Accuracy of artificial intelligence CT quantification in predicting COVID-19 subjects’ prognosis
et al., PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0294899, Dec 2023
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 136 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 90 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Iran showing lower vitamin D levels in critical vs. non-critical patients (20 vs. 26, p = 0.18).
Arian et al., 8 Dec 2023, retrospective, Iran, peer-reviewed, 8 authors, study period November 2020 - January 2021.
Contact: hszadeh@ut.ac.ir.
Accuracy of artificial intelligence CT quantification in predicting COVID-19 subjects’ prognosis
PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0294899
Background Artificial intelligence (AI)-aided analysis of chest CT expedites the quantification of abnormalities and may facilitate the diagnosis and assessment of the prognosis of subjects with COVID-19.
Objectives This study investigates the performance of an AI-aided quantification model in predicting the clinical outcomes of hospitalized subjects with COVID-19 and compares it with radiologists' performance.
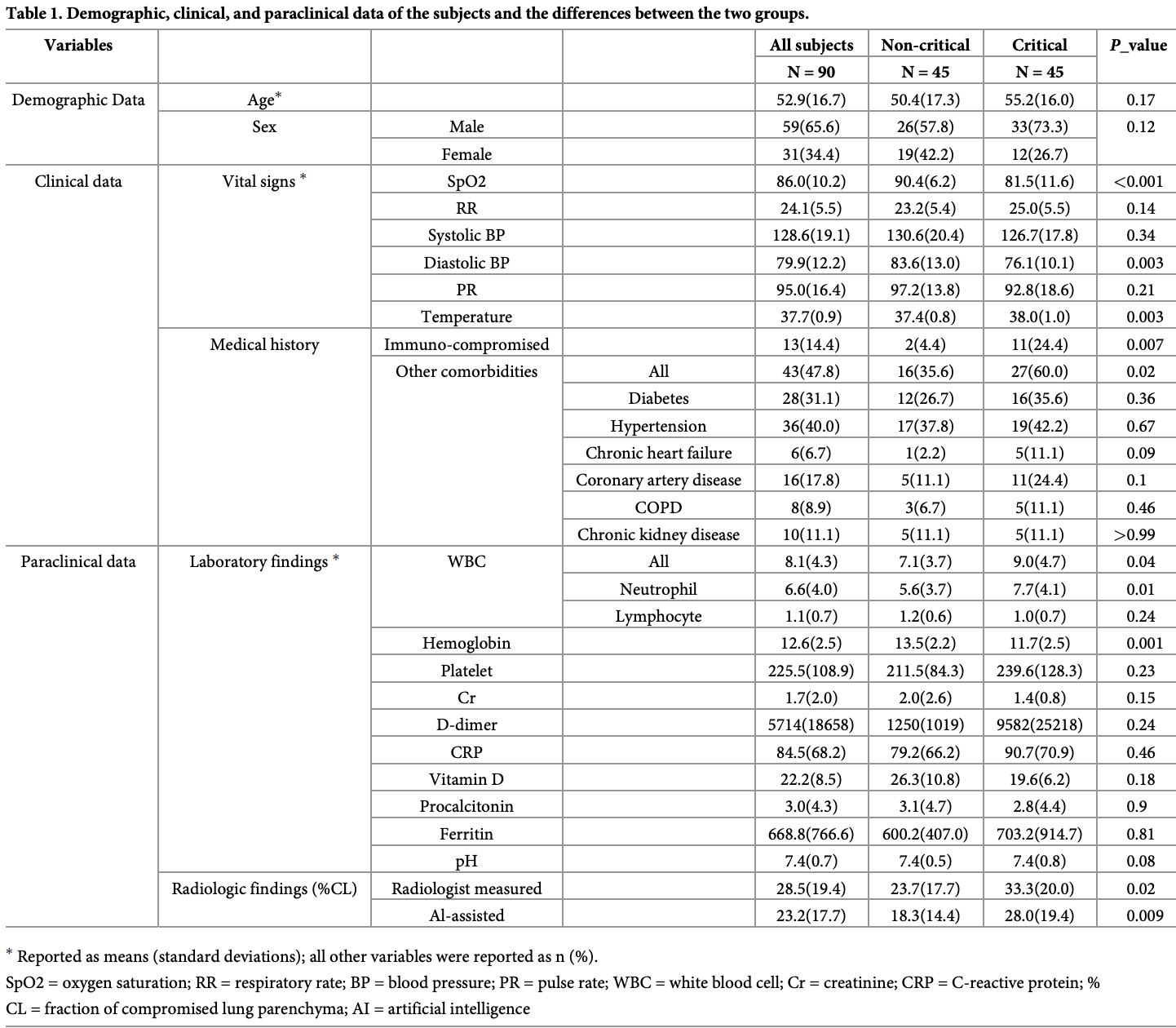
Subjects and methods A total of 90 subjects with COVID-19 (men, n = 59 [65.6%]; age, 52.9±16.7 years) were recruited in this cross-sectional study. Quantification of the total and compromised lung parenchyma was performed by two expert radiologists using a volumetric image analysis software and compared against an AI-assisted package consisting of a modified U-Net model for segmenting COVID-19 lesions and an off-the-shelf U-Net model augmented with COVID-19 data for segmenting lung volume. The fraction of compromised lung parenchyma (%CL) was calculated. Based on clinical results, the subjects were divided into two categories: critical (n = 45) and noncritical (n = 45). All admission data were compared between the two groups.
Results There was an excellent agreement between the radiologist-obtained and AI-assisted measurements (intraclass correlation coefficient = 0.88, P < 0.001). Both the AI-assisted and
Author Contributions Conceptualization: Arvin Arian. Validation: Shahriar Kolahi, Masoumeh Gity.
Data curation: Visualization: Navid Hasanzadeh. Writing -original draft: Arvin Arian, Mostafa Zoorpaikar, Saman Sotoudeh-Paima.
Writing -review & editing: Hamid Soltanian-Zadeh.
References
Abkhoo, Shaker, Mehrabinejad, Azadbakht, Sadighi et al., Factors predicting outcome in intensive care unit-admitted COVID-19 patients: using clinical, laboratory, and radiologic characteristics, Critical Care Research and Practice, doi:10.1155/2021/9941570
Arian, Mehrabinejad, Zoorpaikar, Hasanzadeh, Sotoudeh-Paima et al., COVID-19 & Normal CT Segmentation Dataset, Mendeley Data, doi:10.17632/pfmgfpwnmm.1
Arru, Ebrahimian, Falaschi, Hansen, Pasche et al., Comparison of deep learning, radiomics and subjective assessment of chest CT findings in SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia, Clinical Imaging, doi:10.1016/j.clinimag.2021.06.036
Arunmozhi, Sarojini, Pavithra, Varghese, Deepti et al., Automated detection of COVID-19 lesion in lung CT slices with VGG-UNet and handcrafted features
Cai, Liu, Xue, Luo, Wang et al., CT quantification and machine-learning models for assessment of disease severity and prognosis of COVID-19 patients, Academic radiology, doi:10.1016/j.acra.2020.09.004
Dong, Tang, Wang, Hui, Gong et al., The role of imaging in the detection and management of COVID-19: a review, IEEE reviews in biomedical engineering, doi:10.1109/RBME.2020.2990959
Ebrahimian, Homayounieh, Rockenbach, Putha, Raj et al., Artificial intelligence matches subjective severity assessment of pneumonia for prediction of patient outcome and need for mechanical ventilation: a cohort study, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-79470-0
