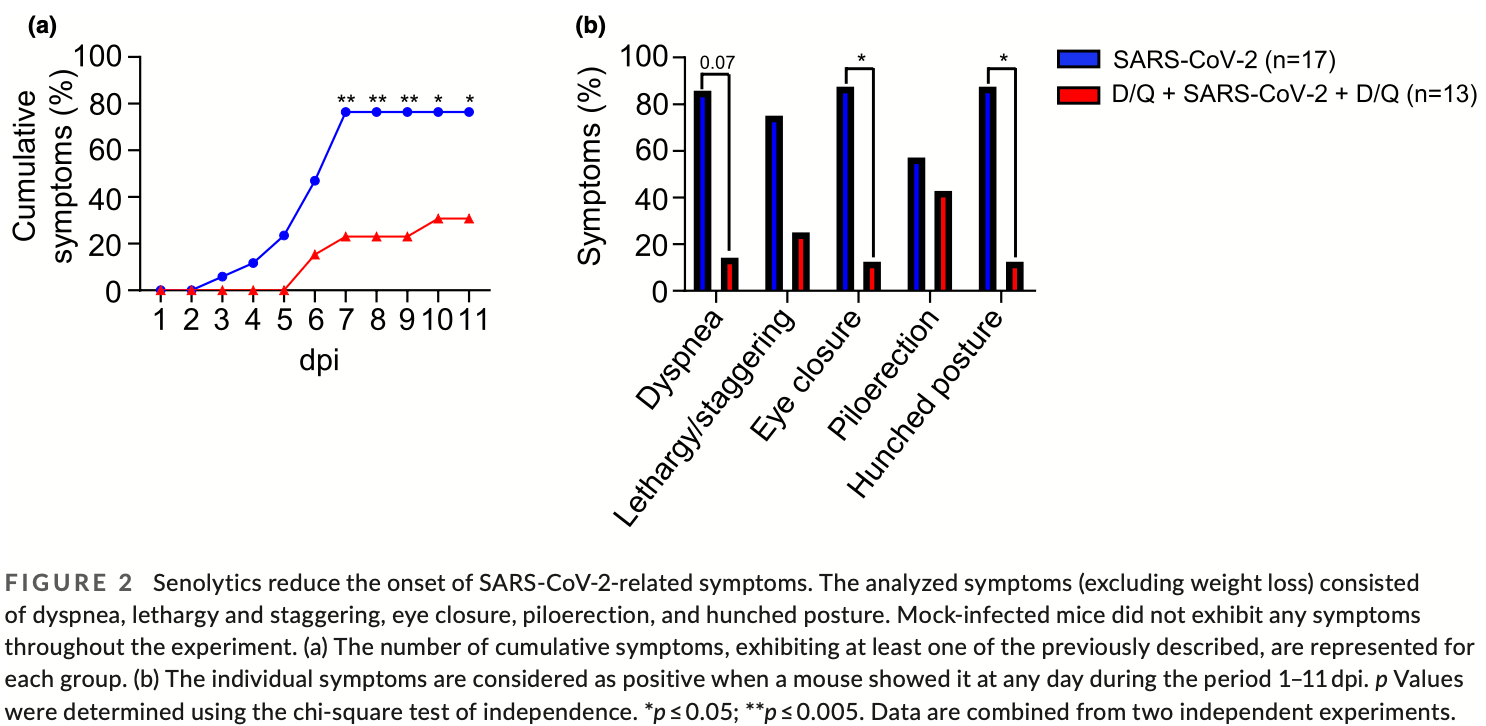
Treatment with the senolytics dasatinib/quercetin reduces SARS-CoV-2 related mortality in mice
et al., Aging Cell, doi:10.1111/acel.13771, Jan 2023
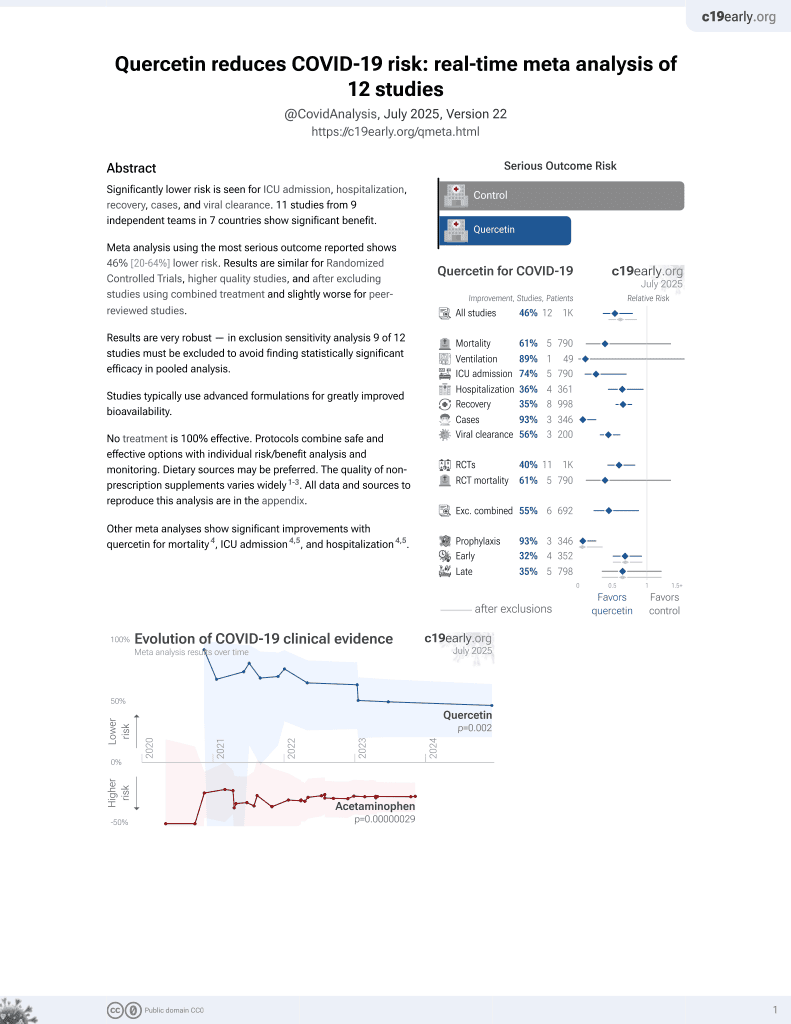
Quercetin for COVID-19
27th treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2021, now with p = 0.002 from 12 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
K18-hACE2 mouse study showing reduced COVID-19 severity with quercetin and dasatinib, for both prophylaxis and early treatment.
Bioavailability. Quercetin has low bioavailability and studies typically use advanced formulations to improve bioavailability which may be required to reach therapeutic concentrations.
Pastor-Fernández et al., 26 Jan 2023, Spain, peer-reviewed, survey, 16 authors.
Contact: cvonkobbe@cbm.csic.es.
Treatment with the senolytics dasatinib/quercetin reduces SARS‐CoV ‐2‐related mortality in mice
Aging Cell, doi:10.1111/acel.13771
The enormous societal impact of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has been particularly harsh for some social groups, such as the elderly. Recently, it has been suggested that senescent cells could play a central role in pathogenesis by exacerbating the proinflammatory immune response against SARS-CoV-2. Therefore, the selective clearance of senescent cells by senolytic drugs may be useful as a therapy to ameliorate the symptoms of COVID-19 in some cases. Using the established COVID-19 murine model K18-hACE2, we demonstrated that a combination of the senolytics dasatinib and quercetin (D/Q) significantly reduced SARS-CoV-2-related mortality, delayed its onset, and reduced the number of other clinical symptoms. The increase in senescent markers that we detected in the lungs in response to SARS-CoV-2 may be related to the post-COVID-19 sequelae described to date. These results place senescent cells as central targets for the treatment of COVID-19, and make D/Q a new and promising therapeutic tool.
