Clinical safety and pharmacokinetics of a novel oral niclosamide formulation compared with marketed niclosamide chewing tablets in healthy volunteers: a three-part randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.05.06.24306928, NCT04644705, May 2024
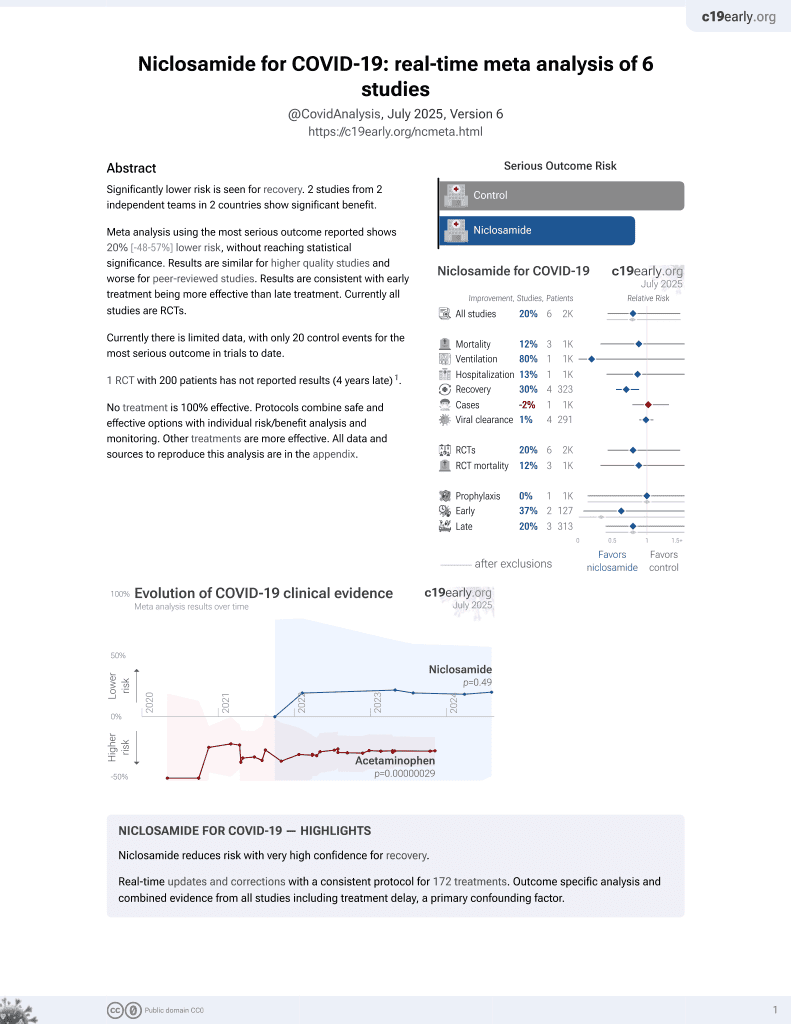
56th treatment shown to reduce risk in
August 2025, now with p = 0.0069 from 7 studies.
Lower risk for recovery.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Phase 1 trial of 28 healthy volunteers showing an investigational niclosamide solution was reasonably well-tolerated up to 1,600mg for 7 days, with no severe adverse events. The most common adverse events were mild to moderate gastrointestinal reactions. Bioavailability did not improve compared to niclosamide tablets. A positive food effect of up to 2-fold higher exposure was observed after a high-fat meal. Very high variability in pharmacokinetic parameters was seen.
Walther et al., 6 May 2024, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, Germany, preprint, 10 authors, study period 17 November, 2020 - 3 May, 2021, trial NCT04644705 (history).
Contact: robert.schultz-heienbrok@charite-research.org.
Clinical safety and pharmacokinetics of a novel oral niclosamide formulation compared with marketed niclosamide chewing tablets in healthy volunteers: a three-part randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
doi:10.1101/2024.05.06.24306928
Aim Niclosamide is an established anthelmintic substance and a promising candidate for treating cancer, viral infections, and other diseases. However, its solubility in aqueous media is low, and the systemic bioavailability of the commercially available chewing tablet is poor, limiting the use of niclosamide for systemic treatment. A liquid oral formulation using polyethylene glycol 400 was developed and investigated in healthy volunteers to assess safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics in comparison to the marketed tablet. (ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT04644705)
Methods The study consisted of three parts: Part A was a double-blind placebo-controlled single ascending dose trial in three dose groups (200, 600, and 1600 mg) with four participants receiving either the investigational niclosamide formulation or placebo (3:1) under fasted and/or fed conditions. Part B was a crossover study comparing 1600 mg investigational niclosamide solution with the marketed 2000 mg chewing tablet in four healthy volunteers. Part C was a double-blind placebo-controlled multiple-dose trial comparing 1200 mg and 1600 mg (verum: placebo 4:2) in two dose groups with six subjects each, who received daily doses for seven days.