Fang, He, Li, Dong, Yang et al., CT radiomics can help screen the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a preliminary study, Science China Information Sciences, doi:10.1007/s11432-020-2849-3
Hasanzadeh, Paima, Bashirgonbadi, Naghibi, Soltanian-Zadeh, Segmentation of covid-19 infections on ct: Comparison of four unet-based networks
Hofmanninger, Prayer, Pan, Ro ¨hrich, Prosch et al., Automatic lung segmentation in routine imaging is primarily a data diversity problem, not a methodology problem, European Radiology Experimental, doi:10.1186/s41747-020-00173-2
Iyer, Raj, Ghildiyal, Nersisson, Performance analysis of lightweight CNN models to segment infectious lung tissues of COVID-19 cases from tomographic images, PeerJ Computer Science, doi:10.7717/peerj-cs.368
Lanza, Muglia, Bolengo, Santonocito, Lisi et al., Quantitative chest CT analysis in COVID-19 to predict the need for oxygenation support and intubation, European radiology, doi:10.1007/s00330-020-07013-2
Mushtaq, Pennella, Lavalle, Colarieti, Steidler et al., Initial chest radiographs and artificial intelligence (AI) predict clinical outcomes in COVID-19 patients: analysis of 697 Italian patients, European radiology, doi:10.1007/s00330-020-07269-8
Nemoto, Futakami, Kunieda, Yagi, Takeda et al., Effects of sample size and data augmentation on U-Net-based automatic segmentation of various organs, Radiological Physics and Technology, doi:10.1007/s12194-021-00630-6
Phua, Weng, Ling, Egi, Lim et al., Intensive care management of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): challenges and recommendations, The lancet respiratory medicine, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30161-2
Pravitasari, Iriawan, Almuhayar, Azmi, Irhamah et al., UNet-VGG16 with transfer learning for MRI-based brain tumor segmentation, TELKOMNIKA (Telecommunication Computing Electronics and Control), doi:10.12928/telkomnika.v18i3.14753
Romei, Falaschi, Danna, Airoldi, Tonerini et al., Lung vessel volume evaluated with CALIPER software is an independent predictor of mortality in COVID-19 patients: a multicentric retrospective analysis, European radiology, doi:10.1007/s00330-021-08485-6
Ronneberger, Fischer, Brox, U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation
Salahshour, Mehrabinejad, Toosi, Gity, Ghanaati et al., Clinical and chest CT features as a predictive tool for COVID-19 clinical progress: introducing a novel semi-quantitative scoring system, European radiology, doi:10.1007/s00330-020-07623-w
Salvatore, Dl, Cesare, Alfredo, Giuliano, Clinical and laboratory data, radiological structured report findings and quantitative evaluation of lung involvement on baseline chest CT in COVID-19 patients to predict prognosis, La radiologia medica, doi:10.1007/s11547-020-01293-w
Scapicchio, Chincarini, Ballante, Berta, Bicci et al., A multicenter evaluation of a deep learning software (LungQuant) for lung parenchyma characterization in COVID-19 pneumonia, European Radiology Experimental, doi:10.1186/s41747-023-00334-z
Shaikh, Andersen, Sohail, Mulero, Awan et al., Current landscape of imaging and the potential role for artificial intelligence in the management of COVID-19, Current Problems in Diagnostic Radiology, doi:10.1067/j.cpradiol.2020.06.009
Shi, Wang, Shi, Wu, Wang et al., Review of artificial intelligence techniques in imaging data acquisition, segmentation, and diagnosis for COVID-19, IEEE reviews in biomedical engineering, doi:10.1109/RBME.2020.2987975
Sotoudeh-Paima, Hasanzadeh, Bashirgonbadi, Aref, Naghibi et al., A Multicentric Evaluation of Deep Learning Models for Segmentation of COVID-19 Lung Lesions on Chest CT Scans, Iranian Journal of Radiology, doi:10.5812/iranjradiol-117992
