Causal relationship between physical activity, leisure sedentary behaviors and COVID-19 risk: a Mendelian randomization study
et al., Journal of Translational Medicine, doi:10.1186/s12967-022-03407-6, May 2022
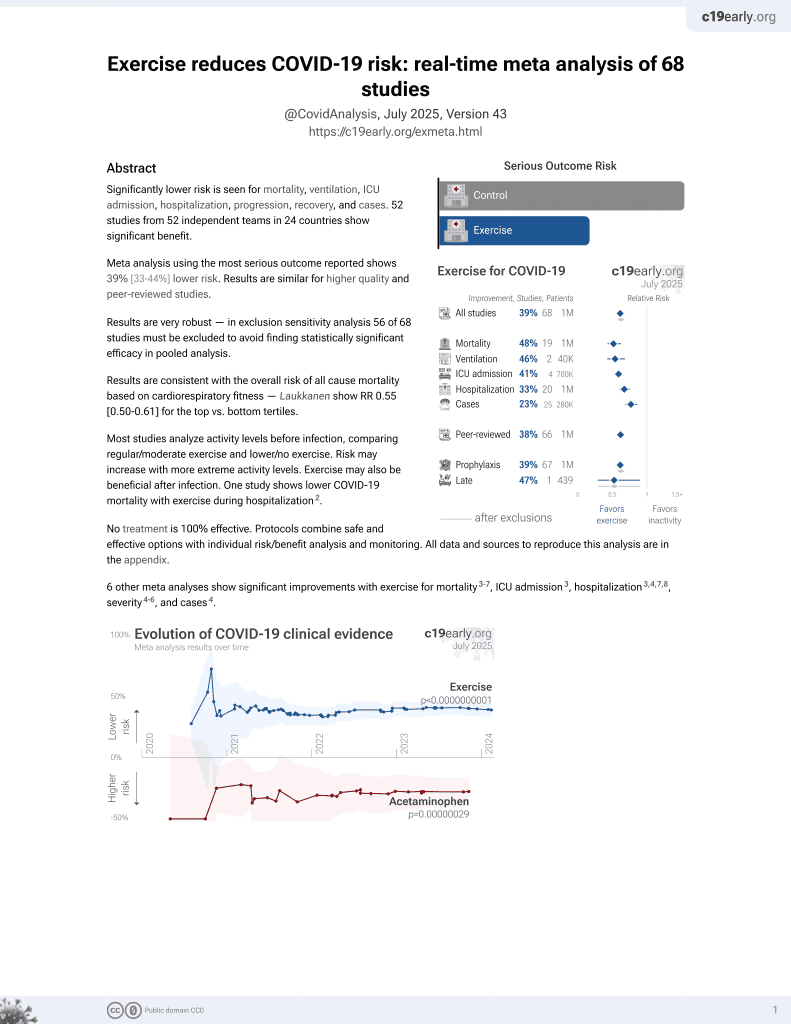
Exercise for COVID-19
9th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 68 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
UK Biobank Mendelian randomization study showing decreased risk of COVID-19 hospitalization with genetically predicted accelerometer-assessed physical activity, and increased risk with television watching.
Chen et al., 13 May 2022, United Kingdom, peer-reviewed, 7 authors.
Contact: caijh6@mail2.sysu.edu.cn (corresponding author), starbless2003@126.com, huangyn68@mail.sysu.edu.cn.
