Vitamin D levels and disease severity in COVID-19
et al., Medical Journal of İzmir Hospital, 26:3, Jul 2022
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
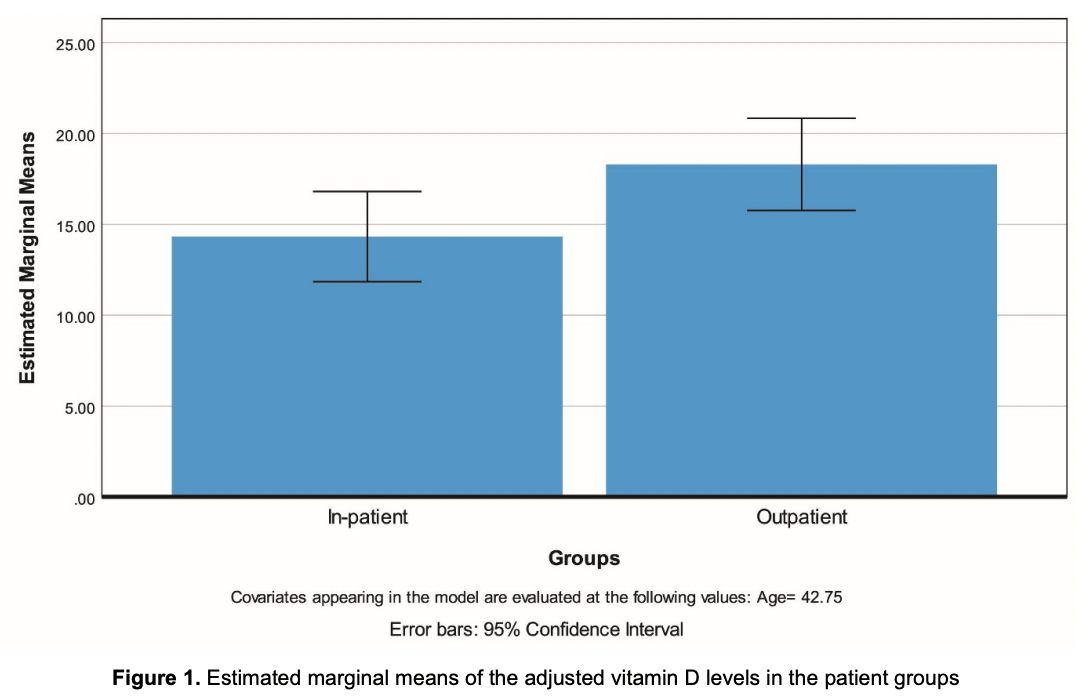
Retrospective 153 COVID-19 patients in Turkey, showing lower age-adjusted vitamin D levels in hospitalized patients vs. outpatients.
Alarslan et al., 31 Jul 2022, retrospective, Turkey, peer-reviewed, 5 authors.
VITAMIN D LEVELS AND DISEASE SEVERITY IN COVID-19 COVID-19'DA D VİTAMİNİ DURUMU VE HASTALIK ŞIDDETİ
Introduction: to evaluate the clinical and biochemical characteristics of patients with with regard to disease severity, and to assess vitamin D levels. were enrolled in this retrospective cohort study. Patients were divided into following three groups in terms of clinical severity: those managed as outpatients (n=75), those managed in wards (n=61) and those requiring intensive care unit (ICU) (n=17).
Material and methods: A total of 153 patients diagnosed with
Results: The levels of WBC, neutrophil, BUN, CRP, AST, ALT, D-dimer, ferritin, procalcitonin and BNP were significantly higher in the intensive care group compared to ward patients and outpatients. Albumin levels, hemoglobin values and lymphocyte percentages were lower in the severe disease group compared to the other two groups. Estimated marginal means of the adjusted vitamin D levels were 14.32 ± 1.26 ng/mL for the inpatients (ward and ICU) and 18.30±1.28 ng/mL for the outpatients (p=0.032).
