Case Cluster of RT-PCR COVID-19 Positive Patients with an Unexpected Benign Clinical Course With Vitamin D, Melatonin, Vitamin C, and Viscum Album
et al., SSRN, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3779211 , Feb 2021
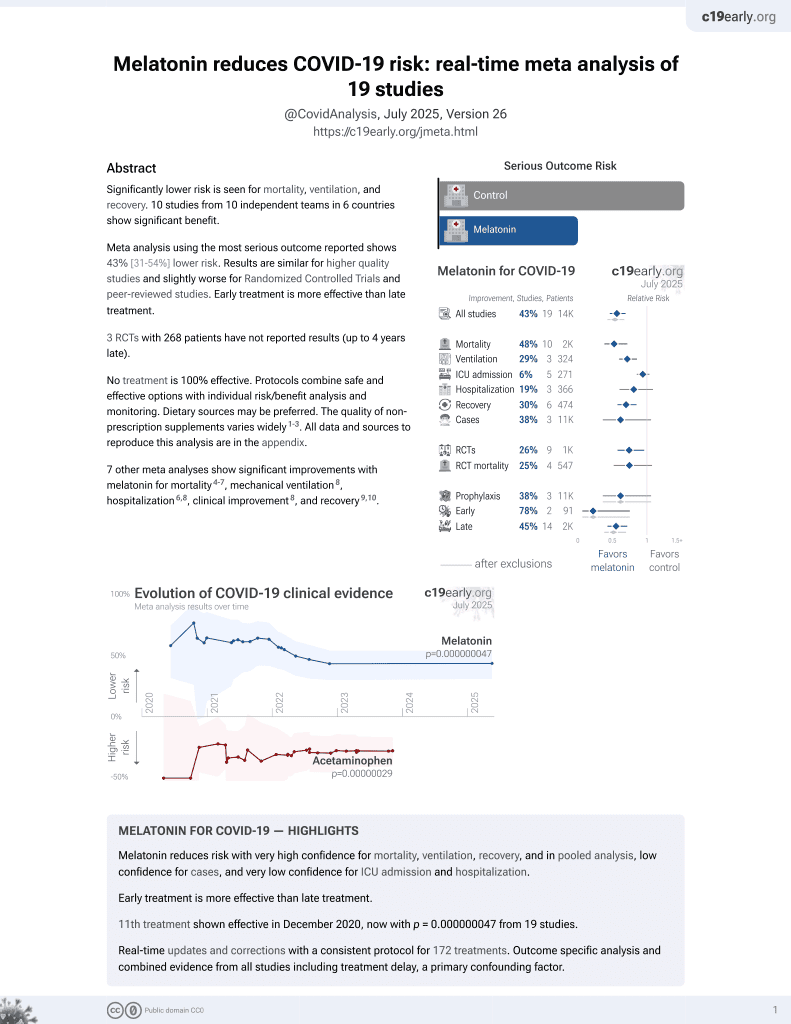
Melatonin for COVID-19
12th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2020, now with p = 0.0000000099 from 19 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Case series of 24 COVID-19 patients (12 confirmed PCR+) treated with vitamin D, vitamin C, and melatonin, showing positive outcomes with no patient having worse than a mild case, including 7 high risk patients.
Hancock et al., 9 Feb 2021, preprint, 4 authors.
Case Cluster of RT-PCR COVID-19 Positive Patients with an Unexpected Benign Clinical Course With Vitamin D, Melatonin, Vitamin C, and Viscum Album
Background: The SARS-COV-2 global pandemic has been noted to have a differential effect on those exposed depending on risk factors such as age, diabetes, cardiovascular disease and cancer.