Causal relationship between physical activity, leisure sedentary behaviors and COVID-19 risk: a Mendelian randomization study
Journal of Translational Medicine, doi:10.1186/s12967-022-03407-6
Background: The 2019 coronavirus disease pandemic poses an enormous threat to public health worldwide, and the ensuing management of social isolation has greatly decreased opportunities for physical activity (PA) and increased opportunities for leisure sedentary behaviors (LSB). Given that both PA and LSB have been established as major influencing factors for obesity, diabetes and cardiometabolic syndrome, whether PA/LSB in turn affects the susceptibility to COVID-19 by disrupting metabolic homeostasis remains to be explored. In this study, we aimed to systematically evaluate the causal relationship between PA/LSB and COVID-19 susceptibility, hospitalization and severity using a Mendelian randomization study. Methods: Data were obtained from a large-scale PA dataset (N = 377,000), LSB dataset (N = 422,218) and COVID-19 Host Genetics Initiative (N = 2,586,691). The causal effects were estimated with inverse variance weighted, MR-Egger, weighted median and MR-PRESSO. Sensitivity analyses were implemented with Cochran's Q test, MR-Egger intercept test, MR-PRESSO, leave-one-out analysis and the funnel plot. Risk factor analyses were further conducted to investigate the potential mediators. Results: Genetically predicted accelerometer-assessed PA decreased the risk for COVID-19 hospitalization (OR = 0.93, 95% CI 0.88-0.97; P = 0.002), while leisure television watching significantly increased the risk of COVID-19 hospitalization (OR = 1.55, 95% CI 1.29-1.88; P = 4.68 × 10 -6 ) and disease severity (OR = 1.85, 95% CI 1.33-2.56; P = 0.0002) after Bonferroni correction. No causal effects of self-reported moderate to vigorous physical activity (MVPA), accelerometer fraction of accelerations > 425 milligravities, computer use or driving on COVID-19 progression were observed. Risk factor analyses indicated that the above causal associations might be mediated by several metabolic risk factors,
such as reducing leisure sedentary behaviors and encouraging proper exercise, to combat COVID-19.
Supplementary Information The online version contains supplementary material available at https:// doi. org/ 10. 1186/ s12967-022-03407-6. Additional file 1: Supplementary tables. Table S1 . Instrument variables of MVPA. Table S2 . Instrument variables of accelerations assessed physical activity. Table S3 . Instrument variables of fraction accelerations > 425 milli-gravities. Table S4 . Instrument variables of television watching. Table S5 . Instrument variables of computer used. Table S6 . Instrument variables of driving. Table S7 .MR estimates of the causal association between physical activity and leisure sedentary behaviors and the risk of COVID-19.
Declarations Consent for publication Not applicable.
Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. • fast, convenient online submission • thorough peer review by experienced researchers in your field
• rapid publication on acceptance • support for research data, including large and complex data types • gold Open Access which fosters wider collaboration and increased citations maximum visibility for your research: over 100M website views per year
Publisher's Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Bahls, Leitzmann, Karch, Physical activity, sedentary behavior and risk of coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study, Clin Res Cardiol
Bergmann, Silverman, COVID-19: coronavirus replication, pathogenesis, and therapeutic strategies, Cleve Clin J Med
Biswas, Sedentary time and its association with risk for disease incidence, mortality, and hospitalization in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Ann Intern Med
Boef, Dekkers, Le Cessie, Mendelian randomization studies: a review of the approaches used and the quality of reporting, Int J Epidemiol
Bowden, Consistent estimation in Mendelian randomization with some invalid instruments using a weighted median estimator, Genet Epidemiol
Bowden, Smith, Burgess, Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression, Int J Epidemiol
Burgess, Thompson, Multivariable Mendelian randomization: the use of pleiotropic genetic variants to estimate causal effects, Am J Epidemiol
Chen, Clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with diabetes and COVID-19 in association with glucose-lowering medication, Diabetes Care
Chen, Kidney damage causally affects the brain cortical structure: a Mendelian randomization study, EBioMedicine
Chen, Risk factors of fatal outcome in hospitalized subjects with coronavirus disease 2019 from a nationwide analysis in China, Chest
Clark, Relationship of television time with accelerometer-derived sedentary time: NHANES, Med Sci Sports Exerc
Doherty, Smith-Byrne, Ferreira, GWAS identifies 14 loci for device-measured physical activity and sleep duration, Nat Commun
Frydenlund, Sedentary leisure time behavior, snacking habits and cardiovascular biomarkers: the Inter99 Study, Eur J Prev Cardiol
Gortmaker, Television viewing as a cause of increasing obesity among children in the United States, 1986-1990, Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med
Green, Beck, Obesity impairs the adaptive immune response to influenza virus, Ann Am Thorac Soc
Guo, The origin, transmission and clinical therapies on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak-an update on the status, Mil Med Res
Hamer, Lifestyle risk factors, inflammatory mechanisms, and COVID-19 hospitalization: a community-based cohort study of 387,109 adults in UK, Brain Behav Immun
