Vitamin A Nutritional Status and Clinical Outcomes in COVID-19: A Systematic Review
et al., Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology, doi:10.3177/jnsv.69.395, Dec 2023
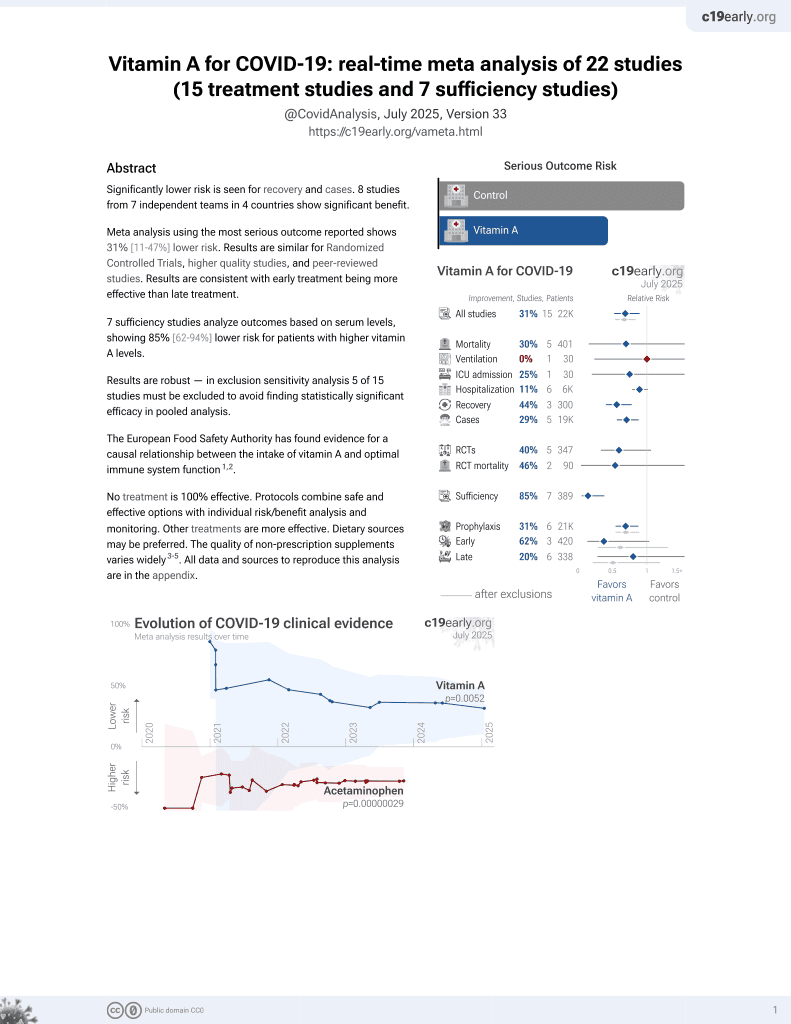
Vitamin A for COVID-19
49th treatment shown to reduce risk in
May 2023, now with p = 0.004 from 14 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Systematic review of seven observational studies with 608 COVID-19 patients, showing an association between lower vitamin A levels and worse clinical outcomes including longer hospitalization, increased need for intensive care and mechanical ventilation, higher risk of respiratory complications like acute respiratory distress syndrome, and greater COVID-19 severity and mortality.
Currently there are 14 vitamin A studies and meta-analysis shows:
| Outcome | Improvement |
|---|---|
| Mortality | 46% lower [-277‑92%] |
| Hospitalization | 19% lower [5‑30%] |
| Cases | 29% fewer [12‑44%] |
Oliveira et al., 31 Dec 2023, peer-reviewed, 11 authors.
Contact: iarakatrynne@hotmail.com.
