baek",
"given": "Juha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6044-0647",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Food and Nutrition, Chonnam National University, Gwangju 61186, Republic of Korea"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Yun",
"given": "Jung-Mi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Food and Nutrition, Chonnam National University, Gwangju 61186, Republic of Korea"
}
],
"family": "Hong",
"given": "Young-Shick",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3462-6090",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Food and Nutrition, Kyungnam University, Changwon 51767, Republic of Korea"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Park",
"given": "Eunju",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrients",
"container-title-short": "Nutrients",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2025-10-23T09:44:30Z",
"timestamp": 1761212670000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2025-10-25T04:24:38Z",
"timestamp": 1761366278000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2025-10-25T04:27:19Z",
"timestamp": 1761366439861,
"version": "build-2065373602"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "21",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
23
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "21",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
11
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2025-10-23T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1761177600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/17/21/3331/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "3331",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
23
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
23
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0003-9861(88)90093-8",
"article-title": "Occurrence in Humans and Guinea Pigs of the Gene Related to Their Missing Enzyme L-Gulono-γ-Lactone Oxidase",
"author": "Nishikimi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "842",
"journal-title": "Arch. Biochem. Biophys.",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "267",
"year": "1988"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12291-013-0375-3",
"article-title": "Vitamin C in Disease Prevention and Cure: An Overview",
"author": "Chambial",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "314",
"journal-title": "Indian J. Clin. Biochem.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.86.16.6377",
"article-title": "Ascorbate Is an Outstanding Antioxidant in Human Blood Plasma",
"author": "Frei",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6377",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "86",
"year": "1989"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1006/abbi.1993.1074",
"article-title": "The Pecking Order of Free Radicals and Antioxidants: Lipid Peroxidation, α-Tocopherol, and Ascorbate",
"author": "Buettner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "535",
"journal-title": "Arch. Biochem. Biophys.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "300",
"year": "1993"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1046/j.1523-5408.2002.00005.x",
"article-title": "Vitamin C Function and Status in Chronic Disease",
"author": "Jacob",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "66",
"journal-title": "Nutr. Clin. Care",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10717540601067786",
"article-title": "Stability of Vitamins C and E in Topical Microemulsions for Combined Antioxidant Therapy",
"author": "Rozman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "235",
"journal-title": "Drug Deliv.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jn/137.10.2171",
"article-title": "New Developments and Novel Therapeutic Perspectives for Vitamin C",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2171",
"journal-title": "J. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "137",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/69.6.1086",
"article-title": "Toward a New Recommended Dietary Allowance for Vitamin C Based on Antioxidant and Health Effects in Humans",
"author": "Carr",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1086",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "69",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00726-007-0555-7",
"article-title": "SVCT1 and SVCT2: Key Proteins for Vitamin C Uptake",
"author": "Savini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "347",
"journal-title": "Amino Acids",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.270.40.23706",
"article-title": "Resolution of the Facilitated Transport of Dehydroascorbic Acid from Its Intracellular Accumulation as Ascorbic Acid",
"author": "Vera",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "23706",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "270",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1023/A:1012186203165",
"article-title": "Pharmacokinetic Model of Ascorbic Acid in Healthy Male Volunteers during Depletion and Repletion",
"author": "Graumlich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1133",
"journal-title": "Pharm. Res.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "14",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/0003-4819-140-7-200404060-00010",
"article-title": "Vitamin C Pharmacokinetics: Implications for Oral and Intravenous Use",
"author": "Padayatty",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "533",
"journal-title": "Ann. Intern. Med.",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "140",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.93.8.3704",
"article-title": "Vitamin C Pharmacokinetics in Healthy Volunteers: Evidence for a Recommended Dietary Allowance",
"author": "Levine",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3704",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "93",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/02601060221078161",
"article-title": "Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Food and Drink Consumption and Related Factors: A Scoping Review",
