Assessment of Oxidative Stress Parameters in Iraqi Male Patients with Covid-19; A Case Control Study
et al., Reports of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, 13:2, Oct 2024
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000028 from 47 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
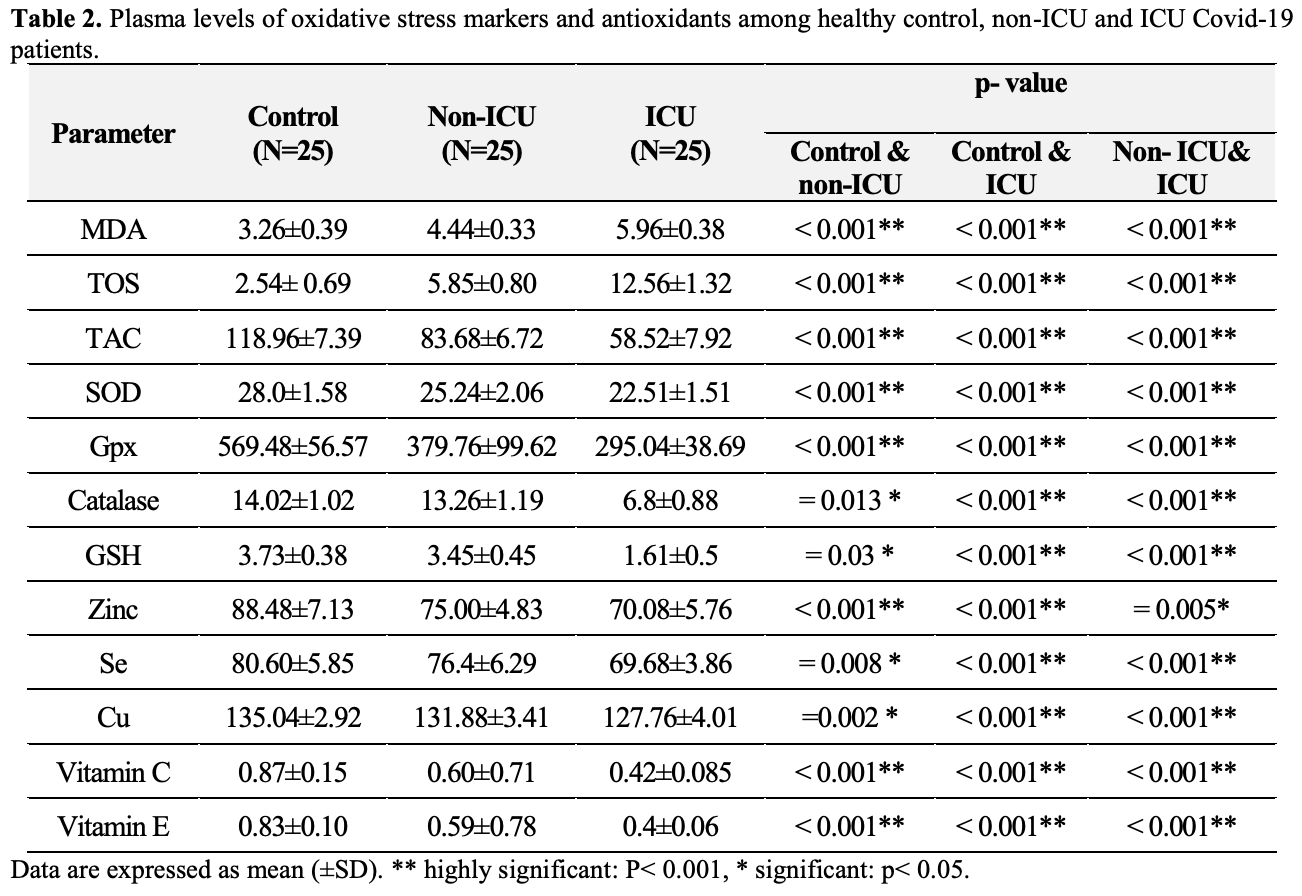
Analysis of 50 symptomatic COVID-19 patients (25 ICU and 25 non-ICU) and 25 healthy controls, showing significantly lower vitamin C, zinc, and selenium levels in COVID-19 patients versus healthy controls, and in ICU patients versus non-ICU patients.
Anber et al., 5 Oct 2024, retrospective, Iraq, peer-reviewed, 3 authors.