Vitamin A Nutritional Status and Clinical Outcomes in COVID-19: A Systematic Review
The role of vitamin A in the pathophysiological context of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) represents a current challenge, given the major impact of COVID-19 on morbidity and mortality and the importance of retinol in pulmonary and immunomodulatory functions. The aim of this review is to assess the relationship between vitamin A nutritional status and clinical outcomes in people with COVID-19. The PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus and ScienceDirect databases were used to search for observational studies that assessed retinol levels in hospitalized individuals with COVID-19, following the PRISMA recommendations. A total of 1,912 articles were identified and seven met the inclusion criteria. Four studies showed borderline or deficient retinol blood levels (retinol ,0.20 mg/L or ,0.70 mol/L) in people with COVID-19, associated with worsened clinical outcomes. In the other three studies lower mean values of this vitamin were identified in COVID-19 symptomatic groups compared to asymptomatic or convalescent groups that showed worse clinical outcomes. The results suggest a possible association between retinol and COVID-19 outcomes. However, there is a clear need to develop clinical trials to elucidate the role of vitamin A in the pathophysiological process of COVID-19.
References
Aklamati, Mulenga, Dueker, Buchholz, Peerson et al., Accelerator mass spectrometry can be used to assess vitamin A metabolism quantitatively in boys in a community setting, J Nutr
Al-Saleh, Alrushud, Alnuwaysir, Elkhatib, Shoukri et al., Essential metals, vitamins and antioxidant enzyme activities in COVID-19 patients and their potential associations with the disease severity, Biometals
Alsharif, Qurashi, Effectiveness of COVID-19 diagnosis and management tools: a review, Radiography
Beigmohammadi, Bitarafan, Abdollahi, Amoozadeh, Salahshour et al., The association between serum levels of micronutrients and the severity of disease in patients with COVID-19, Nutrition
Bielsa-Berrocal, Bordejé-Laguna, Tural-Llàcher, Barallat, Manresa-Domínguez et al., Low levels of few micronutrients may impact COVID-19 disease progression: an observational study on the first wave, Metabolites
Bost, Richard, Redonnet-Vernhet, Parant, Bolet et al., Review of nutritional components in Covid-19: what about micronutrients?, Ann Biol Clin
Chen, Liu, Liu, Liu, Liu et al., Analysis of clinical features of 29 patients with 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia, Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi
Gieng, Green, Green, Rosales, Model-based compartmental analysis indicates a reduced mobilization of hepatic vitamin A during inflammation in rats, J Lipid Res
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, Krüger, Herrler et al., SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor, Cell
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Hussain, Kaler, Tabrez, Tabrez, Tabrez, Novel COVID-19: A comprehensive review of transmission, manifestation, and pathogenesis, Cureus
Koo, Jetten, Belloni, Yoon, Kim et al., Role of retinoid receptors in the regulation of mucin gene expression by retinoic acid in human tracheobronchial epithelial cells, Biochem J
Mccullough, Clewes, Thurnham, The effect of vitamin A on epithelial integrity, Proc Nutr Soc
Midha, Kumar, Kumar, Madan, Mega doses of retinol: a possible immunomodulation in COVID-19 illness in resource-limited settings, Rev Med Virol
Murni, Prawirohartono, Triasih, Potential role of vitamins and zinc on acute respiratory infections including Covid-19, Global Pediatric Health
Sarohan, Akelma, Araç, Aslan, Cen, Retinol depletion in COVID-19, Clin Nutr Open Sci
Sarohan, Kızıl, Akram, Cen, A novel hypothesis for COVID-19 pathogenesis: Retinol depletion and retinoid signaling disorder, Cell Signal
Singh, Chawla, Kumar, Singh, Role of vitamin A supplementation in prevention and control of coronavirus disease-19: A narrative review, Int J Prev Med
Stephensen, Lietz, Vitamin A in resistance to and recovery from infection: relevance to SARS-CoV2, Br J Nutr
Stephensen, Vitamin A, infection, and immune function, Annu Rev Nutr
Sterne, Hernán, Reeves, Savovic, Berkman et al., ROB-INS-I: A tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions, BMJ
Tepasse, Vollenberg, Fobker, Kabar, Schmidt et al., Vitamin A plasma levels in COVID-19 patients: a prospective multicenter study and hypothesis, Nutrients