Results . .
Supporting information
S1
References
Amaravadi, Kimmelman, Debnath, Targeting Autophagy in Cancer: Recent Advances and Future Directions, Cancer Discovery, doi:10.1158/2159-8290.cd-19-0292
Arend, Joshi, Samant, Li, Conner et al., Inhibition of wnt/β-catenin pathway by niclosamide: A therapeutic target for ovarian cancer, Gynecologic Oncology, doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2014.04.005
Backer, Sjöbring, Sonne, Weiss, Hostrup et al., A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 1 trial of inhaled and intranasal niclosamide: A broad spectrum antiviral candidate for treatment of COVID-19, The Lancet Regional Health -Europe, doi:10.1016/j.lanepe.2021.100084
Burock, Daum, Keilholz, Neumann, Walther et al., Phase II trial to investigate the safety and efficacy of orally applied niclosamide in patients with metachronous or sychronous metastases of a colorectal cancer progressing after therapy: the NIKOLO trial, BMC Cancer, doi:10.1186/s12885-018-4197-9
Chen, Mook, Premont, Wang, Niclosamide: Beyond an antihelminthic drug, Cellular Signalling, doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2017.04.001
De Almeida, Da Silva, Rodrigues, Oliveira, Ishimoto et al., Identification of immunomodulatory drugs that inhibit multiple inflammasomes and impair SARS-COV-2 infection, Science Advances, doi:10.1126/sciadv.abo5400
Gassen, Niemeyer, Muth, Corman, Martinelli et al., SKP2 attenuates autophagy through Beclin1-ubiquitination and its inhibition reduces MERS-Coronavirus infection, Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/s41467-019-13659-4
Gassen, Papies, Bajaj, Emanuel, Dethloff et al., SARS-COV-2-mediated dysregulation of metabolism and autophagy uncovers host-targeting antivirals, Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/s41467-021-24007-w
Hammer, Ana, Schiller, Fordtran, Studies of osmotic diarrhoea induced in normal subjects by ingestion of polyethylene glycol and lactulose, Journal of Clinical Investigation, doi:10.1172/jci114267
Jara, Warnken, Sahakijpijarn, Thakkar, Kulkarni et al., Oral delivery of niclosamide as an amorphous solid dispersion that generates amorphous nanoparticles during dissolution, Pharmaceutics, doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics14122568
Jeon, Ko, Lee, Choi, Byun et al., Identification of Antiviral Drug Candidates against SARS-CoV-2 from FDA-Approved Drugs, Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, doi:10.1128/aac.00819-20
Kahn, Can we safely target the WNT pathway?, Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, doi:10.1038/nrd4233
Kortüm, Radhakrishnan, Zincke, Sachse, Burock et al., Combinatorial treatment with statins and niclosamide prevents CRC dissemination by unhinging the MACC1β-catenin-S100A4 axis of metastasis, Oncogene, doi:10.1038/s41388-022-02407-6
Liu, Xiao, Niu, Li, Zhang, Wnt/β-catenin signalling: function, biological mechanisms, and therapeutic opportunities, Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00762-6
Ma, Yang, Dai, Li, Lin et al., Polyethylene Glycol 400 (PEG400) affects the systemic exposure of oral drugs based on multiple mechanisms: Taking berberine as an example, RSC Advances, doi:10.1039/c6ra26284h
Masini, Bugliani, Lupi, Guerra, Boggi et al., Autophagy in human type 2 diabetes pancreatic beta cells, Diabetologia, doi:10.1007/s00125-009-1347-2
Mcilwain, Grusdat, Pozdeev, Xu, Shinde et al., T-cell STAT3 is required for the maintenance of humoral immunity to LCMV, European Journal of Immunology, doi:10.1002/eji.201445060
Menu, Vince, The NLRP3 inflammasome in health and disease: the good, the bad and the ugly, Clinical and Experimental Immunology, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.2011.04440.x
Miner, Labitzke, Liu, Wang, Henckels et al., Drug repurposing: The Anthelmintics Niclosamide and nitazoxanide are potent TMEM16A antagonists that fully Bronchodilate Airways, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2019.00051
Parikh, Liu, Wu, Evans, Dall'era et al., Phase Ib trial of reformulated niclosamide with abiraterone/prednisone in men with castration-resistant prostate cancer, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-85969-x
Schiattarella, Hill, Therapeutic targeting of autophagy in cardiovascular disease, Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology, doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2015.11.019
Schulze, Waddington, Ell, Parsons, Coffin et al., Concentrationdependent effects of polyethylene glycol 400 on gastrointestinal transit and drug absorption, Pharmaceutical Research, doi:10.1023/b:pham.0000008046.64409.bd
Schweizer, Haugk, Mckiernan, Gulati, Cheng et al., A phase I study of niclosamide in combination with enzalutamide in men with castration-resistant prostate cancer, PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0198389
Sennoune, Nandagopal, Ramachandran, Mathew, Sivaprakasam et al., Potent inhibition of macropinocytosis by niclosamide in cancer cells: A novel mechanism for the anticancer efficacy for the antihelminthic, Cancers, doi:10.3390/cancers15030759
Singh, Weiss, Goodman, Fisk, Kulkarni et al., Niclosamide-A promising treatment for COVID-19, British Journal of Pharmacology, doi:10.1111/bph.15843
Sutar, Nabeela, Singh, Alqarihi, Solis et al., Niclosamide-loaded nanoparticles disrupt Candida biofilms and protect mice from mucosal candidiasis, PLOS Biology, doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.3001762
Weiss, Bischof, Landersdorfer, Nguyen, Davies et al., Single-dose pharmacokinetics and lung function of nebulized niclosamide ethanolamine in Sheep, Pharmaceutical Research, doi:10.1007/s11095-023-03559-0
