Effectiveness of Zinc and ROS on Testosterone Hormone Levels forRecovering COVID-19 Patients
et al., Biochemical and Cellular Archives, 22:1, Apr 2023
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000028 from 47 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
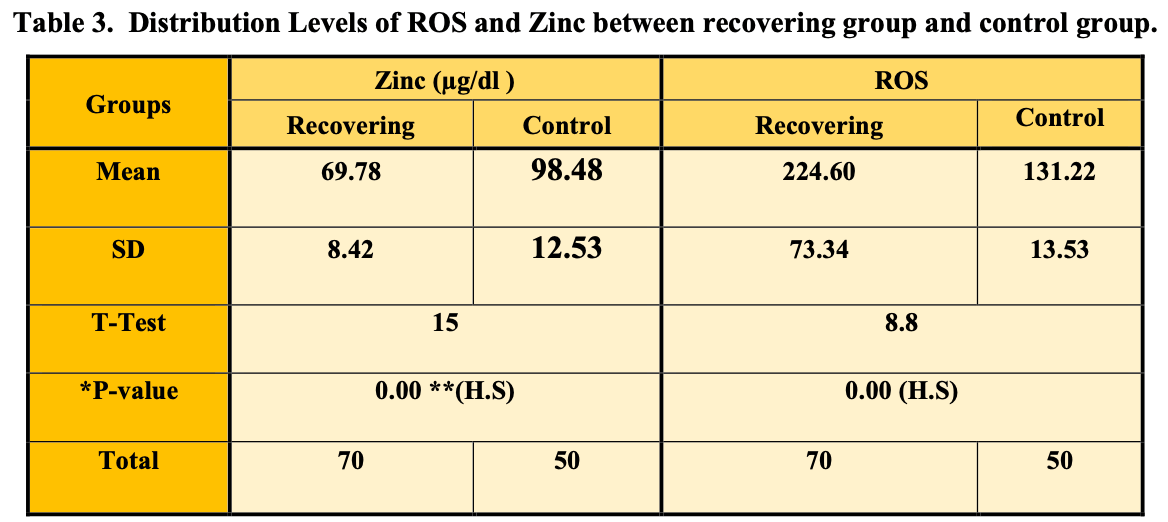
Analysis of 70 recovered COVID-19 patients and 50 controls in Iraq, showing significantly lower zinc levels in COVID-19 patients.
Abbas et al., 1 Apr 2023, Iraq, peer-reviewed, 3 authors.
Effectiveness of Zinc and ROS on Testosterone Hormone Levels for Recovering COVID-19 Patients
Background: COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019), cause severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) across all age groups, it's a positive-sense singlestranded RNA virus, and a member of the Betacoronavirus genus taxonomically (Jiang et al, 2020) . Given the importance roles of zinc in combating oxidative damage and viral infections, Zinc also has confirmed roles in both male and female reproduction. The possible depletion of zinc with the oxidative events of COVID-19 is especially relevant to the fertility of affected couples (Sethuram et al, 2021) . Aim of study: Is to determine the relation between Zinc value and oxidative stress level represented by ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species) and testosterone level among the recovered COVID-19 patients in reproductive age.
References
Abobaker, Raba, Does COVID-19 affect male fertility, World J Urol
Aboelnaga, Abdelrazek, Abdullah, El Shaer, Late Impact of COVID-19 Pneumonia on Testosterone Levels in Recovered, Post-Hospitalized Male Patients, Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism
Carrillo, Izquierdo-Useros, Ávila-Nieto, Pradenas, Clotet et al., Humoral immune responses and neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2; implications in pathogenesis and protective immunity, Biochemical and biophysical research communications
Choe, Kim, Kang, Suh, Kang et al., Antibody Responses One Year after Mild SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Journal of Korean medical science
Delgado-Roche, Mesta, Oxidative stress as key player in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) infection, Archives of medical research
Douglas, O'bryan, Hedger, Lee, Yarski et al., The novel angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) homolog, ACE2, is selectively expressed by adult Leydig cells of the testis, Endocrinology
Elham, Azam, Azam, Mostafa, Nasrin et al., Serum vitamin D, calcium, and zinc levels in patients with COVID-19, Clinical Nutrition ESPEN
Jiang, Xia, Ying, Lu, A novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) causing pneumonia-associated respiratory syndrome, Cellular & molecular immunology
Kadihasanoglu, Aktas, Yardimci, Aral, Kadioglu, SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia affects male reproductive hormone levels: A prospective, cohort study, The Journal of Sexual Medicine
Lü, Lin, Yao, Chen, Chemical and molecular mechanisms of antioxidants: experimental approaches and model systems, Journal of cellular and molecular medicine
Marie-Pierrette, COVID-19 infection and oxidative stress: an under-explored approach for prevention and treatment?, The Pan African Medical Journal
Molnar, Gair, Chapter 23.2. Adaptive Immune Response
Nag, Chaudhry, Mishra, Rai, Gupta, A prospective study on rapidly declining SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies within one to three months of testing IgG positive: can it lead to potential reinfections?, Cureus
Nassar, Leslie, Physiology, testosterone
Okçelik, COVID-19 pneumonia causes lower testosterone levels, Andrologia
Prasad, Zinc: an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent: role of zinc in degenerative disorders of aging, Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology
Rahman, Islam, Rahman, Alamin, Neurobiochemical cross-talk between COVID-19 and Alzheimer's disease, Molecular Neurobiology
Salonia, Pontillo, Capogrosso, Gregori, Tassara et al., Severely low testosterone in males with COVID-19: A case-control study
Sethuram, Bai, Abu-Soud, Potential role of zinc in the COVID-19 disease process and its probable impact on reproduction, Reproductive Sciences
Shen, Xiao, Aierken, Yue, Wu et al., The ACE2 expression in Sertoli cells and germ cells may cause male reproductive disorder after SARS-CoV-2 infection, Journal of cellular and molecular medicine
Smith, Walker, The regulation of spermatogenesis by androgens, Seminars in cell & developmental biology
Velthuis, Van Den Worm, Sims, Baric, Snijder et al., Zn2+ inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture, PLoS pathogens
Wang, Xu, scRNA-seq profiling of human testes reveals the presence of the ACE2 receptor, a target for SARS-CoV-2 infection in spermatogonia, Leydig and Sertoli cells, Cells
Wessels, Rolles, Rink, The potential impact of zinc supplementation on COVID-19 pathogenesis, Frontiers in immunology
Xu, Wang, Feng, Yu, Chen et al., Effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection on male sex-related hormones in recovering patients, Andrology
Yang, Chen, Huang, Zhong, Su et al., Pathological findings in the testes of COVID-19 patients: clinical implications, European urology focus
Zhang, Rong, Li, Flaviviridae viruses and oxidative stress: implications for viral pathogenesis. Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity
