Response to Nigella sativa in Patients with Confirmed and Suspected COVID-19
et al., Healthbook Times, doi:10.36000/hbT.2021.01.001, Mar 2021
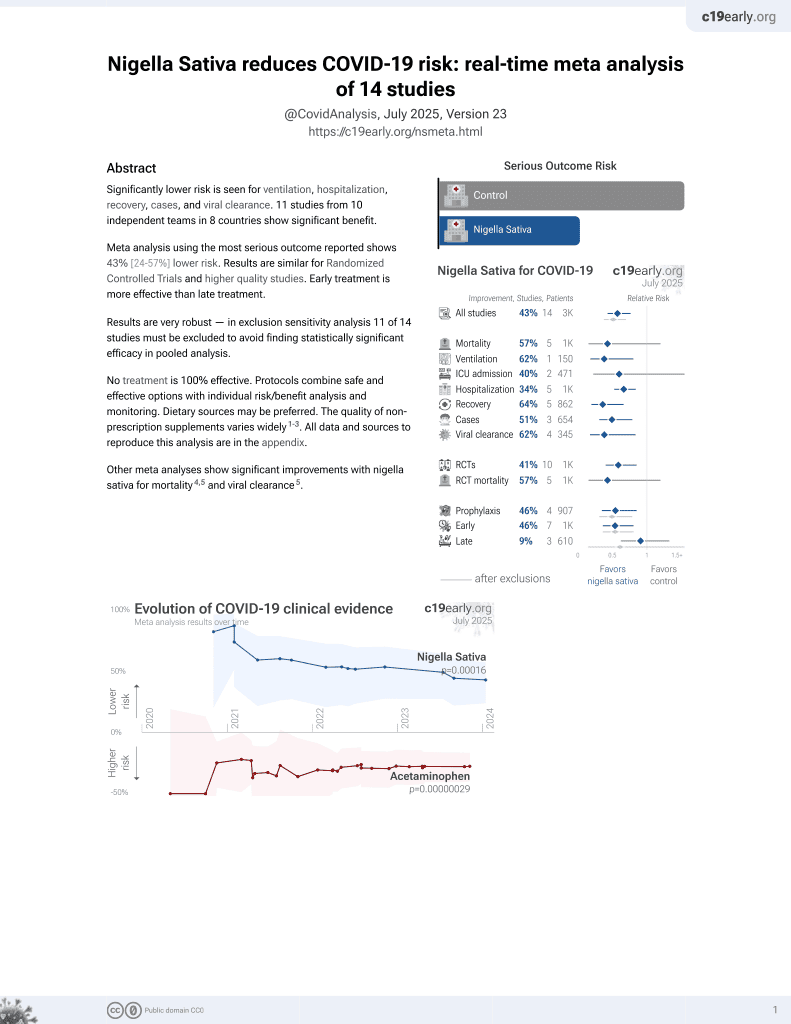
14th treatment shown to reduce risk in
January 2021, now with p = 0.00016 from 14 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
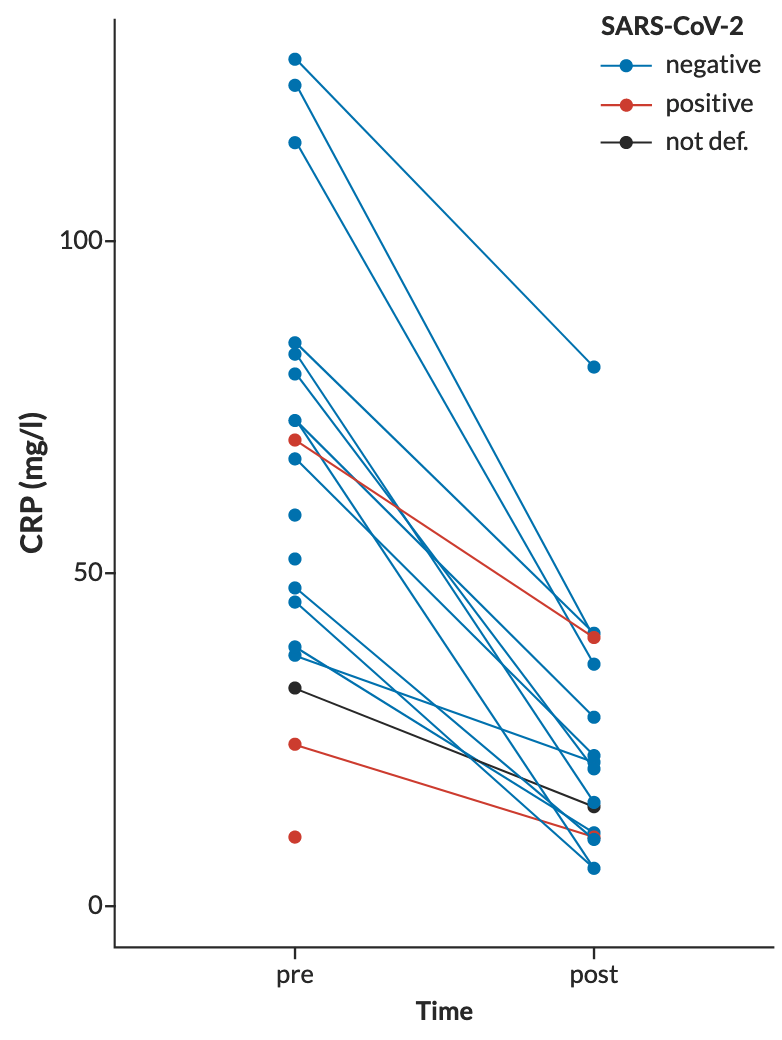
Retrospective 35 patients treated with Nigella Sativa showing good outcomes and relatively fast recovery. There was no control group.
Fetian et al., 4 Mar 2021, peer-reviewed, 4 authors.
Response to Nigella sativa in Patients with Confirmed and Suspected COVID-19
heakthbook TIMES, doi:10.36000/hbt.2021.01.001
deaths due had been reported. The disease is transmitted via inhalation or contact with infected droplets. The incubation period ranges from 2 to 14 days and can reach up to 21 days. Many people are asymptomatic. The estimated fatality rate ranges from 2%−3%. Special molecular tests are being used to detect the virus in respiratory secretions. Elevated levels of C-reactive protein have been detected in the blood sample, while the white blood cell counts were considered normal. The computerized tomographic chest scan is usually abnormal even in those with no symptoms or mild disease. Current treatment options are essentially supportive, as the role of antiviral agents is yet to be established. Preventative measures can be utilized to slow the spread of infection, such as isolation of suspected cases or those with mild symptoms and strict infection control measures at hospitals. Though the virus is far more infectious than its two ancestors, Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV), 2019-nCoV has a lower mortality rate. To date, the impact of this pandemic is uncertain, and the global research community is working diligently to find a satisfactory therapy. To date, there is no approved oral treatment.
healthbook TIMES 75 Response to Nigella sativa in COVID-19 patients • Currently, there is a quite number of treatment options for viral infections with SARS-CoV-2 available. The majority of treatment options are of a supportive nature, and none is an absolute satisfactory therapeutic management. Thus, there are challenging further trends and trials for viral infection treatment management with SARS-CoV-2, with minimal or no side effects. • N. sativa exhibits the potential to be a distinguished drug for treating COVID-19 and different microbial infections. A pilot clinical study using N. sativa with big data and analytics is highly in demand based on the data presented above, which will propagate its unique properties to COVID-19 treatment management.
TAKE-HOME MESSAGES D I S C LO S U R E S TAT E M E N T The authors have not declared any financial or personal connections in connection with this post. The authors would like to thank Fabio Valeri for assistance with statistical analysis and careful review of the case report.