Assessment of Oxidative Stress Parameters in Iraqi Male Patients with Covid-19; A Case Control Study
Background: SARS-CoV-2 infection can cause significant alterations in our lives. Oxidative stress (OS) has been proposed to play a major role in COVID-19 pathogenesis, and the determination of OS biomarkers provides insight into disease severity. Methods: The study was conducted during the second wave of the pandemic in 2020. Fifty blood samples were collected from patients admitted to one of the COVID-19 isolation centers in Baghdad, Iraq. The samples were subdivided into 25 patients admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) and 25 non-ICU patients, compared to 25 healthy controls. All participants were aged 35-52 years.
Results: The study showed that the mean (±SD) serum total oxidant status (TOS) and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels were significantly increased (p< 0.001) in the ICU group compared to the control and non-ICU groups. Conversely, the levels of serum total antioxidant capacity (TAC) and serum antioxidative enzymes superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPX), catalase, and glutathione (GSH) were significantly decreased (p< 0.001) in the ICU group compared to both the control and non-ICU groups. Serum zinc levels were significantly decreased (p< 0.001) in both ICU and non-ICU groups compared to the control group, while serum selenium (Se), copper (Cu), and vitamins C and E were significantly decreased (p< 0.001) in the ICU group compared to both the control and non-ICU groups.
Conclusion: The presence of OS biomarkers in the sera of COVID-19 patients offers a potential new approach for the treatment of this disease.
Ethical Information and conflict of interest The entire work had permitted by the Ethical Committees of local authorities. All participants provided an inscribed informed consent, and the research had conducted in line with the ethical morals identified in the 1975 treaty of Helsinki. The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest related to the present research.
References
Baqi, Farag, Bilbeisi, Askandar, Afifi, Oxidative Stress and Its Association with COVID-19:A Narrative Review, Kurdistan J Applied Res
Barazzoni, Bischoff, Breda, Wickramasinghe, Krznaric et al., ESPEN expert statements and practical guidance [
Beutler, Duron, Kelly, The improved method for the determination of blood glutathione, J Lab Clin Med
Brito, Dingeo, Del Campo, Samouda, Frano et al., Strengthening the Immune System and Reducing Inflammation and Oxidative Stress through Diet and Nutrition:Considerations during the COVID-19 Crisis, Nutrients
Cecchini, Cecchini, SARS-CoV-2 infection pathogenesis is related to oxidative stress as a response to aggression, Med Hypotheses
Chiscano-Camón, Ruiz-Rodriguez, Ruiz-Sanmartin, Roca, Ferrer, Vitamin C levels in patients with SARS-CoV-2-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome, Crit Care
Delgado-Roche, Mesta, Oxidative Stress as Key Player in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (SARS-CoV) Infection, Arch Med Res
Delgado-Roche, Mesta, Oxidative Stress as Key Player in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (SARS-CoV) Infection, Arch Med Res
Delgado-Roche, Mesta, Oxidative Stress as Key Player in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (SARS-CoV) Infection, Arch Med Res
Derouiche, Oxidative stress associated with SARS-Cov-2 (COVID-19) increases the severity of the lung disease-a systematic review, J Infect Dis Epidemol
Dinçer, Alademir, Ilkova, Akçay, Susceptibility of glutatione and glutathionerelated antioxidant activity to hydrogen peroxide in patients with type 2 diabetes:effect of glycemic control, Clin Biochem
Dorjgochoo, Yt, Wh, Shu Xo, Yang et al., Major metabolite of F2isoprostane in urine may be a more sensitive biomarker of oxidative stress than isoprostane itself, Am J Clin Nutr
Dworzański, Strycharz-Dudziak, Kliszczewska, Kiełczykowska, Dworzańska et al., Glutathione peroxidase (GPx) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity in patients with diabetes mellitus type 2 infected with Epstein-Barr virus, PLoS One
Erel, A new automated colorimetric method for measuring total oxidant status, Clin Biochem
