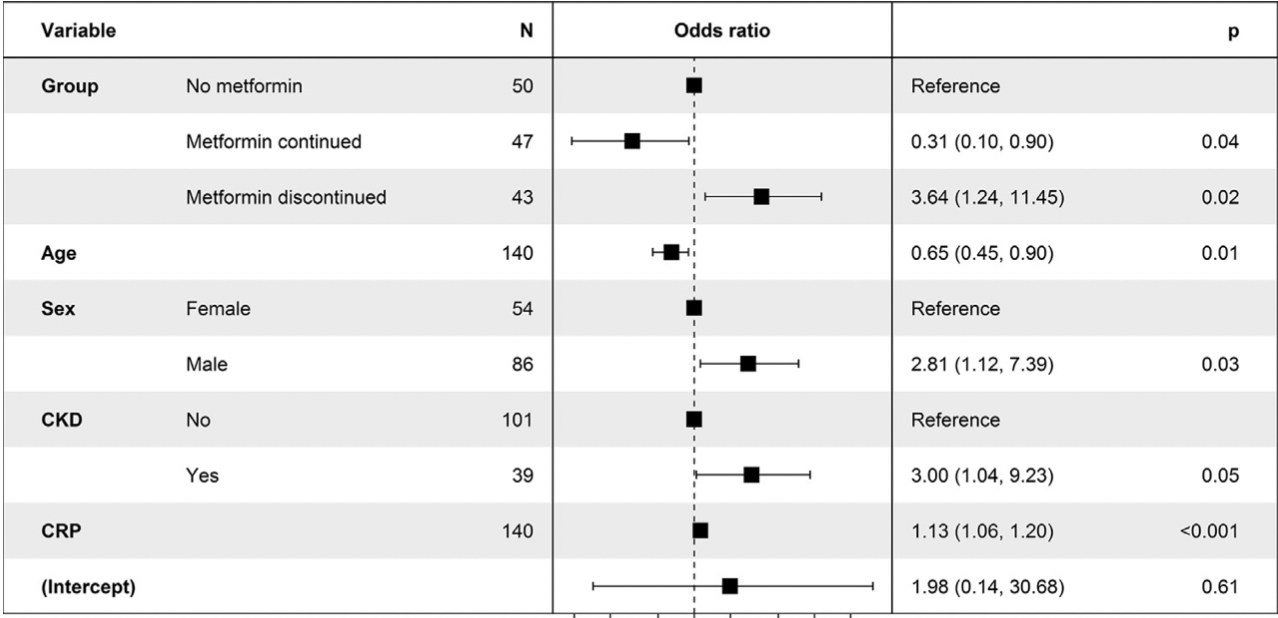
The association between metformin treatment and COVID-19 outcomes according to metformin continuation during hospitalisation
et al., Diabetes & Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.diabet.2021.101297, Nov 2021
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 140 diabetic patients in France, showing lower mortality for patients where metformin use was continued after hospitalization.
|
risk of death/ICU, 55.5% lower, RR 0.45, p = 0.04, treatment 9 of 47 (19.1%), control 22 of 50 (44.0%), NNT 4.0, adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, metformin continued, multivariable.
|
|
risk of death/ICU, 68.4% higher, RR 1.68, p = 0.02, treatment 34 of 43 (79.1%), control 22 of 50 (44.0%), adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, metformin discontinued, multivariable.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Al-Salameh et al., 30 Nov 2021, retrospective, France, peer-reviewed, 4 authors.
Abstract: Diabetes & Metabolism 47 (2021) 101297
Available online at
ScienceDirect
www.sciencedirect.com
Original article
The association between metformin treatment and COVID-19 outcomes
according to metformin continuation during hospitalisation
Abdallah Al-Salameha,b,*, Youssef Bennisc,d, Bertrand Carioue, Jean-Daniel Lalaua,b,*
a
Department of Endocrinology- Diabetes Mellitus and Nutrition, Amiens University Hospital, Amiens, France
PeriTox, UMR_I 01, University of Picardie Jules Verne, Amiens, France
Department of Clinical Pharmacology, Amiens University Hospital, Amiens, France
d
MP3CV Laboratory, UR UPJV 7517, University of Picardie Jules Verne, Amiens, France
e
^pital Guillaume et Rene Laennec, 44093
Departement d’Endocrinologie, Diabetologie et Nutrition, l'institut du thorax, Inserm, CNRS, UNIV Nantes, CHU Nantes, Ho
Nantes Cedex 01, France
b
c
A R T I C L E
I N F O
Article history:
Received 25 August 2021
Received in revised form 9 October 2021
Accepted 11 October 2021
Available online 23 October 2021
Keywords:
Coronavirus disease 2019
metformin
hospitalisation
Along with antidiabetic effects, metformin has anti-infective and
anti-inflammatory properties [1]. We [2] and others [3] have showed
that metformin treatment is associated with better outcomes in diabetic patients hospitalised for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
However, it is not known whether this beneficial association is due to
metformin treatment prior to hospital admission, its continuation
during the hospital stay, or both. Here, we assessed differences in
outcomes for patients who continued to take metformin in hospital
versus those who did not. We also studied the correlations between
blood levels of metformin and common inflammatory markers.