| Histological processing The samples fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin solution (Panreac Química, SLU) were mounted in synthetic paraffin with a melting point of 56 °C (Casa Álvarez Material Científico), using a Citadel 2000 Tissue Processor (Thermo Fisher Scientific), with an automatic program applying alcohols of increasing concentration and xylene substitute (Citrus Clearing Solvent, Thermo Fisher Scientific). Blocks were made in a cold plate block forming unit (Histo Star Embedding Workstation, Thermo Fisher Scientific) . Histological sections were obtained with a rotary microtome (Finesse Me+ Microtome, Thermo Fisher Scientific) at 3-4 μm thickness. A Gemini AS Automated Slide Stainer (Thermo Fisher Scientific) was used to stain the sections with hematoxylin-eosin and finally mounted using a CTM6 Coverslipper (Thermo Fisher Scientific), with a xylene-based mounting medium (ClearVue Mountant, Thermo Fisher Scientific).
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Tissue samples were cut at 3 μm thickness, mounted on superfrost®plus slides and dried overnight. For IHC, an automated immunostaining platform was used (Autostainer Link, Dako or Ventana Discovery ULTRA; Roche). Antigen retrieval was performed with CC1 32 min, only for p21 and High pH buffer, Dako, Agilent (p19 and SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid); endogenous peroxidase was blocked (hydrogen peroxide at 3%) and slides were then incubated with the appropriate primary antibody as detailed: rat monoclonal anti-p21 CIP1 (291H;..
References
Blagosklonny, From causes of aging to death from COVID-19, Aging
Boumaza, Gay, Mezouar, Bestion, Diallo et al., Monocytes and macrophages, targets of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2: The clue for coronavirus disease 2019 immunoparalysis, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiab044
Camell, Yousefzadeh, Zhu, Prata, Huggins et al., Senolytics reduce coronavirus-related mortality in old mice, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abe4832
Cayetano Von Kobbe, None
Chen, Lau, Lamirande, Paddock, Bartlett et al., Cellular immune responses to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) infection in senescent BALB/c mice: CD4 + T cells are important in control of SARS-CoV infection, Journal of Virology, doi:10.1128/jvi.01281-09
Daamen, Bachali, Owen, Kingsmore, Hubbard et al., Comprehensive transcriptomic analysis of COVID-19 blood, lung, and airway, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-86002-x
Donlan, Sutherland, Marie, Preissner, Bradley et al., IL-13 is a driver of COVID-19 severity, JCI Insight, doi:10.1172/jci.insight.150107
Evangelou, Veroutis, Paschalaki, Foukas, Lagopati et al., Pulmonary infection by SARS-CoV-2 induces senescence accompanied by an inflammatory phenotype in severe COVID-19: Possible implications for viral mutagenesis, The European Respiratory Journal, doi:10.1183/13993003.02951-2021
Fe R E N C E S Al-Aly, Xie, Bowe, High-dimensional characterization of post-acute sequalae of COVID-19, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03553-9
Golden, Cline, Zeng, Garrison, Carey et al., Human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 transgenic mice infected with SARS-CoV-2 develop severe and fatal respiratory disease, JCI Insight, doi:10.1172/jci.insight.142032
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
Idda, Mcclusky, Lodde, Munk, Abdelmohsen et al., Survey of senescent cell markers with age in human tissues, Aging, doi:10.18632/aging.102903
Islam, Chamberlain, Mui, Little, Elevated Interleukin-10 levels in COVID-19: Potentiation of proinflammatory responses or impaired anti-inflammatory action?, Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.677008
Kirkland, Tchkonia, Senolytic drugs: From discovery to translation (review), Journal of Internal Medicine, doi:10.1111/joim.13141
Lee, Peng, Yang, Liou, Liao et al., C-C chemokine Ligand-5 is critical for facilitating macrophage infiltration in the early phase of liver ischemia/reperfusion injury, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-017-03956-7
Lee, Yu, Trimpert, Benthani, Mairhofer et al., Virus-induced senescence is a driver and therapeutic target in COVID-19, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03995-1
Li, Jiang, Li, Lin, Wang et al., Clinical and pathological investigation of patients with severe COVID-19, JCI Insight, doi:10.1172/jci.insight.138070
Ling, Chen, Lui, Wong, Wong et al., Longitudinal cytokine profile in patients with mild to critical COVID-19, Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.763292
Maghazachi, Al-Aoukaty, Schall, C-C chemokines induce the chemotaxis of NK and IL-2-activated NK cells: Role for G proteins, Journal of Immunology
Majumdar, Murphy, Chemokine regulation during epidemic coronavirus infection, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.600369
Malavolta, Giacconi, Brunetti, Provinciali, Maggi, Exploring the relevance of senotherapeutics for the current SARS-CoV-2 emergency and similar future global health threats, Cell, doi:10.3390/cells9040909
Mccormick, Heller, Commentary: IL-4 and IL-13 receptors and signaling, Cytokine, doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2015.05.023
Mccray, Jr, Pewe, Wohlford-Lenane, Hickey et al., Lethal infection of K18-hACE2 mice infected with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, Journal of Virology, doi:10.1128/JVI.02012-06
