Patients hospitalized with COVID-19 have low levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D
et al., Endocrine, doi:10.1007/s12020-020-02597-7, Jan 2021
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 136 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
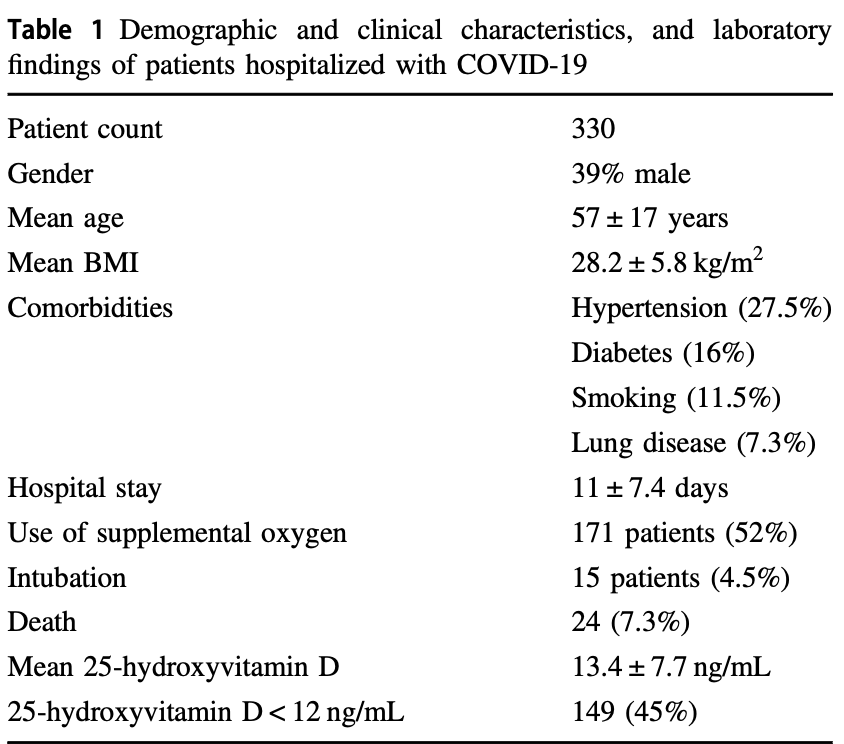
Retrospective 330 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Armenia, showing significantly higher prevalence of vitamin D deficiency (<12ng/mL) compared to health controls (45% vs. 13%).
Hutchings et al., 16 Jan 2021, retrospective, Armenia, peer-reviewed, 12 authors.
Abstract: Endocrine (2021) 71:267–269
https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-020-02597-7
RESEARCH LETTER
Patients hospitalized with COVID-19 have low levels of
25-hydroxyvitamin D
Nicholas Hutchings 1,2 Varta Babalyan2 Sisak Baghdasaryan2 Mushegh Qefoyan2 Narina Sargsyants3
Elena Aghajanova4 Anna Martirosyan5 Ruzanna Harutyunyan5 Olga Lesnyak6 Anna Maria Formenti7
Andrea Giustina7 John P. Bilezikian2,8
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
1234567890();,:
1234567890();,:
Received: 24 November 2020 / Accepted: 17 December 2020 / Published online: 16 January 2021
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC part of Springer Nature 2021
The coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) causes COVID-19. The
disease has already afflicted over 54 million persons
worldwide and has caused over 1.3 million deaths [1].