The study population and methods have been described elsewhere [4]. Briefly, we collected data on consecutive diabetic patients
admitted to Amiens University Hospital (Amiens, France) with PCRconfirmed COVID-19 between the start of the outbreak in France and
May 23rd, 2020 (n = 145). We recorded each patient’s baseline characteristics, medications, laboratory results, and COVID-19 outcomes.
Medical and prescription records were screened for metformin prescription / administration during the hospital stay. Plasma and erythrocyte metformin levels were analysed in a subset of the patients
(n = 25), according to a previously described method [5]. All the
patients were followed up until discharge or death.
Patients were categorised into “continuation of metformin
throughout the hospital stay”, “discontinuation of metformin on
tologie et Nutrition,
* Corresponding author at: Service d’Endocrinologie, Diabe
^ pital Nord, CHU Amiens-Picardie, Amiens, F-80054 cedex 01, France.
Ho
E-mail addresses: Al-Salameh.Abdallah@chu-amiens.fr (A. Al-Salameh), Lalau.JeanDaniel@chu-amiens.fr (J.-D. Lalau).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabet.2021.101297
1262-3636/© 2021 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
admission”, and “no metformin” groups. Between-group comparisons were performed with the Mann−Whitney−Wilcoxon test (for
two groups) or the Kruskal−Wallis test (for more than two groups)
for numerical variables and Fisher’s exact test for categorical variables. The association between these groups and the primary endpoint
(a composite of intensive care unit admission or death) was probed
in a logistic regression analysis. The secondary endpoints were the
components of the primary endpoint, the need for mechanical ventilation and a..
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabet.2021.101297",
"ISSN": [
"1262-3636"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.diabet.2021.101297",
"alternative-id": [
"S126236362100080X"
],
"article-number": "101297",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "The association between metformin treatment and COVID-19 outcomes according to metformin continuation during hospitalisation"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Diabetes & Metabolism"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabet.2021.101297"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2021 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7951-9926",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Al-Salameh",
"given": "Abdallah",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0186-4797",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bennis",
"given": "Youssef",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cariou",
"given": "Bertrand",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lalau",
"given": "Jean-Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Diabetes & Metabolism"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.com",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-25T17:23:05Z",
"timestamp": 1635182585000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-29T08:03:08Z",
"timestamp": 1638172988000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-03T01:31:51Z",
"timestamp": 1643851911270
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 2,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "1262-3636"
}
],
"issue": "6",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "6",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1635724800000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://www.elsevier.com/open-access/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "am",
"delay-in-days": 376,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-12T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1668211200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S126236362100080X?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S126236362100080X?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "101297",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308445",
"article-title": "Anti-inflammatory effects of metformin irrespective of diabetes status",
"author": "Cameron",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "652",
"journal-title": "Circ Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2021.101297_bib0001",
"volume": "119",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"article-title": "Metformin use is associated with a reduced risk of mortality in patients with diabetes hospitalised for COVID-19",
"author": "Lalau",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2021.101297_bib0002",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2021.587801",
"article-title": "Metformin and covid-19: focused review of mechanisms and current literature suggesting benefit",
"author": "Ibrahim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front Endocrinol",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2021.101297_bib0003",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/dmrr.3388",
"article-title": "Characteristics and outcomes of COVID-19 in hospitalized patients with and without diabetes",
"author": "Al-Salameh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e3388",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Res Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2021.101297_bib0004",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "[Microassay of plasma and erythrocyte metformin by high performance liquid chromatography]",
"author": "Lacroix",
"first-page": "98",
"journal-title": "Ann Biol Clin (Paris)",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2021.101297_bib0005",
"volume": "49",
"year": "1991"
},
{
"article-title": "Metformin as a cellular protector; a synoptic view of modern evidences",
"author": "Wiernsperger",
"first-page": "31",
"journal-title": "J Nephropharmacology",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2021.101297_bib0006",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.07.006",
"article-title": "Metformin and COVID-19: from cellular mechanisms to reduced mortality",
"author": "Scheen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "423",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.diabet.2021.101297_bib0007",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 7,
"references-count": 7,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Diabetes & Metabolism"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Endocrinology",
"General Medicine",
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism",
"Internal Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"The association between metformin treatment and COVID-19 outcomes according to metformin continuation during hospitalisation"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "47"
}