Mchugh, Gil, Senescence and aging: Causes, consequences, and therapeutic avenues, Journal of Cell Biology, doi:10.1083/jcb.201708092
Mohiuddin, Kasahara, The emerging role of cellular senescence in complications of COVID-19, Cancer Treatment and Research Communications, doi:10.1016/j.ctarc.2021.100399
Nehme, Borghesan, Mackedenski, Bird, Demaria, Cellular senescence as a potential mediator of COVID-19 severity in the elderly, Aging Cell, doi:10.1111/acel.13237
Oladunni, Park, Pino, Gonzalez, Akhter et al., Lethality of SARS-CoV-2 infection in K18 human angiotensinconverting enzyme 2 transgenic mice, Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19891-7
Ovadya, Krizhanovsky, Li, Karamanis, Ognibene et al., Severe obesity, increasing age and male sex are independently associated with worse in-hospital outcomes, and higher in-hospital mortality, in a cohort of patients with COVID-19 in the Bronx, The Journal of Clinical Investigation, doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154262
Palmer, Xu, Zhu, Pirtskhalava, Weivoda et al., Targeting senescent cells alleviates obesityinduced metabolic dysfunction, Aging Cell, doi:10.1111/acel.12950
Rathnasinghe, Strohmeier, Amanat, Gillespie, Krammer et al., Comparison of transgenic and adenovirus hACE2 mouse models for SARS-CoV-2 infection, Emerging Microbes & Infections, doi:10.1080/22221751.2020.1838955
Ruan, Yang, Wang, Jiang, Song, Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China, Intensive Care Medicine, doi:10.1007/s00134-020-05991-x
Schafer, White, Iijima, Haak, Ligresti et al., Cellular senescence mediates fibrotic pulmonary disease, Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/ncomms14532
Schall, Bacon, Toy, Goeddel, Selective attraction of monocytes and T lymphocytes of the memory phenotype by cytokine RANTES, Nature, doi:10.1038/347669a0
Sierra-Ramirez, López-Aceituno, Costa-Machado, Plaza, Barradas et al., Transient metabolic improvement in obese mice treated with navitoclax or dasatinib/ quercetin, Aging, doi:10.18632/aging.103607
Tsuji, Minami, Hashimoto, Konishi, Suzuki et al., SARS-CoV-2 infection triggers paracrine senescence and leads to a sustained senescence-associated inflammatory response, Nature Aging, doi:10.1038/s43587-022-00170-7
Vaz De Paula, De Azevedo, Nagashima, Martins, Malaquias et al., SARS-CoV-2 infection of human ACE2-transgenic mice causes severe lung inflammation and impaired function, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41590-020-0778-2
Yang, Shen, Li, Yuan, Wei et al., Plasma IP-10 and MCP-3 levels are highly associated with disease severity and predict the progression of COVID-19, The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2020.04.027
Ye, Wang, Mao, The pathogenesis and treatment of the 'cytokine storm' in COVID-19, The Journal of Infection, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2020.03.037
Yinda, Port, Bushmaker, Offei Owusu, Purushotham et al., K18-hACE2 mice develop respiratory disease resembling severe COVID-19, PLoS Pathogens, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1009195
Zhang, Kishimoto, Grammatikakis, Gottimukkala, Cutler et al., Senolytic therapy alleviates Aβ-associated oligodendrocyte progenitor cell senescence and cognitive deficits in an Alzheimer's disease model, Nature Neuroscience, doi:10.1038/s41593-019-0372-9
Zhao, Qin, Zhang, Li, Liang et al., Longitudinal COVID-19 profiling associates IL-1RA and IL-10 with disease severity and RANTES with mild disease, JCI Insight, doi:10.1172/jci.insight.139834
Zheng, Wong, Li, Verma, Ortiz et al., Treatment with the senolytics dasatinib/quercetin reduces SARS-CoV-2-related mortality in mice, The New England Journal of Medicine
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1111/acel.13771",
"ISSN": [
"1474-9718",
"1474-9726"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/acel.13771",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1111/acel.13771"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2022-04-22"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2022-12-20"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2023-01-26"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8060-073X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Metabolic Syndrome Group‐BIOPROMET Madrid Institute for Advanced Studies‐IMDEA Food, CEI UAM+CSIC Madrid Spain"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Pastor‐Fernández",
"given": "Andrés",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine and Surgical Animal, Faculty of Veterinary/VISAVET Centre Complutense University of Madrid Madrid Spain"
}
],
"family": "Bertos",
"given": "Antonio R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Metabolic Syndrome Group‐BIOPROMET Madrid Institute for Advanced Studies‐IMDEA Food, CEI UAM+CSIC Madrid Spain"
}
],
"family": "Sierra‐Ramírez",
"given": "Arantzazu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Departamento de Biología Molecular Universidad Autónoma de Madrid (UAM) Madrid Spain"
},
{
"name": "Centro de Biología Molecular Severo Ochoa (CSIC‐UAM) Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC) Madrid Spain"
}
],
"family": "del Moral‐Salmoral",
"given": "Javier",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Departamento de Biología Molecular Universidad Autónoma de Madrid (UAM) Madrid Spain"
},
{
"name": "Centro de Biología Molecular Severo Ochoa (CSIC‐UAM) Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC) Madrid Spain"