Hamilton, Hamilton, Zderic, Role of low energy expenditure and sitting in obesity, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease, Diabetes
Huang, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan China, Lancet
Jin, Chemoprophylaxis, diagnosis, treatments, and discharge management of COVID-19: an evidence-based clinical practice guideline (updated version), Mil Med Res
Klimentidis, Raichlen, Bea, Genome-wide association study of habitual physical activity in over 377,000 UK Biobank participants identifies multiple variants including CADM2 and APOE, Int J Obes (Lond)
Kupferschmidt, Vogel, How bad is Omicron? Some clues are emerging, Science
Lighter, Obesity in patients younger than 60 years is a risk factor for COVID-19 hospital admission, Clin Infect Dis
Locke, Genetic studies of body mass index yield new insights for obesity biology, Nature
Luykx, Lin, Are psychiatric disorders risk factors for COVID-19 susceptibility and severity? a two-sample, bidirectional, univariable, and multivariable Mendelian randomization study, Transl Psychiatry
Manning, A genome-wide approach accounting for body mass index identifies genetic variants influencing fasting glycemic traits and insulin resistance, Nat Genet
Morris, Large-scale association analysis provides insights into the genetic architecture and pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes, Nat Genet
Otten, Effects of television viewing reduction on energy intake and expenditure in overweight and obese adults: a randomized controlled trial, Arch Intern Med
Palaiodimos, Severe obesity, increasing age and male sex are independently associated with worse in-hospital outcomes, and higher inhospital mortality, in a cohort of patients with COVID-19 in the Bronx, New York Metabolism
Patterson, Sedentary behaviour and risk of all-cause, cardiovascular and cancer mortality, and incident type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and dose response meta-analysis, Eur J Epidemiol
Pinto, Combating physical inactivity during the COVID-19 pandemic, Nat Rev Rheumatol
Ponsford, Cardiometabolic traits, sepsis, and severe COVID-19: a Mendelian randomization investigation, Circulation
Richardson, Sanderson, Palmer, Evaluating the relationship between circulating lipoprotein lipids and apolipoproteins with risk of coronary heart disease: A multivariable Mendelian randomisation analysis, PLoS Med
Richmond, Daveysmith, Mendelian randomization: concepts and scope, Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med
Sallis, Physical inactivity is associated with a higher risk for severe COVID-19 outcomes: a study in 48 440 adult patients, Br J Sports Med
Schmid, Leitzmann, Television viewing and time spent sedentary in relation to cancer risk: a meta-analysis, J Natl Cancer Inst
Sekula, Mendelian randomization as an approach to assess causality using observational data, J Am Soc Nephrol
Smith, Hemani, Mendelian randomization: genetic anchors for causal inference in epidemiological studies, Hum Mol Genet
Steenkamp, Small steps, strong shield: directly measured, moderate physical activity in 65 361 adults is associated with significant protective effects from severe COVID-19 outcomes, Br J Sports Med, doi:10.1136/bjsports-2021-105159
Tag, Genome-wide meta-analyses identify multiple loci associated with smoking behavior, Nat Genet
The, The COVID-19 Host genetics initiative, a global initiative to elucidate the role of host genetic factors in susceptibility and severity of the SARS-CoV-2 virus pandemic, Eur J Hum Genet
Tremblay, Sedentary Behavior Research Network (SBRN) -terminology consensus project process and outcome, Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act
Van De Vegte, Genome-wide association studies and Mendelian randomization analyses for leisure sedentary behaviours, Nat Commun
Wilmot, Sedentary time in adults and the association with diabetes, cardiovascular disease and death: systematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetologia
Yeung, Li, He, Kwok, Schooling, Association of smoking, lung function and COPD in COVID-19 risk: a two-step Mendelian randomization study, Addiction, doi:10.1111/add.15852
Zhang, Causal associations between blood lipids and covid-19 risk: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study, Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol
Zheng, Risk factors of critical & mortal COVID-19 cases: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis, J Infect
Zhou, Wei, Primary stratification and identification of suspected Corona virus disease (2019 (COVID-19) from clinical perspective by a simple scoring proposal, Mil Med Res
Zhu, Association of blood glucose control and outcomes in patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing type 2 diabetes, Cell Metab
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12967-022-03407-6",
"ISSN": [