Case presentation: We report a case series of 12 confirmed positive patients and 12 presumptive positive patients all of whom had either an entirely asymptomatic or relatively mild clinical course. 2 patients had active cancer, 3 patients were cancer survivors, 1 patient without cancer was 74 years old. All patients were treated early in their disease course with vitamin D loading (50,000iu daily for 3 days), 60 to 240mg melatonin, and 2000mg oral vitamin C. The 6 high risk patients and one 59 year old patient were treated with at least 2 intravenous doses of vitamin C. The 2 patients with active cancer received 75 grams of vitamin C (one daily, the other every other day). All of the high risk patients had a nearly asymptomatic clinical course and were tested after 10 days and all had a RT PCR for COVID-19 that was negative. The 17 remaining patients also had a relatively benign course though 4 patients (2 in their 20s, 2 in their 50s) received this treatment course later in the course of their illness, these were notably the only patients who had more than a mild sore throat or low grade fever.
Conclusion: We report these unexpectedly positive clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients including patients with different risk factors, under supplemental vitamin C and D and melatonin. These supplements have a favorable safety profile and are already being suggested as potentially disease altering therapies in the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic.
References
Adams, William, Baker, Sobieraj, Myth Busters: Dietary Supplements and COVID-19, Annals of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1177/1060028020928052
Anderson, Reiter, Melatonin: Roles in Influenza, Covid-19, and Other Viral Infections, Reviews in Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/rmv.2109
Cardinali, Melatonin-Induced Oncostasis, Mechanisms and Clinical Relevance
Carr, A New Clinical Trial to Test High-Dose Vitamin C in Patients with COVID-19
Collins, Gustafson, Hydroxychloroquine
Dong, Du, Gardner, An interactive web-based dashboard to track COVID-19 in real time, The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30120-1
Evans, Cancer Patients' Experiences of Using Mistletoe (Viscum Album)
Ganatra, The Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Threat for Patients with Cardiovascular Disease and Cancer
Gasmi, Individual Risk Management Strategy and Potential Therapeutic Options for the COVID-19 Pandemic
Grant, Evidence That Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths
Guan, Comorbidity and Its Impact on 1590 Patients with Covid-19 in China
Hegde, Pushpa, Maddur, Friboulet, Bayry et al., Viscum Album Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Effect by Selectively Inhibiting Cytokine-Induced Expression of Cyclooxygenase-2, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0026312
Kakodkar, Baig, A Comprehensive Literature Review on the Clinical Presentation, and Management of the Pandemic Coronavirus Disease
Liang, Cancer Patients in SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Mahase, Covid-19: Death Rate Is 0.66% and Increases with Age, Study Estimates, BMJ
Oei, Li, Thronicke, Schad, Mistletoe and Immunomodulation: Insights and Implications for Anticancer Therapies, Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, doi:10.1155/2019/5893017
Saha, Differential Effects of Viscum Album Preparations on the Maturation and Activation of Human Dendritic Cells and CD4+ T Cell Responses
Steinborn, Klemd, Sanchez-Campillo, Rieger, Scheffen et al., Viscum Album Neutralizes Tumor-Induced Immunosuppression in a Human in Vitro Cell Model, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0181553
Tusenius, Van Hattum, Gorter, Exploratory Study on the Effects of Treatment with Two Mistletoe Preparations on Chronic Hepatitis C
Wu, Melatonin Receptor Agonist Protects against Acute Lung Injury Induced by Ventilator through Up-Regulation of IL-10 Production
Xu, Factors Associated with Prolonged Viral RNA Shedding in Patients with COVID-19." 22 "Office of Dietary Supplements -Vitamin C
Zhang, COVID-19
Zhang, Vitamin C Supplementation in the Critically Ill
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.2139/ssrn.3779211",
"ISSN": [
"1556-5068"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3779211",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hancock",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ketterl",
"given": "Petra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Viñas",
"given": "Xavier",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Werthmann",
"given": "Paul G.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"SSRN Electronic Journal"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-11T05:50:14Z",
"timestamp": 1613022614000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-11T05:50:33Z",
"timestamp": 1613022633000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-05T01:49:23Z",
"timestamp": 1649123363569
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "1556-5068"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.2139",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.ssrn.com/abstract=3779211"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"SSRN Journal"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Case Cluster of RT-PCR COVID-19 Positive Patients with an Unexpected Benign Clinical Course With Vitamin D, Melatonin, Vitamin C, and Viscum Album"
],
"type": "journal-article"
}
hancock