Turrubiates-Hernández, Hernández-Bello, Oregón-Romero, González-Estevez, Valle, Participación de la vitamina A en la producción de iga secretora en el epitelio del tracto respiratorio para la potencial protección de infección por SARS-CoV-2, Rev Alerg Mex
Voelkle, Gregoriano, Neyer, Koch, Kutz et al., Prevalence of micronutrient deficiencies in patients hospitalized with COVID-19: an observational cohort study, Nutrients
Vollenberg, Tepasse, Fobker, Hüsing-Kabar, Significantly reduced retinol binding protein 4 (RBP4) levels in critically ill COVID-19 patients, Nutrients
Wang, Swartz-Basile, Rubin, Levin, Retinoic acid stimulates early cellular proliferation in the adapting remnant rat small intestine after partial resection, J Nutr
Who, Indicators for assessing vitamin A deficiency and their application in monitoring and evaluating intervention programmes
Who, WHO coronavirus (covid-19) dashboard
Who, WHO global database on vitamin A deficiency
Xu, Qi, Li, Yang, Wang et al., The differential immune responses to COVID-19 in peripheral and lung revealed by single-cell RNA sequencing, Cell Discov
Yilmaz, Bulut, Omaygenc, Akca, Can et al., Baseline serum vitamin A and vitamin C levels and their association with disease severity in COVID-19 patients, Acta Biomed
Zhang, Cui, Zhang, Wang, Low-dose vitamin A therapy on T lymphocyte function in neonatal pneumonia, Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci
Zhao, Meng, Kumar, Wu, Huang et al., Lymphopenia is associated with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infections: A systemic review and meta-analysis, Int J Infect Dis
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3177/jnsv.69.395",
"ISSN": [
"0301-4800",
"1881-7742"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3177/jnsv.69.395",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Federal University of Piauí"
}
],
"family": "F OLIVEIRA",
"given": "Iara Katrynne",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Federal University of Piauí"
}
],
"family": "C CARVALHO",
"given": "Vanessa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Federal University of Piauí"
}
],
"family": "S SANTOS",
"given": "Gabriela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Federal University of Piauí"
}
],
"family": "V N MONTEIRO",
"given": "Nayara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Federal University of Piauí"
}
],
"family": "A F AZEVEDO",
"given": "Margarete",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Estácio CEUT Faculty"
}
],
"family": "R LIMA",
"given": "Carlos Henrique",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Federal University of Piauí"
}
],
"family": "M M NETO",
"given": "Emídio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Federal University of Piauí"
}
],
"family": "C MARTINS",
"given": "Maria do Carmo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of São Paulo, School of Public Health"
}
],
"family": "A LUZIA",
"given": "Liania",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of São Paulo, School of Public Health"
}
],
"family": "H C RONDÓ",
"given": "Patrícia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Federal University of Piauí"
}
],
"family": "A PAIVA",
"given": "Adriana",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology",
"container-title-short": "J Nutr Sci Vitaminol",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-30T22:14:16Z",
"timestamp": 1703974456000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-30T22:14:16Z",
"timestamp": 1703974456000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-30T22:40:43Z",
"timestamp": 1703976043075
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "6",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
31
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "6",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jnsv/69/6/69_395/_pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1759",
"original-title": [],
"page": "395-401",
"prefix": "10.3177",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
31
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
31
]
]
},
"publisher": "Center for Academic Publications Japan",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jnsv/69/6/69_395/_article"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Nutrition and Dietetics",
"Medicine (miscellaneous)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Vitamin A Nutritional Status and Clinical Outcomes in COVID-19: A Systematic Review",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "69"
}