}
],
"family": "Merino",
"given": "Javier",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Centro de Biología Molecular Severo Ochoa (CSIC‐UAM) Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC) Madrid Spain"
},
{
"name": "Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red de Enfermedades Hepáticas y Digestivas (CIBERehd) del Instituto de Salud Carlos III Madrid Spain"
}
],
"family": "de Ávila",
"given": "Ana I.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Gene Therapy and Regulation of Gene Expression CIMA Universidad de Navarra Pamplona Spain"
}
],
"family": "Olagüe",
"given": "Cristina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Centro Nacional de Biotecnología (CNB‐CSIC) Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC) Madrid Spain"
}
],
"family": "Villares",
"given": "Ricardo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Gene Therapy and Regulation of Gene Expression CIMA Universidad de Navarra Pamplona Spain"
}
],
"family": "González‐Aseguinolaza",
"given": "Gloria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute of Biomedicine of Seville (IBiS), Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) University of Seville, Virgen del Rocio University Hospital Seville Spain"
}
],
"family": "Rodríguez",
"given": "María Ángeles",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Departamento de Biología Molecular Universidad Autónoma de Madrid (UAM) Madrid Spain"
},
{
"name": "Centro de Biología Molecular Severo Ochoa (CSIC‐UAM) Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC) Madrid Spain"
}
],
"family": "Fresno",
"given": "Manuel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Departamento de Biología Molecular Universidad Autónoma de Madrid (UAM) Madrid Spain"
},
{
"name": "Centro de Biología Molecular Severo Ochoa (CSIC‐UAM) Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC) Madrid Spain"
}
],
"family": "Gironés",
"given": "Nuria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute of Biomedicine of Seville (IBiS), Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) University of Seville, Virgen del Rocio University Hospital Seville Spain"
}
],
"family": "Bustos",
"given": "Matilde",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Gene Therapy and Regulation of Gene Expression CIMA Universidad de Navarra Pamplona Spain"
}
],
"family": "Smerdou",
"given": "Cristian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3515-4125",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Metabolic Syndrome Group‐BIOPROMET Madrid Institute for Advanced Studies‐IMDEA Food, CEI UAM+CSIC Madrid Spain"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Fernandez‐Marcos",
"given": "Pablo Jose",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3895-3790",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Centro de Biología Molecular Severo Ochoa (CSIC‐UAM) Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC) Madrid Spain"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "von Kobbe",
"given": "Cayetano",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Aging Cell",
"container-title-short": "Aging Cell",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-27T07:39:19Z",
"timestamp": 1674805159000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-27T07:39:25Z",
"timestamp": 1674805165000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100004587",
"award": [
"COV20‐00755",
"COV20‐00792"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Instituto de Salud Carlos III"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100004837",
"award": [
"SAF2017‐85766‐R",
"PID2020‐114077RB‐I00",
"RYC‐2017‐22335",
"PID2020‐113888RB‐I00"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100016970",
"award": [
"CSIC‐COV19‐014"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "China Shipbuilding Industry"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-28T06:10:22Z",
"timestamp": 1674886222064
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
26
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-26T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1674691200000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/tdm_license_1.1",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-26T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1674691200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/acel.13771",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full-xml/10.1111/acel.13771",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/acel.13771",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1111",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
26
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
26
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586‐021‐03553‐9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_2_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.103493",
"article-title": "From causes of aging to death from COVID‐19",
"author": "Blagosklonny M. V.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1004",
"journal-title": "Aging",
