Therapeutic effect of Vitamin A on severe COVID-19 patients
et al., EurAsian Journal of Biosciences, 14:7347-7350, Dec 2020
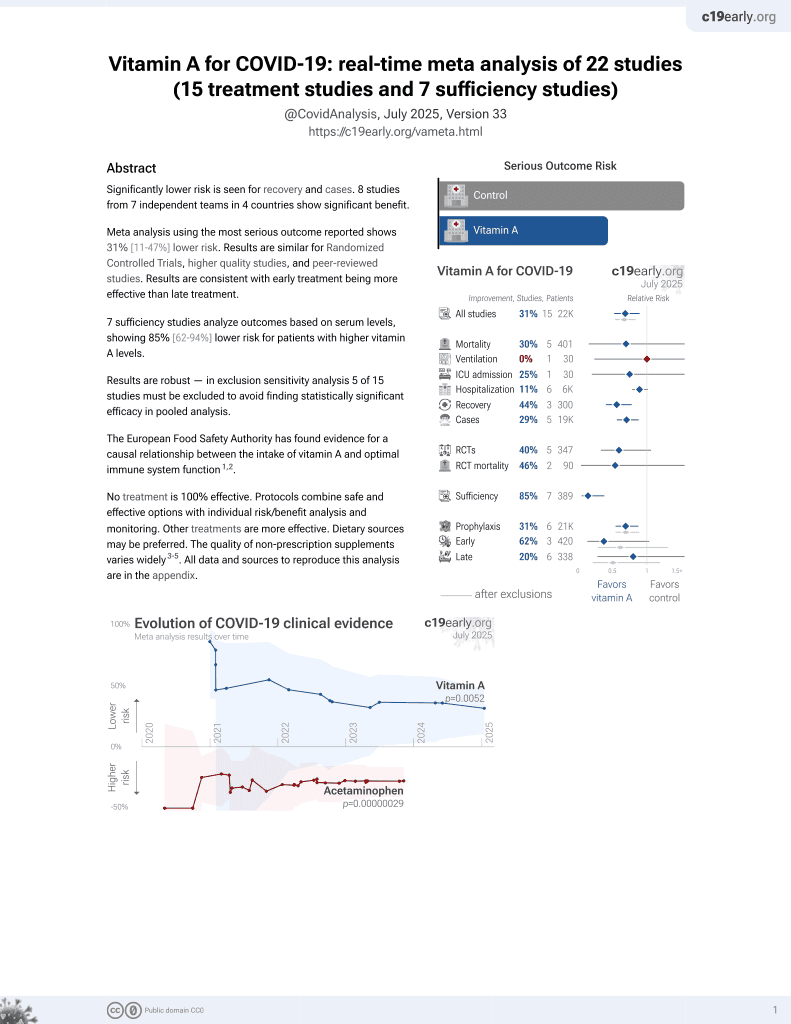
Vitamin A for COVID-19
49th treatment shown to reduce risk in
May 2023, now with p = 0.004 from 14 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
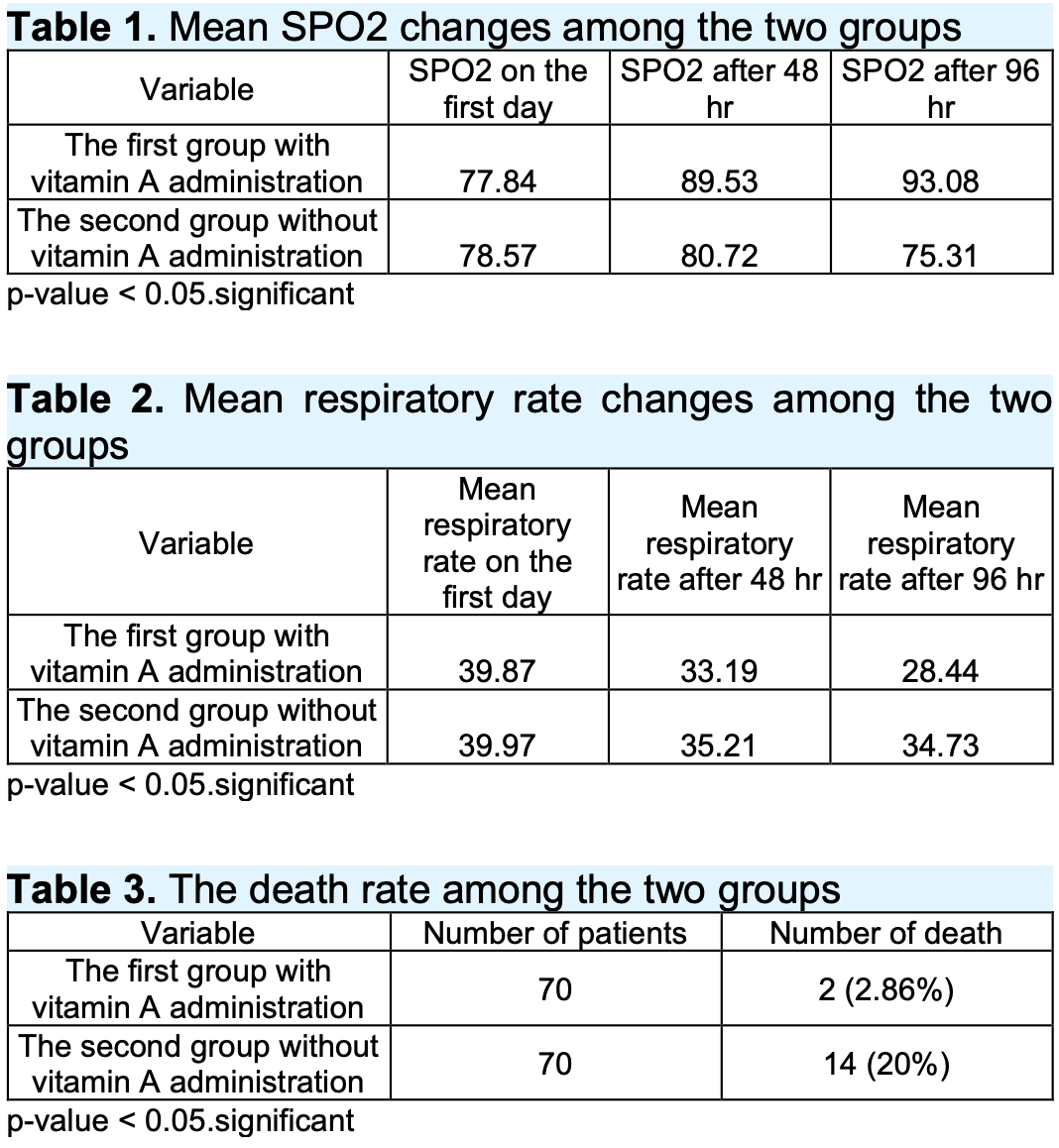
Retrospective 70 severe condition patients treated with vitamin A (200,000IU for two days), salbutamol, and budesonide, and 70 patients not treated with vitamin A, showing significantly lower mortality with the addition of vitamin A.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
minimal details of groups provided.
|
risk of death, 85.7% lower, RR 0.14, p = 0.002, treatment 2 of 70 (2.9%), control 14 of 70 (20.0%), NNT 5.8.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Al-Sumiadai et al., 31 Dec 2020, retrospective, Iraq, peer-reviewed, 3 authors.
