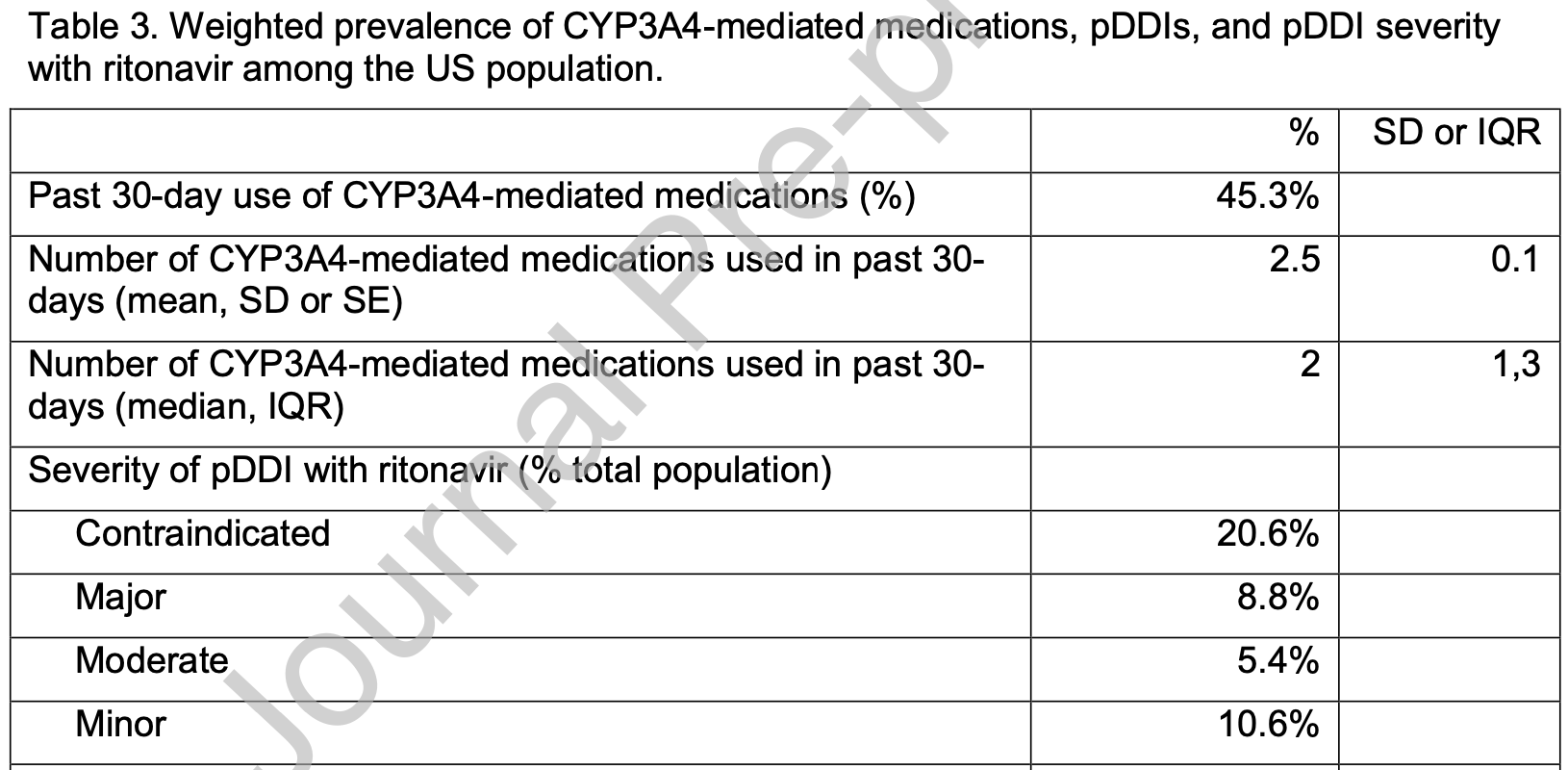
Prevalence of Potential Drug-Drug Interactions with Ritonavir-Containing COVID-19 therapy in the United States: An Analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
et al., Clinical Therapeutics, doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2023.03.012, Mar 2023
Analysis of 15,685 adults in the USA estimating that 29.3% of the population risk a major or contraindicated drug interaction with paxlovid, which may increase significantly for patients over 60 or with several comorbidities that also increase COVID-19 risk.
Igho-Osagie et al., 23 Mar 2023, USA, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
Contact: kaylen.brzozowski@trinetx.com.