Wu, Wu, Wang, Chang, Shan et al., Secretory autophagy promotes RAB37-mediated insulin secretion under glucose stimulation both in vitro and in vivo, Autophagy, doi:10.1080/15548627.2022.2123098
Wu, Zhang, Tong, Yan, Cho et al., Repurposing of niclosamide as a STAT3 inhibitor to enhance the anticancer effect of chemotherapeutic drugs in treating colorectal cancer, Life Sciences, doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118522
Zhang, Ran, Shang, Zhang, Wang et al., Niclosamide as a repurposing drug against gram-positive bacterial infections, Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, doi:10.1093/jac/dkac319
Zhang, Wang, Targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in cancer, Journal of Hematology & Oncology, doi:10.1186/s13045-020-00990-3
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2024.05.06.24306928",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/2024.05.06.24306928",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec><jats:title>Aim</jats:title><jats:p>Niclosamide is an established anthelmintic substance and a promising candidate for treating cancer, viral infections, and other diseases. However, its solubility in aqueous media is low, and the systemic bioavailability of the commercially available chewing tablet is poor, limiting the use of niclosamide for systemic treatment. A liquid oral formulation using polyethylene glycol 400 was developed and investigated in healthy volunteers to assess safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics in comparison to the marketed tablet. (ClinicalTrials.gov:<jats:ext-link xmlns:xlink=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" ext-link-type=\"clintrialgov\" xlink:href=\"NCT04644705\">NCT04644705</jats:ext-link>)</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>The study consisted of three parts: Part A was a double-blind placebo-controlled single ascending dose trial in three dose groups (200, 600, and 1600 mg) with four participants receiving either the investigational niclosamide formulation or placebo (3:1) under fasted and/or fed conditions. Part B was a crossover study comparing 1600 mg investigational niclosamide solution with the marketed 2000 mg chewing tablet in four healthy volunteers. Part C was a double-blind placebo-controlled multiple-dose trial comparing 1200 mg and 1600 mg (verum: placebo 4:2) in two dose groups with six subjects each, who received daily doses for seven days.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>No serious or severe adverse events occurred. The most frequent adverse events were mild to moderate gastrointestinal reactions. There was also no apparent dependence between drug exposure levels (AUC, Cmax) and the severity and incidence of adverse events detectable. A relevant food effect was observed with a mean AUC<jats:sub>last</jats:sub>about 2-fold higher in fed condition compared to fasted condition. In Part B, dose-normalized C<jats:sub>max</jats:sub>and AUC<jats:sub>last</jats:sub>were similar for niclosamide solution and tablet. Absorption of niclosamide solution was highly variable. Some individuals showed high absorption (C<jats:sub>max</jats:sub>>2µg/ml) whereas others did absorb only marginally. Importantly, there was no dose linearity in the range of 200 mg – 1600 mg. No signs of relevant systemic drug accumulation after multiple administrations were observed.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>Overall safety and tolerability observed in healthy subjects were benign. This is also true for individual “high absorbers” (C<jats:sub>max</jats:sub>>2µg/ml), encouraging further research into niclosamide as a potential therapeutic agent. Galenic optimization, however, will remain challenging as evident from the observed exposure variability and non-linear PK. Non-linearity, if confirmed by additional data, might make niclosamide more suitable for multi-dose rather than high single dose regimens. The observed food effect should also be considered when further investigating systemic niclosamide exposures.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
6
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2102-5835",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Walther",
"given": "Niklas",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schultz-Heienbrok",
"given": "Robert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Staß",
"given": "Heino",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Corman",
"given": "Victor M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gassen",
"given": "Nils C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Müller",
"given": "Marcel A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Drosten",
"given": "Christian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Witzenrath",
"given": "Martin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Hweeling",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Posch",
"given": "Maximilian G.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-07T21:26:12Z",
"timestamp": 1715117172000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-10T18:15:15Z",
"timestamp": 1715364915000
},
"group-title": "Pharmacology and Therapeutics",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-11T00:25:19Z",
"timestamp": 1715387119438
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "medRxiv"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
6
]
]
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1101/2024.05.06.24306928",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "246",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