"author": "Shimpo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "177",
"journal-title": "Nutr. Health",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chroma.2012.04.067",
"article-title": "Sequential Determination of Fat- and Water-Soluble Vitamins in Green Leafy Vegetables during Storage",
"author": "Santos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "179",
"journal-title": "J. Chromatogr. A",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "1261",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1248/bpb.27.1093",
"article-title": "Effects of Oolong Tea on Plasma Antioxidative Capacity in Mice Loaded with Restraint Stress Assessed Using the Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity (ORAC) Assay",
"author": "Kurihara",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1093",
"journal-title": "Biol. Pharm. Bull.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/jf010586o",
"article-title": "Development and Validation of an Improved Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity Assay Using Fluorescein as the Fluorescent Probe",
"author": "Ou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4619",
"journal-title": "J. Agric. Food Chem.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0076-6879(94)34095-1",
"article-title": "Total Antioxidant Status in Plasma and Body Fluids",
"author": "Miller",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "279",
"journal-title": "Methods Enzymol.",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "234",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/ac048630x",
"article-title": "Statistical Total Correlation Spectroscopy: An Exploratory Approach for Latent Biomarker Identification from Metabolic 1H NMR Data Sets",
"author": "Cloarec",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1282",
"journal-title": "Anal. Chem.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/86.5.1687",
"article-title": "Influence of Acute Phytochemical Intake on Human Urinary Metabolomic Profiles",
"author": "Walsh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1687",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "86",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/48.3.601",
"article-title": "Comparative Bioavailability to Humans of Ascorbic Acid Alone or in a Citrus Extract",
"author": "Vinson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "501",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "48",
"year": "1988"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu5114451",
"article-title": "A Randomized Steady-State Bioavailability Study of Synthetic versus Natural (Kiwifruit-Derived) Vitamin C",
"author": "Carr",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4451",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu5114284",
"article-title": "Synthetic or Food-Derived Vitamin C—Are They Equally Bioavailable?",
"author": "Carr",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4284",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AEM.02157-10",
"article-title": "Metagenomic Analysis of Kimchi, a Traditional Korean Fermented Food",
"author": "Jung",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2264",
"journal-title": "Appl. Environ. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1462-2920.13589",
"article-title": "Formation of Propionate and Butyrate by the Human Colonic Microbiota",
"author": "Louis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "29",
"journal-title": "Environ. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines11041048",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_26",
"unstructured": "Qian, W., Li, M., Yu, L., Tian, F., Zhao, J., and Zhai, Q. (2023). Effects of Taurine on Gut Microbiota Homeostasis: An Evaluation Based on Two Models of Gut Dysbiosis. Biomedicines, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox10081278",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_27",
"unstructured": "Otten, A.T., Bourgonje, A.R., Harmsen, H.J.M., Alizadeh, B.Z., Dijkstra, G., and Faber, K.N. (2021). Vitamin C Supplementation in Healthy Individuals Leads to Shifts of Bacterial Populations in the Gut—A Pilot Study. Antioxidants, 10."
},
{
"key": "ref_28",
"unstructured": "Hazan, S., Dave, S., Papoutsis, A.J., Deshpande, N., Howell, M.C., and Martin, L.M. (Future Microbiol., 2022). Vitamin C Improves Gut Bifidobacteria in Humans, Future Microbiol., online ahead of print."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nm.3145",
"article-title": "Intestinal Microbiota Metabolism of L-Carnitine, a Nutrient in Red Meat, Promotes Atherosclerosis",
"author": "Koeth",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "576",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature09922",
"article-title": "Gut Flora Metabolism of Phosphatidylcholine Promotes Cardiovascular Disease",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "57",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "472",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/clinchem/45.4.459",
"article-title": "Defect in Dimethylglycine Dehydrogenase, a New Inborn Error of Metabolism: NMR Spectroscopy Study",
"author": "Moolenaar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "459",
"journal-title": "Clin. Chem.",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "45",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40168-021-01101-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_32",
"unstructured": "Guzior, D.V., and Quinn, R.A. (2021). Review: Microbial Transformations of Human Bile Acids. Microbiome, 9."
}
],
"reference-count": 32,
"references-count": 32,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/17/21/3331"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Comparative Bioavailability of Vitamin C After Short-Term Consumption of Raw Fruits and Vegetables and Their Juices: A Randomized Crossover Study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.3390/mdpi_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "17"
}