"1479-5876"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12967-022-03407-6",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>The 2019 coronavirus disease pandemic (COVID-19) poses an enormous threat to public health worldwide, and the ensuing management of social isolation has greatly decreased opportunities for physical activity (PA) and increased opportunities for leisure sedentary behaviors (LSB). Given that both PA and LSB have been established as major influencing factors for obesity, diabetes and cardiometabolic syndrome, whether PA/LSB in turn affects the susceptibility to COVID-19 by disrupting metabolic homeostasis remains to be explored. In this study, we aimed to systematically evaluate the causal relationship between PA/LSB and COVID-19 susceptibility, hospitalization and severity using a Mendelian randomization study.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Data were obtained from a large-scale PA dataset (N = 377,000), LSB dataset (N = 422,218) and COVID-19 Host Genetics Initiative (N = 2,586,691). The causal effects were estimated with inverse variance weighted, MR-Egger, weighted median and MR-PRESSO. Sensitivity analyses were implemented with Cochran’s Q test, MR-Egger intercept test, MR-PRESSO, leave-one-out analysis and the funnel plot. Risk factor analyses were further conducted to investigate the potential mediators.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Genetically predicted accelerometer-assessed PA decreased the risk for COVID-19 hospitalization (OR = 0.93, 95% CI 0.88–0.97; P = 0.002), while leisure television watching significantly increased the risk of COVID-19 hospitalization (OR = 1.55, 95% CI 1.29–1.88; P = 4.68 × 10<jats:sup>–6</jats:sup>) and disease severity (OR = 1.85, 95% CI 1.33–2.56; P = 0.0002) after Bonferroni correction. No causal effects of self-reported moderate to vigorous physical activity (MVPA), accelerometer fraction of accelerations > 425 milligravities, computer use or driving on COVID-19 progression were observed. Risk factor analyses indicated that the above causal associations might be mediated by several metabolic risk factors, including smoking, high body mass index, elevated serum triglyceride levels, insulin resistance and the occurrence of type 2 diabetes.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Our findings supported a causal effect of accelerometer-assessed PA on the reduced risk of COVID-19 hospitalization as well as television watching on the increased risk of COVID-19 hospitalization and severity, which was potentially mediated by smoking, obesity and type 2 diabetes-related phenotypes. Particular attention should be given to reducing leisure sedentary behaviors and encouraging proper exercise during isolation and quarantine for COVID-19.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"3407"
],
"article-number": "216",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "21 January 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "24 April 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "13 May 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Consent for publication",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "Not applicable."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "The authors declare that they have no competing interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Xiong",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hong",
"given": "Xiaosi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gao",
"given": "Wenjing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Luo",
"given": "Shulu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cai",
"given": "Jiahao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Guochang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Yinong",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Translational Medicine",
"container-title-short": "J Transl Med",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-13T11:09:48Z",
"timestamp": 1652440188000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-13T12:09:17Z",
"timestamp": 1652443757000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"KTa377a204193688"
],
"name": "Research foundation of Guangzhou Women and Children’s Medical Center for Clinical Doctor"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100018479",
"award": [
"KT072c1204164651"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Guangzhou Institute of Pediatrics, Guangzhou Women and Childrens Medical Center"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-13T12:42:22Z",
"timestamp": 1652445742937
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
13
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-13T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1652400000000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-13T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1652400000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s12967-022-03407-6.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12967-022-03407-6/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s12967-022-03407-6.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1186",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
13
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
13
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.3949/ccjm.87a.20047",
"author": "CC Bergmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "321",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Cleve Clin J Med",
"key": "3407_CR1",
"unstructured": "Bergmann CC, Silverman RH. COVID-19: coronavirus replication, pathogenesis, and therapeutic strategies. Cleve Clin J Med. 2020;87(6):321–7.",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "YR Guo",
"first-page": "11",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Mil Med Res",
"key": "3407_CR2",
"unstructured": "Guo YR, et al. The origin, transmission and clinical therapies on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak—an update on the status. Mil Med Res. 2020;7(1):11.",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"author": "C Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "497",
"issue": "10223",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "3407_CR3",
"unstructured": "Huang C, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan China. Lancet. 2020;395(10223):497–506.",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "YH Jin",