"key": "e_1_2_10_3_1",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiab044",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_4_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abe4832",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_5_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/jvi.01281‐09",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598‐021‐86002‐x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci.insight.150107",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_8_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.02951‐2021",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_9_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci.insight.142032",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_10_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140‐6736(20)30183‐5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_11_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.677008",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_12_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13141",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_13_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.102903",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_14_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598‐017‐03956‐7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_15_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586‐021‐03995‐1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_16_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci.insight.138070",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_17_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.763292",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_18_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.153.11.4969",
"article-title": "C‐C chemokines induce the chemotaxis of NK and IL‐2‐activated NK cells: Role for G proteins",
"author": "Maghazachi A. A.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4969",
"journal-title": "Journal of Immunology",
"key": "e_1_2_10_19_1",
"volume": "153",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2020.600369",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_20_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells9040909",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_21_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cyto.2015.05.023",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_22_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.02012‐06",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_23_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1083/jcb.201708092",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_24_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ctarc.2021.100399",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_25_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/acel.13237",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_26_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467‐020‐19891‐7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_27_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jCI95149",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_28_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154262",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_29_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/acel.12950",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_30_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2020.1838955",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_31_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134‐020‐05991‐x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_32_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ncomms14532",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_33_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/347669a0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_34_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.103607",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_35_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s43587‐022‐00170‐7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_36_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598‐020‐75659‐5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_37_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_38_1",
"unstructured": "WHO.WHO Coronavirus (COVID‐19) dashboard.https://covid19.who.int"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41590‐020‐0778‐2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_39_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaci.2020.04.027",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_40_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.03.037",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_41_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1009195",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_42_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41593‐019‐0372‐9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_43_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci.insight.139834",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_44_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586‐020‐2943‐z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_45_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001017",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_46_1"
}
],
"reference-count": 45,
"references-count": 45,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/acel.13771"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Cell Biology",
"Aging"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Treatment with the senolytics dasatinib/quercetin reduces\n <scp>SARS‐CoV</scp>\n ‐2‐related mortality in mice",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy"
}