Wasilewski, Mruk, Mazur, Po ´łtorak-Szymczak, Sklinda et al., COVID-19 severity scoring systems in radiological imaging-a review, Polish journal of radiology, doi:10.5114/pjr.2020.98009
Yang, Li, Liu, Zhen, Zhang et al., Chest CT severity score: an imaging tool for assessing severe COVID-19, Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging, doi:10.1148/ryct.2020200047
Youden, Index for rating diagnostic tests, Cancer, doi:10.1002/1097-0142(1950)3:1%3C32::AID-CNCR2820030106%3E3.0.CO;2-3
Yu, Liu, Xu, Zhang, Lan et al., Prediction of the development of pulmonary fibrosis using serial thin-section CT and clinical features in patients discharged after treatment for COVID-19 pneumonia, Korean journal of radiology, doi:10.3348/kjr.2020.0215
Zhao, Zhong, Xie, Yu, Liu, Relation between chest CT findings and clinical conditions of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pneumonia: a multicenter study, Ajr Am J Roentgenol, doi:10.2214/AJR.20.22976
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0294899",
"ISSN": [
"1932-6203"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0294899",
"abstract": "<jats:sec id=\"sec001\">\n<jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n<jats:p>Artificial intelligence (AI)-aided analysis of chest CT expedites the quantification of abnormalities and may facilitate the diagnosis and assessment of the prognosis of subjects with COVID-19.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec id=\"sec002\">\n<jats:title>Objectives</jats:title>\n<jats:p>This study investigates the performance of an AI-aided quantification model in predicting the clinical outcomes of hospitalized subjects with COVID-19 and compares it with radiologists’ performance.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec id=\"sec003\">\n<jats:title>Subjects and methods</jats:title>\n<jats:p>A total of 90 subjects with COVID-19 (men, n = 59 [65.6%]; age, 52.9±16.7 years) were recruited in this cross-sectional study. Quantification of the total and compromised lung parenchyma was performed by two expert radiologists using a volumetric image analysis software and compared against an AI-assisted package consisting of a modified U-Net model for segmenting COVID-19 lesions and an off-the-shelf U-Net model augmented with COVID-19 data for segmenting lung volume. The fraction of compromised lung parenchyma (%CL) was calculated. Based on clinical results, the subjects were divided into two categories: critical (n = 45) and noncritical (n = 45). All admission data were compared between the two groups.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec id=\"sec004\">\n<jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n<jats:p>There was an excellent agreement between the radiologist-obtained and AI-assisted measurements (intraclass correlation coefficient = 0.88, <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> < 0.001). Both the AI-assisted and radiologist-obtained %CLs were significantly higher in the critical subjects (P = 0.009 and 0.02, respectively) than in the noncritical subjects. In the multivariate logistic regression analysis to distinguish the critical subjects, an AI-assisted %CL ≥35% (odds ratio [OR] = 17.0), oxygen saturation level of <88% (OR = 33.6), immunocompromised condition (OR = 8.1), and other comorbidities (OR = 15.2) independently remained as significant variables in the models. Our proposed model obtained an accuracy of 83.9%, a sensitivity of 79.1%, and a specificity of 88.6% in predicting critical outcomes.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec id=\"sec005\">\n<jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n<jats:p>AI-assisted measurements are similar to quantitative radiologist-obtained measurements in determining lung involvement in COVID-19 subjects.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arian",
