Exercise reduces COVID-19 risk: real-time meta analysis of 68 studies (Version 43)
, Jan 2026
Exercise for COVID-19
9th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 68 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,300+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
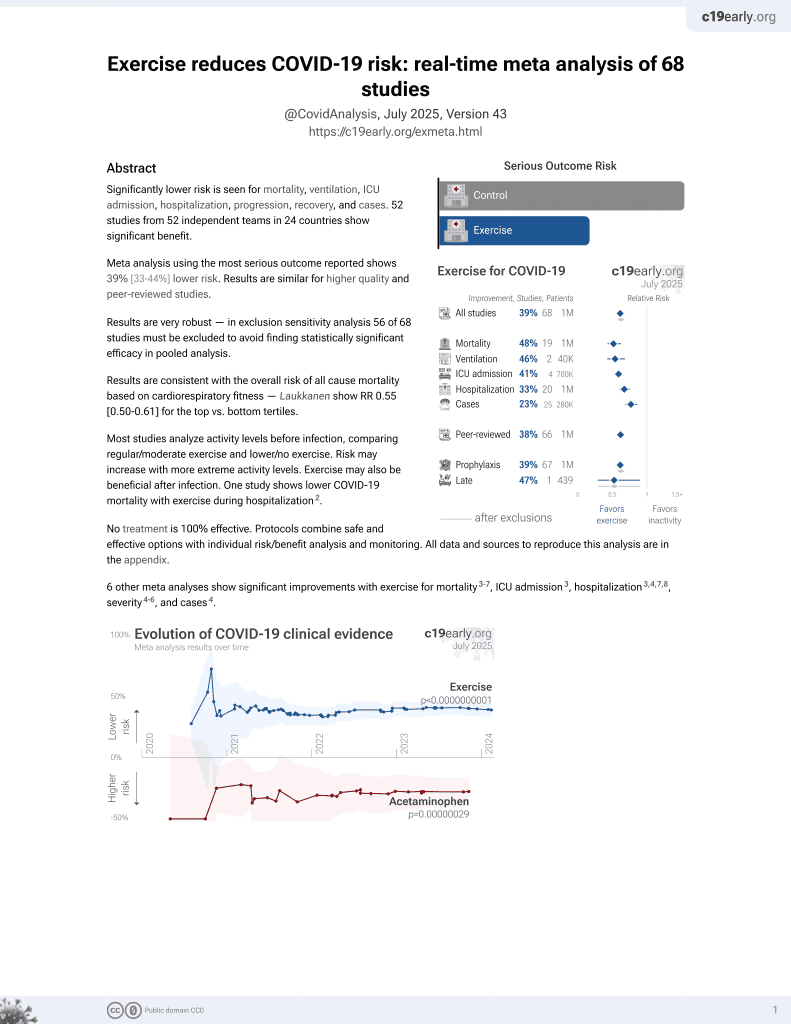
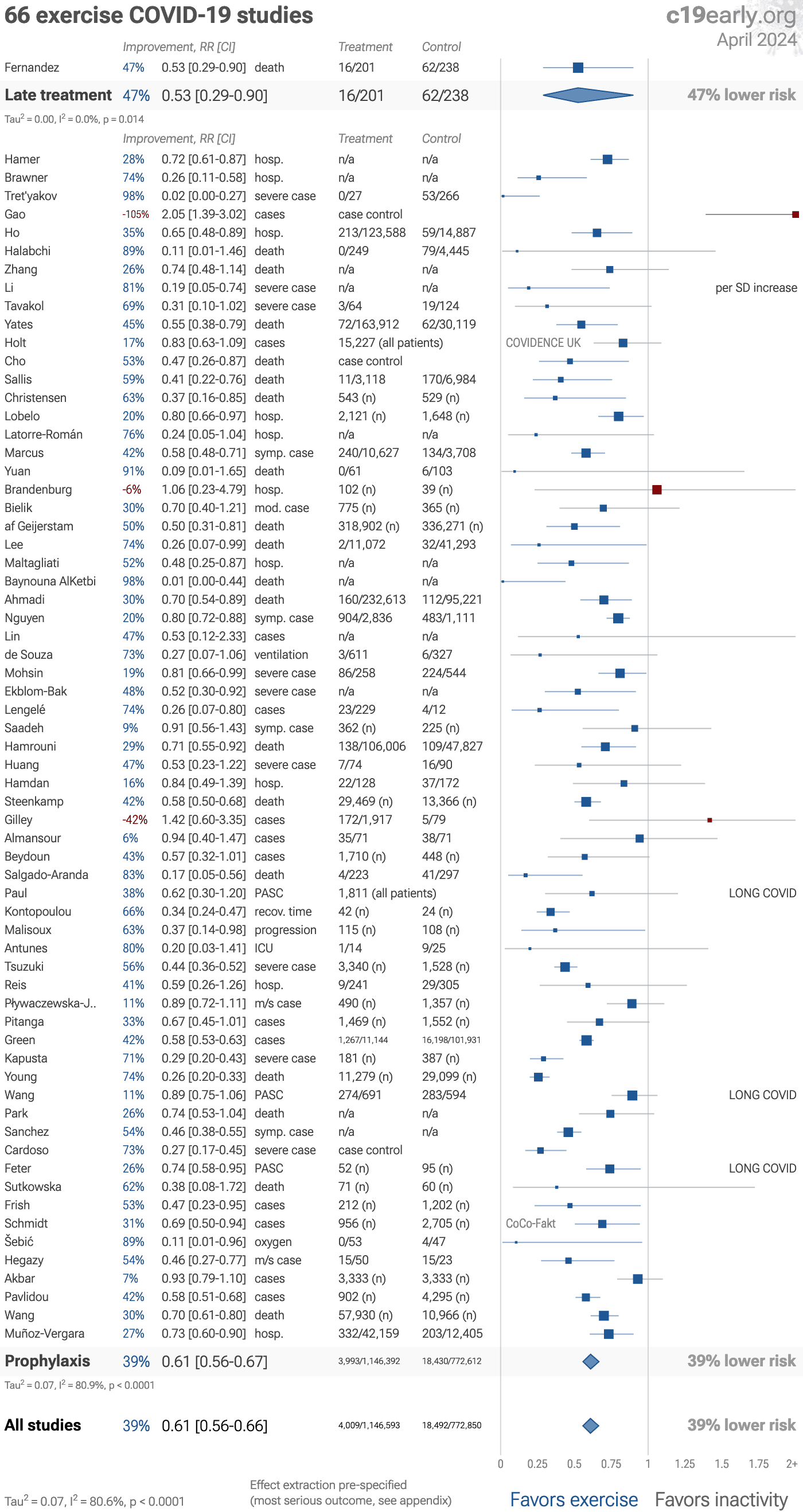
Significantly lower risk is seen for mortality, ventilation, ICU admission, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and cases. 52 studies from 52 independent teams in 24 countries show significant benefit.
Meta analysis using the most serious outcome reported shows 39% [33‑44%] lower risk. Results are similar for higher quality and peer-reviewed studies.
Results are very robust — in exclusion sensitivity analysis 56 of 68 studies must be excluded to avoid finding statistically significant efficacy in pooled analysis.
Results are consistent with the overall risk of all cause mortality based on cardiorespiratory fitness — Laukkanen show RR 0.55 [0.50-0.61] for the top vs. bottom tertiles.
Control Exercise
Most studies analyze activity levels before infection, comparing regular/moderate exercise and lower/no exercise. Risk may increase with more extreme activity levels. Exercise may also be beneficial after infection. One study shows lower COVID-19 mortality with exercise during hospitalization2. Exercise during infection may increase the risk of transmission to others3, precautions should be taken to avoid transmission if potentially infected.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols combine safe and effective options with individual risk/benefit analysis and monitoring. All data and sources to reproduce this analysis are in the appendix.
6 other meta analyses show significant improvements with exercise for mortality4-8, ICU admission4, hospitalization4,5,8,9, severity5-7, and cases5.
6 meta analyses show significant improvements with exercise for mortality1-5,
ICU admission1,
hospitalization1,2,5,6 ,
severity2-4, and
cases2.
1.
Rahmati et al., Baseline physical activity is associated with reduced mortality and disease outcomes in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Reviews in Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/rmv.2349.
2.
Ezzatvar et al., Physical activity and risk of infection, severity and mortality of COVID-19: a systematic review and non-linear dose–response meta-analysis of data from 1 853 610 adults, British Journal of Sports Medicine, doi:10.1136/bjsports-2022-105733.
3.
Sittichai et al., Effects of physical activity on the severity of illness and mortality in COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Frontiers in Physiology, doi:10.3389/fphys.2022.1030568.
4.
Liu et al., Baseline physical activity and the risk of severe illness and mortality from COVID-19: A dose–response meta-analysis, Preventive Medicine Reports, doi:10.1016/j.pmedr.2023.102130.
Covid Analysis et al., Jan 2026, preprint, 1 author.