Fooladi, Matin, Mahmoodpoor, Copper as a potential adjunct therapy for critically ill COVID-19 patients, Clin Nutr ESPEN
Giménez, Inserra, Tajer, Mariani, Ferder et al., Lungs as target of COVID-19 infection:Protective common molecular mechanisms of vitamin D and melatonin as a new potential synergistic treatment, Life Sci
Hasan Anber, Mohammed Saleh, Al-Obidy, Hepatocellular Damage and Severity of COVID-19 Infection in Iraqi Patients:A Biochemical Study, Rep Biochem Mol Biol
Ito, Sono, Ito, Measurement and Clinical Significance of Lipid Peroxidation as a Biomarker of Oxidative Stress:Oxidative Stress in Diabetes, Atherosclerosis, and Chronic Inflammation, Antioxidants
Jan, Usman, Zainab, COVID-19:a brief overview on the role of vitamins specifically vitamin C as immune modulators and in prevention and treatment of SARS-Cov-2 infections, Biomed J Sci Tech Res
Joël, Mouna-Messaouda, Cb, Olivier, Smail, Electrochemical Methodology for Evaluating Skin Oxidative Stress Status (SOSS), Diseases
Kardos, Héja, Simon, Jablonkai, Kovács et al., Copper signalling:causes and consequences, Cell Commun Signal
Khomich, Kochetkov, Bartosch, Ivanov, Redox Biology of Respiratory Viral Infections, Viruses
Lykkesfeldt, Determination of ascorbic acid and dehydroascorbic acid in biological samples by high-performance liquid chromatography using subtraction methods:reliable reduction with tris[2-carboxyethyl]phosphine hydrochloride, Anal Biochem
Maradi, Joshi, Balamurugan, Thomas, Goud, Importance of Microminerals for Maintaining Antioxidant Function After COVID-19-induced Oxidative Stress, Rep Biochem Mol Biol
Meret, Henkin, Chem, Varly's Practical Clinical Biochemistry
Mesaros, Arora, Wholer, Vachani, Blair, 8-Oxo-2'-deoxyguanosine as a biomarker of tobacco-smoking-induced oxidative stress, Free Radic Biol Med
Mp, COVID-19 infection and oxidative stress:an under-explored approach for prevention and treatment?, Pan Afr Med J
Mp, COVID-19 infection and oxidative stress:an under-explored approach for prevention and treatment?, Pan Afr Med J
Muhammad, Kani, Iliya, Muhammad, Binji et al., Deficiency of antioxidants and increased oxidative stress in COVID-19 patients:A cross-sectional comparative study in Jigawa, Northwestern Nigeria, SAGE Open Med
Munster, Koopmans, Van Doremalen, Van Riel, De, A Novel Coronavirus Emerging in China -Key Questions for Impact Assessment, N Engl J Med
Neeld, Pearson, Macro-and micromethods for the determination of serum vitamin A using trifluoroacetic acid, J Nutr
Pincemail, Cavalier, Charlier, Cheramy-Bien, Brevers et al., Oxidative Stress Status in COVID-19 Patients Hospitalized in Intensive Care Unit for Severe Pneumonia. A Pilot Study, Antioxidants
Qin, Cao, Wen, Yu, Liu et al., An antioxidant enzyme therapeutic for COVID-19, Adv Mater
Rahimi, Vesal, Edalatifard, Coronavirus and Its effect on the respiratory system:Is there any association between pneumonia and immune cells, J Family Med Prim Care
Shakoor, Feehan, Dhaheri, Ali, Platat et al., Immune-boosting role of vitamins D, C, E, zinc, selenium and omega-3 fatty acids:Could they help against COVID-19?, Maturitas
Steven, Frenis, Oelze, Kalinovic, Kuntic et al., Vascular Inflammation and Oxidative Stress:Major Triggers for Cardiovascular Disease, Oxid Med Cell Longev
Strycharz-Dudziak, Kiełczykowska, Drop, Świątek, Kliszczewska et al., Total Antioxidant Status (TAS), Superoxide Dismutase (SOD), and Glutathione Peroxidase (GPx) in Oropharyngeal Cancer Associated with EBV Infection, Oxid Med Cell Longev
Taheri, Bahrami, Habibi, Nouri, A Review on the Serum Electrolytes and Trace Elements Role in the Pathophysiology of COVID-19, Biol Trace Elem Res
Yasui, Yasui, Suzuki, Saitou, Yamamoto et al., Analysis of the predictive factors for a critical illness of COVID-19 during treatmentrelationship between serum zinc level and critical illness of COVID-19, Int J Infect Dis
Zabetakis, Lordan, Norton, Tsoupras, COVID-19:The Inflammation Link and the Role of Nutrition in Potential Mitigation, Nutrients
Zhang, Taylor, Bennett, Saad, Rayman, Association between regional selenium status and reported outcome of COVID-19 cases in China, Am J Clin Nutr
Zhang, Taylor, Bennett, Saad, Rayman, Association between regional selenium status and reported outcome of COVID-19 cases in China, Am J Clin Nutr
anber