6
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.1101",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bph.15843",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024051011150454000_2024.05.06.24306928v1.1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cellsig.2017.04.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024051011150454000_2024.05.06.24306928v1.2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12885-018-4197-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024051011150454000_2024.05.06.24306928v1.3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41388-022-02407-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024051011150454000_2024.05.06.24306928v1.4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/15548627.2022.2123098",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024051011150454000_2024.05.06.24306928v1.5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cancers15030759",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024051011150454000_2024.05.06.24306928v1.6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/dkac319",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024051011150454000_2024.05.06.24306928v1.7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-24007-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024051011150454000_2024.05.06.24306928v1.8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/aac.00819-20",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024051011150454000_2024.05.06.24306928v1.9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pbio.3001762",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024051011150454000_2024.05.06.24306928v1.10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lanepe.2021.100084",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024051011150454000_2024.05.06.24306928v1.11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-85969-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024051011150454000_2024.05.06.24306928v1.12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11095-023-03559-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024051011150454000_2024.05.06.24306928v1.13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1023/b:pham.0000008046.64409.bd",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024051011150454000_2024.05.06.24306928v1.14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pharmaceutics14122568",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024051011150454000_2024.05.06.24306928v1.15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/c6ra26284h",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024051011150454000_2024.05.06.24306928v1.16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI114267",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024051011150454000_2024.05.06.24306928v1.17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0198389",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024051011150454000_2024.05.06.24306928v1.18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciadv.abo5400",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024051011150454000_2024.05.06.24306928v1.19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118522",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024051011150454000_2024.05.06.24306928v1.20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-019-13659-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024051011150454000_2024.05.06.24306928v1.21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2019.00051",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024051011150454000_2024.05.06.24306928v1.22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ygyno.2014.04.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024051011150454000_2024.05.06.24306928v1.23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2249.2011.04440.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024051011150454000_2024.05.06.24306928v1.24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/eji.201445060",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024051011150454000_2024.05.06.24306928v1.25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-0292",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024051011150454000_2024.05.06.24306928v1.26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00125-009-1347-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024051011150454000_2024.05.06.24306928v1.27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.yjmcc.2015.11.019",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024051011150454000_2024.05.06.24306928v1.28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00762-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024051011150454000_2024.05.06.24306928v1.29"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13045-020-00990-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024051011150454000_2024.05.06.24306928v1.30"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrd4233",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024051011150454000_2024.05.06.24306928v1.31"
}
],
"reference-count": 31,
"references-count": 31,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://medrxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2024.05.06.24306928"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Clinical safety and pharmacokinetics of a novel oral niclosamide formulation compared with marketed niclosamide chewing tablets in healthy volunteers: a three-part randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial",
"type": "posted-content"
}