"first-page": "41",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Mil Med Res",
"key": "3407_CR4",
"unstructured": "Jin YH, et al. Chemoprophylaxis, diagnosis, treatments, and discharge management of COVID-19: an evidence-based clinical practice guideline (updated version). Mil Med Res. 2020;7(1):41.",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "TT Zhou",
"first-page": "16",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Mil Med Res",
"key": "3407_CR5",
"unstructured": "Zhou TT, Wei FX. Primary stratification and identification of suspected Corona virus disease (2019 (COVID-19) from clinical perspective by a simple scoring proposal. Mil Med Res. 2020;7(1):16.",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41584-020-0427-z",
"author": "AJ Pinto",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "347",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Rheumatol",
"key": "3407_CR6",
"unstructured": "Pinto AJ, et al. Combating physical inactivity during the COVID-19 pandemic. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16(7):347–8.",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.acx9782",
"author": "K Kupferschmidt",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1304",
"issue": "6573",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "3407_CR7",
"unstructured": "Kupferschmidt K, Vogel G. How bad is Omicron? Some clues are emerging. Science. 2021;374(6573):1304–5.",
"volume": "374",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bjsports-2021-105159",
"author": "L Steenkamp",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Br J Sports Med",
"key": "3407_CR8",
"unstructured": "Steenkamp L, et al. Small steps, strong shield: directly measured, moderate physical activity in 65 361 adults is associated with significant protective effects from severe COVID-19 outcomes. Br J Sports Med. 2022;2(9). https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2021-105159",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-15553-w",
"author": "YJ van de Vegte",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1770",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "3407_CR9",
"unstructured": "van de Vegte YJ, et al. Genome-wide association studies and Mendelian randomization analyses for leisure sedentary behaviours. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):1770.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12966-017-0525-8",
"author": "MS Tremblay",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "75",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act",
"key": "3407_CR10",
"unstructured": "Tremblay MS, et al. Sedentary Behavior Research Network (SBRN) - terminology consensus project process and outcome. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2017;14(1):75.",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/archpedi.1996.02170290022003",
"author": "SL Gortmaker",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "356",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med",
"key": "3407_CR11",
"unstructured": "Gortmaker SL, et al. Television viewing as a cause of increasing obesity among children in the United States, 1986–1990. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1996;150(4):356–62.",
"volume": "150",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00125-012-2677-z",
"author": "EG Wilmot",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2895",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Diabetologia",
"key": "3407_CR12",
"unstructured": "Wilmot EG, et al. Sedentary time in adults and the association with diabetes, cardiovascular disease and death: systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetologia. 2012;55(11):2895–905.",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M14-1651",
"author": "A Biswas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "123",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "3407_CR13",
"unstructured": "Biswas A, et al. Sedentary time and its association with risk for disease incidence, mortality, and hospitalization in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2015;162(2):123–32.",
"volume": "162",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jnci/dju098",
"author": "D Schmid",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "dju098",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "J Natl Cancer Inst",
"key": "3407_CR14",
"unstructured": "Schmid D, Leitzmann MF. Television viewing and time spent sedentary in relation to cancer risk: a meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014;106(7):dju098.",
"volume": "106",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10654-018-0380-1",
"author": "R Patterson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "811",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Eur J Epidemiol",
"key": "3407_CR15",
"unstructured": "Patterson R, et al. Sedentary behaviour and risk of all-cause, cardiovascular and cancer mortality, and incident type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and dose response meta-analysis. Eur J Epidemiol. 2018;33(9):811–29.",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa415",
"author": "J Lighter",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "896",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "3407_CR16",
"unstructured": "Lighter J, et al. Obesity in patients younger than 60 years is a risk factor for COVID-19 hospital admission. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71(15):896–7.",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "L Palaiodimos",
"first-page": "154262",
"journal-title": "New York Metabolism",