References
Ali, Is SARS-CoV-2 associated with liver dysfunction in COVID-19 patients?, Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol
Bagnato, Role of the endothelin axis and its antagonists in the treatment of cancer, Br J Pharmacol
Bakathir, Detection of the antibacterial effect of nigella sativa ground seedswith water, Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med
Ballou, Kushner, C-reactive protein and the acute phase response, Adv Intern Med
Bari, C reactive protein may not be reliable as a marker of severe bacterial infection in patients receiving tocilizumab, BMJ Case Rep
Bonetti, Endothelial dysfunction: a marker of atherosclerotic risk, Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol
Chen, Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study, Lancet
Chen, Favipiravir versus Arbidol for COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Cyranoski, We need to be alert': Scientists fear second coronavirus wave as China's lockdowns ease, Nature
Dai, The novel ETA receptor antagonist HJP-272 prevents cerebral microvascular hemorrhage in cerebral malaria and synergistically improves survival in combination with an artemisinin derivative, Life Sci
Dajani, Overview of the preclinical pharmacological properties of Nigella sativa (black seeds): a complementary drug with historical and clinical significance, J Physiol Pharmacol
Davì, Demonstration of Rickettsia Conoriiinduced coagulative and platelet activation in vivo in patients with Mediterranean spotted fever, Thromb Haemost
Dietmann, Opposed circulating plasma levels of endothelin-1 and C-type natriuretic peptide in children with Plasmodium falciparum malaria, Malar J
Fa, Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and lymphocyte-to-C-reactive protein ratio in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A meta-analysis, J Med Virol
Ferran, Coronavirus tests are pretty accurate, but far from perfect. The Conversation
Fetian, Nigella sativa Immunomodulatory Activity as a Potential Treatment of Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) -A Review of Current Literature, healthbook Times
Forouzanfar, Black cumin (Nigella sativa) and its constituent (thymoquinone): a review on antimicrobial effects, Iran J Basic Med Sci
Goto, Endothelin receptor antagonist attenuates oxidative stress in a neonatal sepsis piglet model, Pediatr Res
Gu, Detection of endothelin-like immunoreactivity in epithelium and fibroblasts of the human umbilical cord, Tissue Cell
Jaarin, Mechanisms of the antihypertensive effects of Nigella sativa oil in L-NAME-induced hypertensive rats, Clinics
Kedzierski, Endothelin system: the doubleedged sword in health and disease, Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol
Li, Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus, Nature
Li, Early Transmission Dynamics in Wuhan, China, of Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia, N Engl J Med
Marnell, C-reactive protein: ligands, receptors and role in inflammation, Clin Immunol
Mazouchian, The effect of thymoquinone, the main constituent of Nigella sativa, on endothelin level of ovalbumin sensitized guinea pigs, Adv Biores
Monika, An investigational study of antibacterial activities of Nigella sativa on Mastits in dairy crossbred cows, Int J Adv Scient Tech Res
Pakdemirli, Positive Chest CT Features in Patients With COVID-19 Pneumonia and Negative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Test, Cureus
Pepys, C-reactive protein: a critical update, J Clin Invest
Petkova, Myocardial expression of endothelin-1 in murine Trypanosoma cruzi infection, Cardiovasc Pathol
Petkova, The role of endothelin in the pathogenesis of Chagas' disease, Int J Parasitol
Samransamruajkit, Plasma endothelin-1 in infants and young children with acute bronchiolitis and viral pneumonia, Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol
Schuetz, Endothelin-1 precursor peptides correlate with severity of disease and outcome in patients with community acquired pneumonia, BMC Infect. Dis
Sessa, The biosynthesis of endothelin-1 by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes, Biochem Biophys Res Commun
Singhal, A Review of Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19), Indian J Pediatr
Tai, Characterization of the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of 2019 novel coronavirus: implication for development of RBD protein as a viral attachment inhibitor and vaccine, Cell Mol Immunol
Tan, C-reactive protein correlates with computed tomographic findings and predicts severe COVID-19 early, J Med Virol
Tavakoly, The effect of Nigella sativa L. supplementation on serum C-reactive protein: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Complement Ther Med
Tian, Predictors of mortality in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and metaanalysis, J Med Virol
Tschaikowsky, Endothelin in septic patients: effects on cardiovascular and renal function and its relationship to proinflammatory cytokines, Crit Care Med
Varga, Endothelial cell infection and endotheliitis in COVID-19, Lancet
Wang, C-Reactive Protein Level May Predict the Risk of COVID-19 Aggravation, Open Forum Infect Dis
Wang, Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients With 2019 Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA
Young, C-reactive protein: a critical review, Pathology
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.36000/hbt.2021.01.001",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.36000/hbT.2021.01.001",
"container-title": "heakthbook TIMES",
"container-title-short": "hbT",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2021-03-04T15:39:52Z",
"timestamp": 1614872392000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-04T16:59:34Z",
"timestamp": 1641315574000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-16T13:22:14Z",
"timestamp": 1676553734004
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
4
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"member": "21476",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.36000",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
4
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
4
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
9
]
]
},
"publisher": "Mediscience GmbH",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://schw-aerztej.healthbooktimes.org/article/29676-response-to-nigella-sativa-in-patients-with-confirmed-and-suspected-covid-19"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Response to Nigella sativa in Patients with Confirmed and Suspected COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article"
}