While most patients recovery uneventfully, some develop
an acute pulmonary syndrome that requires hospitalization
for supportive care [2]. Risk factors for symptomatic manifestations include male sex, diabetes mellitus, obesity, and
hypertension [3, 4]. Another recently recognized potential
risk factor is vitamin D deficiency. Vitamin D is an
important modulator of innate and acquired immunity
[5, 6]. Low levels are associated with bacterial and viral
infections [7]. In addition, in countries with lower mean
levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D, mortality from COVID-19
is higher [8]. Preliminary studies suggest that vitamin D
supplementation may improve outcomes [9]. While much of
the data implicating vitamin D and COVID-19 has been
indirect, recent reports have shown markedly reduced levels
of 25-hydroxyvitamin D among those hospitalized with
COVID-19 [10, 11]. These observations are consistent with
* Nicholas Hutchings
nicholas.hutchings@uci.edu
1
School of Medicine, University of California, Irvine, CA, USA
2
Osteoporosis Center of Armenia, Yerevan, Armenia
3
Ministry of Health, Yerevan, Armenia
4
Muratsan University Hospital, Yerevan, Armenia
5
Saint Gregory the Illuminator Medical Center, Yerevan, Armenia
6
North West State Medical University named after I.I. Mechnikov,
Saint Petersburg, Russia
7
Institute of Endocrine and Metabolic Sciences, San Raffaele,
Vita-Salute University and IRCCS Hospital, Milano, Italy
8
Endocrinology Division, Department of Medicine, New YorkPresbyterian Hospital / Columbia University Irving Medical
Center, New York, NY, USA
a plausible pathophysiological role of vitamin D in the
disease process [6].
With an ethnically and culturally homogeneous population of approximately 3 million [12], Armenia has seen
~116,000 cases and 1700 deaths as of November 2020 [13].
At the Saint Gregory the Illuminator Medical Center
(SGIMC) in Yerevan, a designated COVID-19 treatment
hospital, we measured levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D. We
compared these levels with values that we have recently
characterized in the free-living, healthy population of
Armenia [14].
Methods
Blood samples for measurement of 25-hydroxyvitamin D
(ElectroChemiLuminescence immunoassay: Cobas e 411
autoanalyzer- Roche; Basel, Switzerland) were obtained from
330 consecutive hospitalized patients. We also recorded age,
gender, height, weight, occupation, chronic conditions, prior
tuberculosis infection, smoking status, use of supplemental
oxygen, intubation status, duration of hospitalization until
discharge, or death.
Results
Samples were collected over 5 weeks in summer, 2020. The
most common comorbidities were hypertension,..
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12020-020-02597-7",
"ISSN": [
"1355-008X",
"1559-0100"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12020-020-02597-7",
"alternative-id": [
"2597"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "24 November 2020"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "17 December 2020"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "16 January 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Compliance with ethical standards",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Conflict of interest",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethical approval",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Columbia University Irving Medical Center, and the Ethics Committee of the Yerevan State Medical University."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Informed consent",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 4,
"value": "Both review boards waived informed consent as a requirement because the study entailed analysis of previously collected and de-identified data."
},
{
"label": "Free to read",
"name": "free",
"value": "This content has been made available to all."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9964-142X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Hutchings",
"given": "Nicholas",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Babalyan",
"given": "Varta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baghdasaryan",
"given": "Sisak",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Qefoyan",
"given": "Mushegh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sargsyants",
"given": "Narina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aghajanova",
"given": "Elena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martirosyan",
"given": "Anna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harutyunyan",
"given": "Ruzanna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lesnyak",
"given": "Olga",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Formenti",
"given": "Anna Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Giustina",
"given": "Andrea",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bilezikian",
"given": "John P.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Endocrine",
"container-title-short": "Endocrine",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-16T12:02:26Z",
"timestamp": 1610798546000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2021-05-08T11:35:28Z",
"timestamp": 1620473728000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-26T07:20:04Z",
"timestamp": 1706253604071
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 22,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
16