"key": "3407_CR17",
"unstructured": "Palaiodimos L, et al. Severe obesity, increasing age and male sex are independently associated with worse in-hospital outcomes, and higher in-hospital mortality, in a cohort of patients with COVID-19 in the Bronx. New York Metabolism. 2020;108:154262.",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2020.04.021",
"author": "L Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1068",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Cell Metab",
"key": "3407_CR18",
"unstructured": "Zhu L, et al. Association of blood glucose control and outcomes in patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing type 2 diabetes. Cell Metab. 2020;31(6):1068-1077.e3.",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20-0660",
"author": "Y Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1399",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "3407_CR19",
"unstructured": "Chen Y, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with diabetes and COVID-19 in association with glucose-lowering medication. Diabetes Care. 2020;43(7):1399–407.",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2020.04.010",
"author": "R Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "97",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "3407_CR20",
"unstructured": "Chen R, et al. Risk factors of fatal outcome in hospitalized subjects with coronavirus disease 2019 from a nationwide analysis in China. Chest. 2020;158(1):97–105.",
"volume": "158",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.04.021",
"author": "Z Zheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e16",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Infect",
"key": "3407_CR21",
"unstructured": "Zheng Z, et al. Risk factors of critical & mortal COVID-19 cases: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. J Infect. 2020;81(2):e16–25.",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bjsports-2021-104080",
"author": "R Sallis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1099",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "Br J Sports Med",
"key": "3407_CR22",
"unstructured": "Sallis R, et al. Physical inactivity is associated with a higher risk for severe COVID-19 outcomes: a study in 48 440 adult patients. Br J Sports Med. 2021;55(19):1099–105.",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbi.2020.05.059",
"author": "M Hamer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "184",
"journal-title": "Brain Behav Immun",
"key": "3407_CR23",
"unstructured": "Hamer M, et al. Lifestyle risk factors, inflammatory mechanisms, and COVID-19 hospitalization: a community-based cohort study of 387,109 adults in UK. Brain Behav Immun. 2020;87:184–7.",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1681/ASN.2016010098",
"author": "P Sekula",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3253",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "J Am Soc Nephrol",
"key": "3407_CR24",
"unstructured": "Sekula P, et al. Mendelian randomization as an approach to assess causality using observational data. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;27(11):3253–65.",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/cshperspect.a040501",
"author": "RC Richmond",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "a040501",
"journal-title": "Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med",
"key": "3407_CR25",
"unstructured": "Richmond RC, DaveySmith G. Mendelian randomization: concepts and scope. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2021;12:a040501.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/aje/kwu283",
"author": "S Burgess",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "251",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Am J Epidemiol",
"key": "3407_CR26",
"unstructured": "Burgess S, Thompson SG. Multivariable Mendelian randomization: the use of pleiotropic genetic variants to estimate causal effects. Am J Epidemiol. 2015;181(4):251–60.",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/hmg/ddu328",
"author": "G Davey Smith",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "R89",
"issue": "R1",
"journal-title": "Hum Mol Genet",
"key": "3407_CR27",
"unstructured": "Davey Smith G, Hemani G. Mendelian randomization: genetic anchors for causal inference in epidemiological studies. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23(R1):R89–98.",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ije/dyv071",
"author": "AG Boef",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "496",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Int J Epidemiol",
"key": "3407_CR28",
"unstructured": "Boef AG, Dekkers OM, le Cessie S. Mendelian randomization studies: a review of the approaches used and the quality of reporting. Int J Epidemiol. 2015;44(2):496–511.",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-018-07743-4",
"author": "A Doherty",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5257",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "3407_CR29",
"unstructured": "Doherty A, Smith-Byrne K, Ferreira T, et al. GWAS identifies 14 loci for device-measured physical activity and sleep duration. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):5257.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41366-018-0120-3",
"author": "YC Klimentidis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1161",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Int J Obes (Lond)",
"key": "3407_CR30",