"given": "Arvin",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mehrabi Nejad",
"given": "Mohammad-Mehdi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zoorpaikar",
"given": "Mostafa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hasanzadeh",
"given": "Navid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sotoudeh-Paima",
"given": "Saman",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kolahi",
"given": "Shahriar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gity",
"given": "Masoumeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7302-6856",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Soltanian-Zadeh",
"given": "Hamid",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "PLOS ONE",
"container-title-short": "PLoS ONE",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"www.plosone.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-08T18:23:35Z",
"timestamp": 1702059815000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-08T18:23:52Z",
"timestamp": 1702059832000
},
"editor": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Faggioni",
"given": "Lorenzo",
"sequence": "first"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-09T00:35:17Z",
"timestamp": 1702082117042
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "12",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
8
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "12",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
8
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-08T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1701993600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0294899",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "340",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e0294899",
"prefix": "10.1371",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
8
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
8
]
]
},
"publisher": "Public Library of Science (PLoS)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30161-2",
"article-title": "Intensive care management of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): challenges and recommendations",
"author": "J Phua",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "506",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "The lancet respiratory medicine",
"key": "pone.0294899.ref001",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11547-020-01293-w",
"article-title": "Clinical and laboratory data, radiological structured report findings and quantitative evaluation of lung involvement on baseline chest CT in COVID-19 patients to predict prognosis",
"author": "C Salvatore",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "29",
"journal-title": "La radiologia medica",
"key": "pone.0294899.ref002",
"volume": "126",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Chest CT severity score: an imaging tool for assessing severe COVID-19",
"author": "R Yang",
"first-page": "e200047",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging",
"key": "pone.0294899.ref003",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5114/pjr.2020.98009",
"article-title": "COVID-19 severity scoring systems in radiological imaging–a review",
"author": "P Wasilewski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "361",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Polish journal of radiology",
"key": "pone.0294899.ref004",
"volume": "85",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00330-020-07623-w",
"article-title": "Clinical and chest CT features as a predictive tool for COVID-19 clinical progress: introducing a novel semi-quantitative scoring system",