Therapeutic effect of Vitamin A on severe COVID-19 patients
Objective: To find the effect of administration of vitamin A on patients with severe COVID-19. Material and Methods: A cross-sectional and retrospective study was done on two groups of patients with severe COVID-19 in isolation centers in Anbar governorate. The first group was patients with severe COVID-19 given two doses of vitamin A (200,000 I.U.) for two days from the first day of admission and three doses per day of salbutamol and budesonide nebulizers.. Data about the respiratory rate and SPO2 were collected after 48 and 96 hours from the administration in addition to the death rate among those patients. In a second group, the data was collected from files of patients with severe COVID-19 previously admitted to isolated centers and not receiving vitamin A. Results: A significant improvement in SPO2 and respiratory rate among severe COVID-19 patients given vitamin A as compared to those not given vitamin A. A lower death rate was recorded among severe COVID-19 patients who received vitamin A from those not received. Conclusions; A great benefit of the using of vitamin A in patients with severe COVID-19. Adding vitamin A to the regime COVID-19 therapy is recommended.
References
Alabama, Mm F, Huang, Galea, Calderon et al., Impact of Vitamin A and Carotenoids on the Risk of Tuberculosis Progression, Clin. Infect. Dis
Cabezas-Wallscheid, Buettner, Sommerkamp, Vitamin A-Retinoic Acid Signaling Regulates Hematopoietic Stem Cell Dormancy, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2017.04.018
Chen, Yang, Yan, Chen, Yu, Influence of vitamin A status on the antiviral immunity of children with hand, foot, and mouth disease, Clin. Nutr
Ertesvag, Engedal, Naderi, Blomhoff, Retinoic acid stimulates the cell cycle machinery in normal T cells: involvement of retinoic acid receptor-mediated IL-2 secretion, Journal of Immunology, doi:10.4049/Immunol.169.10.5555
Fisher, Heymann, Q&A: The novel coronavirus outbreak causing COVID-19, BMC Medicine, doi:10.1186/s12916-020-01533-w.PMC7047369
Fuchs, Green, Regulation of terminal differentiation of cultured human keratinocytes by vitamin A, Cell, doi:10.1016/0092-8674(81)90169-0
Gallegos, WHO Declares Public Health Emergency for Novel Coronavirus, Medscape Medical News
Ghazzay, Al-Ani, Therapeutic Effect of Vitamin A on COVID-19 Patients and Its Prophylactic Effect on Contacts, SRP, doi:10.31838/SRP.2021.1.33
Imai, District Clinician Manual. Hospital care for adolescents and adults
Johnson, Russell, Beta-Carotene
Liu, Fang, Deng, Liu, Wang et al., Clinical characteristics of novel coronavirus cases in tertiary hospitals in Hubei Province, Chinese Medical Journal
Makinde, Rotimi, Ikumawoyi, Adeyemo, Olayemi, Effect of vitamin A and vitamin C supplementation on oxidative stress in HIV and HIV-TB co-infection at Lagos University Teaching Hospital (LUTH) Nigeria, Afr. Health Sci
Mora, Iwata, Von Andrian, Vitamin effects on the immune system: vitamins A and D take center stage, Nature Reviews. Immunology, doi:10.1038/nri2378.PMC2906676
Mucida, Park, Kim, Turovskaya, Scott et al., Reciprocal TH17 and regulatory T cell differentiation mediated by retinoic acid, Science, doi:10.1126/science.1145697
Olson, Vitamin, Present knowledge in nutrition
Ramzy, Mcneil, Declares Global Emergency as Wuhan Coronavirus Spreads, The New York Times
Ross, Encyclopedia of Dietary Supplements
Ross, Vitamin A and Carotenoids
Ross, Vitamin A and retinoic acid in T cell-related immunity, The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, doi:10.3945/an.112.034637
Solomons, Vitamin A
Sun, Hall, Blank, Bouladoux, Oukka et al., Small intestine lamina propria dendritic cells promote de novo generation of Foxp3 T reg cells via retinoic acid, The Journal of Experimental Medicine, doi:10.1084/jem.20070602.PMC2118682
Wang, Du, Zhu, Cao, An et al., Comorbidities and multi-organ injuries in the treatment of COVID-19, Lancet, doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30558-4.PMC7270177
Who, The global prevalence of vitamin A deficiency in populations at risk 1995-2005