"unstructured": "Klimentidis YC, Raichlen DA, Bea J, et al. Genome-wide association study of habitual physical activity in over 377,000 UK Biobank participants identifies multiple variants including CADM2 and APOE. Int J Obes (Lond). 2018;42(6):1161–76.",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00392-021-01846-7",
"author": "M Bahls",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1564",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Clin Res Cardiol",
"key": "3407_CR31",
"unstructured": "Bahls M, Leitzmann MF, Karch A, et al. Physical activity, sedentary behavior and risk of coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Clin Res Cardiol. 2021;110(10):1564–73.",
"volume": "110",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41431-020-0636-6",
"author": "C-HGI The",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "715",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Eur J Hum Genet",
"key": "3407_CR32",
"unstructured": "The C-HGI. The COVID-19 Host genetics initiative, a global initiative to elucidate the role of host genetic factors in susceptibility and severity of the SARS-CoV-2 virus pandemic. Eur J Hum Genet. 2020;28(6):715–8.",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/add.15852",
"author": "SL Au Yeung",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Addiction",
"key": "3407_CR33",
"unstructured": "Au Yeung SL, Li AM, He B, Kwok KO, Schooling CM. Association of smoking, lung function and COPD in COVID-19 risk: a two-step Mendelian randomization study. Addiction. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1111/add.15852.",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ije/dyv080",
"author": "J Bowden",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "512",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Int J Epidemiol",
"key": "3407_CR34",
"unstructured": "Bowden J, Davey Smith G, Burgess S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int J Epidemiol. 2015;44(2):512–25.",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/gepi.21965",
"author": "J Bowden",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "304",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Genet Epidemiol",
"key": "3407_CR35",
"unstructured": "Bowden J, et al. Consistent estimation in Mendelian randomization with some invalid instruments using a weighted median estimator. Genet Epidemiol. 2016;40(4):304–14.",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103592",
"author": "X Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "103592",
"journal-title": "EBioMedicine",
"key": "3407_CR36",
"unstructured": "Chen X, et al. Kidney damage causally affects the brain cortical structure: a Mendelian randomization study. EBioMedicine. 2021;72:103592.",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature14177",
"author": "AE Locke",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "197",
"issue": "7538",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "3407_CR37",
"unstructured": "Locke AE, et al. Genetic studies of body mass index yield new insights for obesity biology. Nature. 2015;518(7538):197–206.",
"volume": "518",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.1003062",
"author": "TG Richardson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e1003062",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "PLoS Med",
"key": "3407_CR38",
"unstructured": "Richardson TG, Sanderson E, Palmer TM, et al. Evaluating the relationship between circulating lipoprotein lipids and apolipoproteins with risk of coronary heart disease: A multivariable Mendelian randomisation analysis. PLoS Med. 2020;17(3):e1003062.",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ng.2383",
"author": "AP Morris",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "981",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Nat Genet",
"key": "3407_CR39",
"unstructured": "Morris AP, et al. Large-scale association analysis provides insights into the genetic architecture and pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet. 2012;44(9):981–90.",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ng.2274",
"author": "AK Manning",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "659",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Nat Genet",
"key": "3407_CR40",
"unstructured": "Manning AK, et al. A genome-wide approach accounting for body mass index identifies genetic variants influencing fasting glycemic traits and insulin resistance. Nat Genet. 2012;44(6):659–69.",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ng.571",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "3407_CR41",
"unstructured": "Consortium TaG. Genome-wide meta-analyses identify multiple loci associated with smoking behavior. Nat Genet. 2010. 42(5: 441–7."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/db07-0882",
"author": "MT Hamilton",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2655",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Diabetes",
"key": "3407_CR42",
"unstructured": "Hamilton MT, Hamilton DG, Zderic TW. Role of low energy expenditure and sitting in obesity, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Diabetes. 2007;56(11):2655–67.",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1249/MSS.0b013e3182019510",
"author": "BK Clark",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "822",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Med Sci Sports Exerc",
"key": "3407_CR43",
"unstructured": "Clark BK, et al. Relationship of television time with accelerometer-derived sedentary time: NHANES. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2011;43(5):822–8.",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/archinternmed.2009.430",
"author": "JJ Otten",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2109",