"author": "F Salahshour",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5178",
"journal-title": "European radiology",
"key": "pone.0294899.ref005",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2021/9941570",
"article-title": "Factors predicting outcome in intensive care unit-admitted COVID-19 patients: using clinical, laboratory, and radiologic characteristics",
"author": "A Abkhoo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Critical Care Research and Practice",
"key": "pone.0294899.ref006",
"volume": "2021",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2214/AJR.20.22976",
"article-title": "Relation between chest CT findings and clinical conditions of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pneumonia: a multicenter study",
"author": "W Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1072",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Ajr Am J Roentgenol",
"key": "pone.0294899.ref007",
"volume": "214",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1109/RBME.2020.2987975",
"article-title": "Review of artificial intelligence techniques in imaging data acquisition, segmentation, and diagnosis for COVID-19",
"author": "F Shi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4",
"journal-title": "IEEE reviews in biomedical engineering",
"key": "pone.0294899.ref008",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1067/j.cpradiol.2020.06.009",
"article-title": "Current landscape of imaging and the potential role for artificial intelligence in the management of COVID-19",
"author": "F Shaikh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "430",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Current Problems in Diagnostic Radiology",
"key": "pone.0294899.ref009",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1109/RBME.2020.2990959",
"article-title": "The role of imaging in the detection and management of COVID-19: a review",
"author": "D Dong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "16",
"journal-title": "IEEE reviews in biomedical engineering",
"key": "pone.0294899.ref010",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5812/iranjradiol-117992",
"article-title": "A Multi-centric Evaluation of Deep Learning Models for Segmentation of COVID-19 Lung Lesions on Chest CT Scans",
"author": "S Sotoudeh-Paima",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Iranian Journal of Radiology",
"key": "pone.0294899.ref011",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "pone.0294899.ref012",
"unstructured": "Arian A, Mehrabinejad MM, Zoorpaikar M, Hasanzadeh N, Sotoudeh-Paima S, Kolahi S, et al. COVID-19 & Normal CT Segmentation Dataset. 2023. Mendeley Data. https://doi.org/10.17632/pfmgfpwnmm.1."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s41747-020-00173-2",
"article-title": "Automatic lung segmentation in routine imaging is primarily a data diversity problem, not a methodology problem",
"author": "J Hofmanninger",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "European Radiology Experimental",
"key": "pone.0294899.ref013",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "pone.0294899.ref014",
"unstructured": "Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. arXiv 2015. arXiv preprint arXiv:150504597. 2015;."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1109/ICBME51989.2020.9319412",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "pone.0294899.ref015",
"unstructured": "Hasanzadeh N, Paima SS, Bashirgonbadi A, Naghibi M, Soltanian-Zadeh H. Segmentation of covid-19 infections on ct: Comparison of four unet-based networks. In: 2020 27th National and 5th International Iranian Conference on Biomedical Engineering (ICBME). IEEE; 2020. p. 222–225."