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-16T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1610755200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-16T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1610755200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s12020-020-02597-7.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12020-020-02597-7/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s12020-020-02597-7.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"page": "267-269",
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
16
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
16
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"key": "2597_CR1",
"unstructured": "Worldometer. COVID-19 Coronavirus Pandemic. Accessed 07 Nov 2020"
},
{
"key": "2597_CR2",
"unstructured": "CDC. Interim Clinical Guidance for Management of Patients with Confirmed Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19). Accessed 07 May 2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.03.017",
"author": "J Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "91",
"journal-title": "Int J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "2597_CR3",
"unstructured": "J. Yang, Y. Zheng, X. Gou, et al. Prevalence of comorbidities and its effects in coronavirus disease 2019 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J. Infect. Dis. 94, 91–95 (2020)",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.6775",
"author": "S Richardson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2052",
"issue": "20",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2597_CR4",
"unstructured": "S.Richardson, J.Hirsch, M.Narasimhan, et al. Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York city area. JAMA 323(20), 2052–2059 (2020)",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mce.2010.02.013",
"author": "M Hewison",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "103",
"journal-title": "Mol. Cell. Endocrinol.",
"key": "2597_CR5",
"unstructured": "M. Hewison, Vitamin D and the intracrinology of innate immunity. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 321, 103–111 (2010)",
"volume": "321",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1530/EJE-20-0665",
"author": "JP Bilezikian",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "R133",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Endocrinol.",
"key": "2597_CR6",
"unstructured": "J.P. Bilezikian, D. Bikle, M. Hewison, et al. Mechanisms in endocrinology: Vitamin D and COVID-19. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 183, R133–R147 (2020)",
"volume": "183",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.i6583",
"author": "A Martineau",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "i6583",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "2597_CR7",
"unstructured": "A. Martineau, D. Jolliffe, R. Hooper, et al. Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data. BMJ 356, i6583 (2017)",
"volume": "356",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-21211/v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2597_CR8",
"unstructured": "P. Ilie, S. Stefanescu, L. Smith, The role of Vitamin D in the prevention of Coronavirus Disease 2019 infection and mortality. Res. Square. Accessed 07 May 2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751",
"author": "M Entrenas Castillo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "105751",
"journal-title": "J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "2597_CR9",
"unstructured": "M. Entrenas Castillo, L.M. Entrenas Costa, Vaquero, J.M. Barrios, et al. Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: a pilot randomized clinical study. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 203, 105751 (2020)",
"volume": "203",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "2597_CR10",
"unstructured": "L. Gennari, I. Campi, D. Merlotti, et al. Vitamin D Deficiency Is Independently Associated with COVID-19 Severity and Mortality. Oral Presentation: American Society for Bone and Mineral Research Annual Meeting, 11 Sep 2020 (virtual)"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgaa733",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2597_CR11",
"unstructured": "J. Hernández, D. Nan, M. Fernandez-Ayala, et al. Vitamin D status in hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, dgaa733. https://doi.org/10.1210/clinem/dgaa733, https://academic.oup.com/jcem/advance-article/doi/10.1210/clinem/dgaa733/5934827. Accessed 06 Jan 2021"
},
{
"key": "2597_CR12",
"unstructured": "Central Intelligence Agency. CIA Factbook: Armenia. Accessed 07 May 2020"
},
{
"key": "2597_CR13",
"unstructured": "Ministry of Health of the Republic of Armenia. Current coronavirus situation in the country. https://www.moh.am/#1/3336 Accessed 09 Nov 2020 [Armenian]"
},
{
"key": "2597_CR14",
"unstructured": "N. Hutchings, V. Babalyan, A. Heijboer, et al. Vitamin D Insufficiency is widespread in Armenia. Poster Presentation. American Society for Bone and Mineral Research Annual Meeting, 11 Sep 2020 (virtual)"
},
{
"key": "2597_CR15",
"unstructured": "L. Gennari, I. Campi, D. Merlotti, et al. Vitamin D deficiency is independently associated with COVID-19 severity and mortality. Oral Presentation: American Society for Bone and Mineral Research Annual Meeting, 11 Sep 2020 (virtual)"
}
],
"reference-count": 15,
"references-count": 15,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s12020-020-02597-7"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Patients hospitalized with COVID-19 have low levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "71"
}