Conclusion: Vitamin D deficiency may have been effective on the aggravation or prognosis of the disease, possibly with its anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, anti-oxidant and immunomodulatory effects. In this respect, the role of vitamin D supplementation on treatment should be examined in further studies by monitoring vitamin D levels in patients.
ÖZ Giriş: Covid-19'lu hastaların klinik ve biyokimyasal özelliklerini hastalık şiddetine göre değerlendirmek ve D vitamini düzeylerini değerlendirmek.
Corresponding Author Pinar ALARSLAN (MD) Department of Endocrine And Metabolic Diseases, Medicana International Istanbul Hospital, Beylikduzu Cd. No: 3, 34520 Beylikduzu/Istanbul, Turkey Phone: +905052714605 E-mail: pinaralarslan@hotmail.com, ORCID: 0000-0003-1790-0796 Pinar ALARSLAN (MD) ORCID: 0000-0003-1790-0796 Esin CELIKER (MD) ORCID: 0000-0001-7530-0647 Zeliha ARSLAN (Assoc. Prof.) ORCID: 0000-0002-1022-3406 Gokcen UNAL KOCABAS (MD) ORCID: 0000-0002-1849-3179 Oguzhan OZYURTKAN (Prof. Dr.) ORCID: 0000-0003-2754-2080S
References
Arnold, COVID-19-Does this disease kill due to ımbalance of the renin angiotensin system (ras) caused by genetic and gender differences in the response to viral ACE 2 Attacks?, Heart Lung Circ
Aygun, Vitamin D can prevent COVID-19 infection-induced multiple organ damage, Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol
Bahat, COVID-19 and the Renin Angiotensin System: Implications for the Older Adults, J Nutr Health Aging
Bao, Li, Zhang, Kang, Chen et al., Comparative analysis of laboratory indexes of severe and non-severe patients infected with COVID-19, Clin Chim Acta
Fiorino, Gallo, Zippi, Sabbatani, Manfredi et al., COVID-19 Perfect Storm (Part II): role of vitamins as therapy or preventive strategy in aged people, Preprints
Giménez, Inserra, Tajer, Mariani, Ferder et al., Lungs as target of COVID-19 infection: Protective common molecular mechanisms of vitamin D and melatonin as a new potential synergistic treatment, Life Sci
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths, Nutrients
Guessous, Dudler, Glatz, Theler, Zoller et al., Vitamin D levels and associated factors: a populationbased study in Switzerland, Swiss Med Wkly
Hanff, Harhay, Brown, Cohen, Mohareb, Is there an association between COVID-19 mortality and the renin-angiotensin system-a call for epidemiologic investigations, Clin Infect Dis
Hansdottir, Monick, Hinde, Lovan, Look et al., Respiratory epithelial cells convert inactive vitamin D to its active form: potential effects on host defense, J Immunol
Higashi, Shimada, Toyo, Oka, Advances in determination of vitamin D related compounds in biological samples using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry: a review, J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, Krüger, Herrler et al., SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor, Cell
Kara, Ekiz, Ricci, Kara, Chang et al., Scientific Strabismus' or Two Related Pandemics: COVID-19 & Vitamin D Deficiency, Br J Nutr
Kuba, Imai, Penninger, Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in lung diseases, Curr Opin Pharmacol
Laird, Rhodes, Kenny, Vitamin D and inflammation: potential implications for severity of COVID-19, Ir Med J
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Greenberg, Aloia et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ
Murdaca, Tonacci, Negrini, Greco, Borro et al., Emerging role of vitamin D in autoimmune diseases: an update on evidence and therapeutic implications, Autoimmun Rev
Peterson, Heffernan, Serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha concentrations are negatively correlated with serum 25 (OH) D concentrations in healthy women, J Inflamm
Shukla, Sharma, Gupta, Raizada, Vinayak, Current scenario of prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in ostensibly healthy Indian Population: A Hospital Based Retrospective Study, Indian J Clin Biochem
Taneri, Gomez-Ochoa, Llanaj, Raguindin, Rojas et al., Anemia and iron metabolism in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Eur J Epidemiol
Zhang, Hou, Li, Li, Laboratory findings of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Scand J Clin Lab Invest