},
{
"DOI": "10.7717/peerj-cs.368",
"article-title": "Performance analysis of lightweight CNN models to segment infectious lung tissues of COVID-19 cases from tomographic images",
"author": "TJ Iyer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e368",
"journal-title": "PeerJ Computer Science",
"key": "pone.0294899.ref016",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1201/9781003198796-11",
"author": "S Arunmozhi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "185",
"key": "pone.0294899.ref017",
"volume-title": "Digital Future of Healthcare",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12928/telkomnika.v18i3.14753",
"article-title": "UNet-VGG16 with transfer learning for MRI-based brain tumor segmentation",
"author": "AA Pravitasari",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1310",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "TELKOMNIKA (Telecommunication Computing Electronics and Control)",
"key": "pone.0294899.ref018",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12194-021-00630-6",
"article-title": "Effects of sample size and data augmentation on U-Net-based automatic segmentation of various organs",
"author": "T Nemoto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "318",
"journal-title": "Radiological Physics and Technology",
"key": "pone.0294899.ref019",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/1097-0142(1950)3:1<32::AID-CNCR2820030106>3.0.CO;2-3",
"article-title": "Index for rating diagnostic tests",
"author": "WJ Youden",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "32",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Cancer",
"key": "pone.0294899.ref020",
"volume": "3",
"year": "1950"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11432-020-2849-3",
"article-title": "CT radiomics can help screen the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a preliminary study",
"author": "M Fang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Science China Information Sciences",
"key": "pone.0294899.ref021",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3348/kjr.2020.0215",
"article-title": "Prediction of the development of pulmonary fibrosis using serial thin-section CT and clinical features in patients discharged after treatment for COVID-19 pneumonia",
"author": "M Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "746",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Korean journal of radiology",
"key": "pone.0294899.ref022",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00330-020-07013-2",
"article-title": "Quantitative chest CT analysis in COVID-19 to predict the need for oxygenation support and intubation",
"author": "E Lanza",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6770",
"journal-title": "European radiology",
"key": "pone.0294899.ref023",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-79470-0",
"article-title": "Artificial intelligence matches subjective severity assessment of pneumonia for prediction of patient outcome and need for mechanical ventilation: a cohort study",
"author": "S Ebrahimian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "858",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Scientific Reports",
"key": "pone.0294899.ref024",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00330-020-07269-8",
"article-title": "Initial chest radiographs and artificial intelligence (AI) predict clinical outcomes in COVID-19 patients: analysis of 697 Italian patients",
"author": "J Mushtaq",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1770",
"journal-title": "European radiology",
"key": "pone.0294899.ref025",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.acra.2020.09.004",
"article-title": "CT quantification and machine-learning models for assessment of disease severity and prognosis of COVID-19 patients",
"author": "W Cai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1665",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Academic radiology",
"key": "pone.0294899.ref026",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clinimag.2021.06.036",
"article-title": "Comparison of deep learning, radiomics and subjective assessment of chest CT findings in SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia",
"author": "C Arru",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "58",
"journal-title": "Clinical Imaging",
"key": "pone.0294899.ref027",
"volume": "80",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s41747-023-00334-z",
"article-title": "A multicenter evaluation of a deep learning software (LungQuant) for lung parenchyma characterization in COVID-19 pneumonia",
"author": "C Scapicchio",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "18",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "European Radiology Experimental",
"key": "pone.0294899.ref028",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00330-021-08485-6",
"article-title": "Lung vessel volume evaluated with CALIPER software is an independent predictor of mortality in COVID-19 patients: a multicentric retrospective analysis",
"author": "C Romei",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4314",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "European radiology",
"key": "pone.0294899.ref029",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 29,
"references-count": 29,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0294899"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Multidisciplinary"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Accuracy of artificial intelligence CT quantification in predicting COVID-19 subjects’ prognosis",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.corrections_policy",
"volume": "18"
}
