Lactoferrin for COVID-19: real-time meta-analysis of 8 studies (Version 15)
, Feb 2026
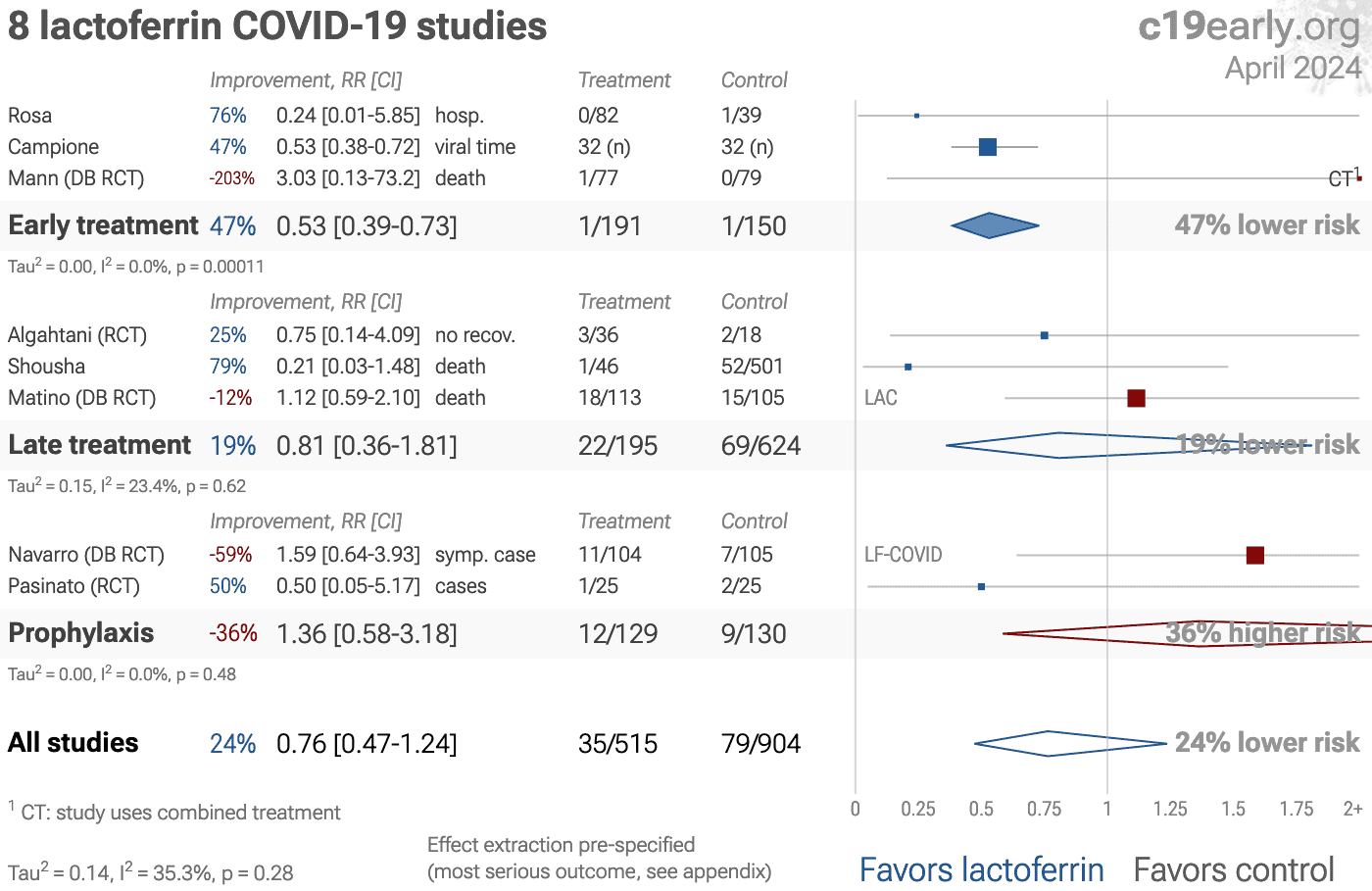
Meta-analysis using the most serious outcome reported shows 24% [-24‑53%] lower risk, without reaching statistical significance. Results are worse for Randomized Controlled Trials and higher quality studies. Early treatment is more effective than late treatment. 3 studies from 3 independent teams in 2 countries show significant benefit.
Control Lactoferrin
1 RCT with 40 patients has not reported results (1 year late)1.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols combine safe and effective options with individual risk/benefit analysis and monitoring. Other treatments are more effective. Dietary sources may be preferred. The quality of non-prescription supplements varies widely2-4. All data and sources to reproduce this analysis are in the appendix.
Notably, only one of the 8 studies used combined intranasal and oral administration, and this study shows significant efficacy. Intranasal administration may block viral entry at the site of infection, while systemic levels achieved via oral administration may be insufficient for inhibition in the respiratory tract.
Covid Analysis et al., Feb 2026, preprint, 1 author.