"issue": "22",
"journal-title": "Arch Intern Med",
"key": "3407_CR44",
"unstructured": "Otten JJ, et al. Effects of television viewing reduction on energy intake and expenditure in overweight and obese adults: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Intern Med. 2009;169(22):2109–15.",
"volume": "169",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1741826711419999",
"author": "G Frydenlund",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1111",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Eur J Prev Cardiol",
"key": "3407_CR45",
"unstructured": "Frydenlund G, et al. Sedentary leisure time behavior, snacking habits and cardiovascular biomarkers: the Inter99 Study. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2012;19(5):1111–9.",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.050753",
"author": "MJ Ponsford",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1791",
"issue": "18",
"journal-title": "Circulation",
"key": "3407_CR46",
"unstructured": "Ponsford MJ, et al. Cardiometabolic traits, sepsis, and severe COVID-19: a Mendelian randomization investigation. Circulation. 2020;142(18):1791–3.",
"volume": "142",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1513/AnnalsATS.201706-447AW",
"author": "WD Green",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "S406",
"issue": "Supplement_5",
"journal-title": "Ann Am Thorac Soc",
"key": "3407_CR47",
"unstructured": "Green WD, Beck MA. Obesity impairs the adaptive immune response to influenza virus. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2017;14(Supplement_5):S406–9.",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/ATVBAHA.121.316324",
"author": "K Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2802",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol",
"key": "3407_CR48",
"unstructured": "Zhang K, et al. Causal associations between blood lipids and covid-19 risk: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2021;41(11):2802–10.",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41398-021-01325-7",
"author": "JJ Luykx",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "210",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Transl Psychiatry",
"key": "3407_CR49",
"unstructured": "Luykx JJ, Lin BD. Are psychiatric disorders risk factors for COVID-19 susceptibility and severity? a two-sample, bidirectional, univariable, and multivariable Mendelian randomization study. Transl Psychiatry. 2021;11(1):210.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpsyt.2021.746276",
"author": "N Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "746276",
"journal-title": "Front Psychiatry",
"key": "3407_CR50",
"unstructured": "Liu N, et al. Genetic predisposition between COVID-19 and four mental illnesses: a bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front Psychiatry. 2021;12:746276.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.289.14.1785",
"author": "FB Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1785",
"issue": "14",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "3407_CR51",
"unstructured": "Hu FB, et al. Television watching and other sedentary behaviors in relation to risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus in women. JAMA. 2003;289(14):1785–91.",
"volume": "289",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pgen.1009922",
"author": "Z Lin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e1009922",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "PLoS Genet",
"key": "3407_CR52",
"unstructured": "Lin Z, Deng Y, Pan W. Combining the strengths of inverse-variance weighting and Egger regression in Mendelian randomization using a mixture of regressions model. PLoS Genet. 2021;17(11):e1009922.",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ije/dyw252",
"author": "J Bowden",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1961",
"journal-title": "Int J Epidemiol",
"key": "3407_CR53",
"unstructured": "Bowden J, Del Greco MF, Minelli C, Davey Smith G, Sheehan NA, Thompson JR. Assessing the suitability of summary data for two-sample Mendelian randomization analyses using MR-Egger regression: the role of the I2 statistic. Int J Epidemiol. 2016;45:1961–74.",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.1003679",
"author": "SS Venkatesh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e1003679",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "PLoS Med",
"key": "3407_CR54",
"unstructured": "Venkatesh SS, Ferreira T, Benonisdottir S, et al. Obesity and risk of female reproductive conditions: a Mendelian randomisation study. PLoS Med. 2022;19(2):e1003679.",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc21-1609",
"author": "F Cheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "701",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "3407_CR55",
"unstructured": "Cheng F, Luk AO, Shi M, et al. Shortened leukocyte telomere length is associated with glycemic progression in type 2 diabetes: a prospective and mendelian randomization analysis. Diabetes Care. 2022;45(3):701–9.",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 55,
"references-count": 55,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://translational-medicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12967-022-03407-6"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Biochemistry, Genetics and Molecular Biology",
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Causal relationship between physical activity, leisure sedentary behaviors and COVID-19 risk: a Mendelian randomization study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "20"
}