Prevalence of Potential Drug-Drug Interactions with Ritonavir-Containing COVID-19 therapy in the United States: An Analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Clinical Therapeutics, doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2023.03.012
This is a PDF file of an article that has undergone enhancements after acceptance, such as the addition of a cover page and metadata, and formatting for readability, but it is not yet the definitive version of record. This version will undergo additional copyediting, typesetting and review before it is published in its final form, but we are providing this version to give early visibility of the article. Please note that, during the production process, errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
suspected major or contraindicated pDDIs (n, %) Number of CYP3A4-mediated medications with suspected major or contraindicated pDDIs used in past 30-days (mean, SD or SE)
References
Ahrenfeldt, Nielsen, Möller, Christensen, Lindahl-Jacobsen, Burden and prevalence of risk factors for severe COVID-19 in the ageing European population -a SHARE-based analysis, Z Gesundh Wiss, doi:10.1007/s10389-021-01537-7
Ajufo, Rao, Navar, Pandey, Ayers et al., population at increased risk of severe illness from COVID-19, American Journal of Preventive Cardiology
Cdc, COVID-19, people with certain medical conditions
Cdc, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Cdc, HIV Nexus clinician resources: HIV treatment and results
Cdc, NHANES about NHANES
Cdc, NHANES tutorials module 3: Weighting
Choi, Park, Lee, Variable effects of underlying diseases on the prognosis of patients with COVID-19, PloS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0254258
Conti, Sellitto, Torsiello, Identification of drug interaction adverse events in patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.7970
Dhhs, NHANES survey methods and analytic guidelines
Emami, Javanmardi, Pirbonyeh, Akbari, Prevalence of underlying diseases in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Arch Acad Emerg Med
Fda, Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA authorizes drug combination for treatment of COVID-19
Fda, Drug development and drug interactions | Table of substrates, inhibitors and inducers
Fda, Drug development and drug interactions | Table of substrates, inhibitors and inducers
Fda, FDA fact sheet for healthcare providers: Emergency use authorization for Lagevrio (molnupiravir) capsules
Fda, FDA fact sheet for healthcare providers: Emergency use authorization for Paxlovid
Gu, Paulose-Ram, Burt, Kit, Prescription cholesterol-lowering medication use in adults aged 40 and over: United States
Hodge, Marra, Marzolini, Drug interactions: a review of the unseen danger of experimental COVID-19 therapies, J Antimicrob Chemother, doi:10.1093/jac/dkaa340
Langford, So, Raybardhan, Leung, Soucy et al., Antibiotic prescribing in patients with COVID-19: rapid review and meta-analysis, Clin Microbiol Infect, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2020.12.018
Low, Setia, Lima, Drug-drug interactions involving antidepressants: focus on desvenlafaxine, Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat, doi:10.2147/NDT.S157708
Marzolini, Kuritzkes, Marra, Boyle, Gibbons et al., Prescribing nirmatrelvir-ritonavir: How to recognize and manage drug-drug interactions, Ann Intern Med, doi:10.7326/M22-0281
Marzolini, Kuritzkes, Marra, Boyle, Gibbons et al., Recommendations for the management of drug-drug interactions between the COVID-19 antiviral nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (Paxlovid) and comedications, Clin Pharmacol Ther, doi:10.1002/cpt.2646
Qato, Alexander, Guadamuz, Lindau, Prescription medication use among children and adolescents in the United States, Pediatrics, doi:10.1542/peds.2018-1042
Rezaee, Pourkarim, Pourtaghi-Anvarian, Entezari-Maleki, Asvadi-Kermani et al., Drug-drug interactions with candidate medications used for COVID-19 treatment: An overview, Pharmacol Res Perspect, doi:10.1002/prp2.705
S K Sr, Kalala, Pm, Sabarathinam, Drug interaction risk between cardioprotective drugs and drugs used in treatment of COVID-19: A evidence-based review from six databases, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2022.102451
Seligman, Ferranna, Bloom, Social determinants of mortality from COVID-19: A simulation study using NHANES, PLoS Med, doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1003490
Shahzadi, Sonmez, Kose, Oktan, Alagoz et al., The prevalence of potential drug-drug interactions in CKD-A retrospective observational study of Cerrahpasa nephrology unit, Medicina, doi:10.3390/medicina58020183
Stader, Khoo, Stoeckle, Back, Hirsch et al., Stopping lopinavir/ritonavir in COVID-19 patients: duration of the drug interacting effect, J Antimicrob Chemother, doi:10.1093/jac/dkaa253
Talha, Dhamoon, Ritonavir
Van Leeuwen, Brundel, Neef, Van Gelder, Mathijssen et al., Prevalence of potential drug-drug interactions in cancer patients treated with oral anticancer drugs, Br J Cancer, doi:10.1038/bjc.2013.48
Wedemeyer, Blume, Pharmacokinetic drug interaction profiles of proton pump inhibitors: an update, Drug Saf, doi:10.1007/s40264-014-0144-0
Zanger, Schwab, Cytochrome P450 enzymes in drug metabolism: Regulation of gene expression, enzyme activities, and impact of genetic variation, Pharmacology & Therapeutics
Zhou, Xue, Cc, Yu, Li et al., Clinically important drug interactions potentially involving mechanism-based inhibition of Cytochrome P450 3A4 and the role of therapeutic drug monitoring, Ther Drug Monit
Zhou, Xue, Yu, Li, Wang, Clinically important drug interactions potentially involving mechanism-based inhibition of cytochrome P450 3A4 and the role of therapeutic drug monitoring, Ther Drug Monit, doi:10.1097/FTD.0b013e31815c16f5
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clinthera.2023.03.012",
"ISSN": [
"0149-2918"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.clinthera.2023.03.012",
"alternative-id": [
"S0149291823001091"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Prevalence of Potential Drug-Drug Interactions with Ritonavir-Containing COVID-19 therapy in the United States: An Analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Clinical Therapeutics"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinthera.2023.03.012"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2023 Published by Elsevier Inc."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Igho-Osagie",
"given": "Ebuwa",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9434-9507",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Brzozowski",
"given": "Kaylen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jin",
"given": "Harry",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brown",
"given": "Jeffrey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "Marissa Grifasi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Puenpatom",
"given": "Amy",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Clinical Therapeutics",
"container-title-short": "Clinical Therapeutics",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicaltherapeutics.com",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-24T07:22:35Z",
"timestamp": 1679642555000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-24T07:22:35Z",
"timestamp": 1679642555000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-25T04:49:04Z",
"timestamp": 1679719744029
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1677628800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-017",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1677628800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-037",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1677628800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-012",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1677628800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-029",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1677628800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-004",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1677628800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0149291823001091?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0149291823001091?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0149291823001091"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pharmacology (medical)",
"Pharmacology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Prevalence of Potential Drug-Drug Interactions with Ritonavir-Containing COVID-19 therapy in the United States: An Analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}