Low blood zinc concentrations in patients with poor clinical outcome during SARS-CoV-2 infection: is there a need to supplement with Zinc COVID-19 patients?
et al., Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection, doi:10.1016/j.jmii.2021.01.012, Feb 2021
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000028 from 47 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
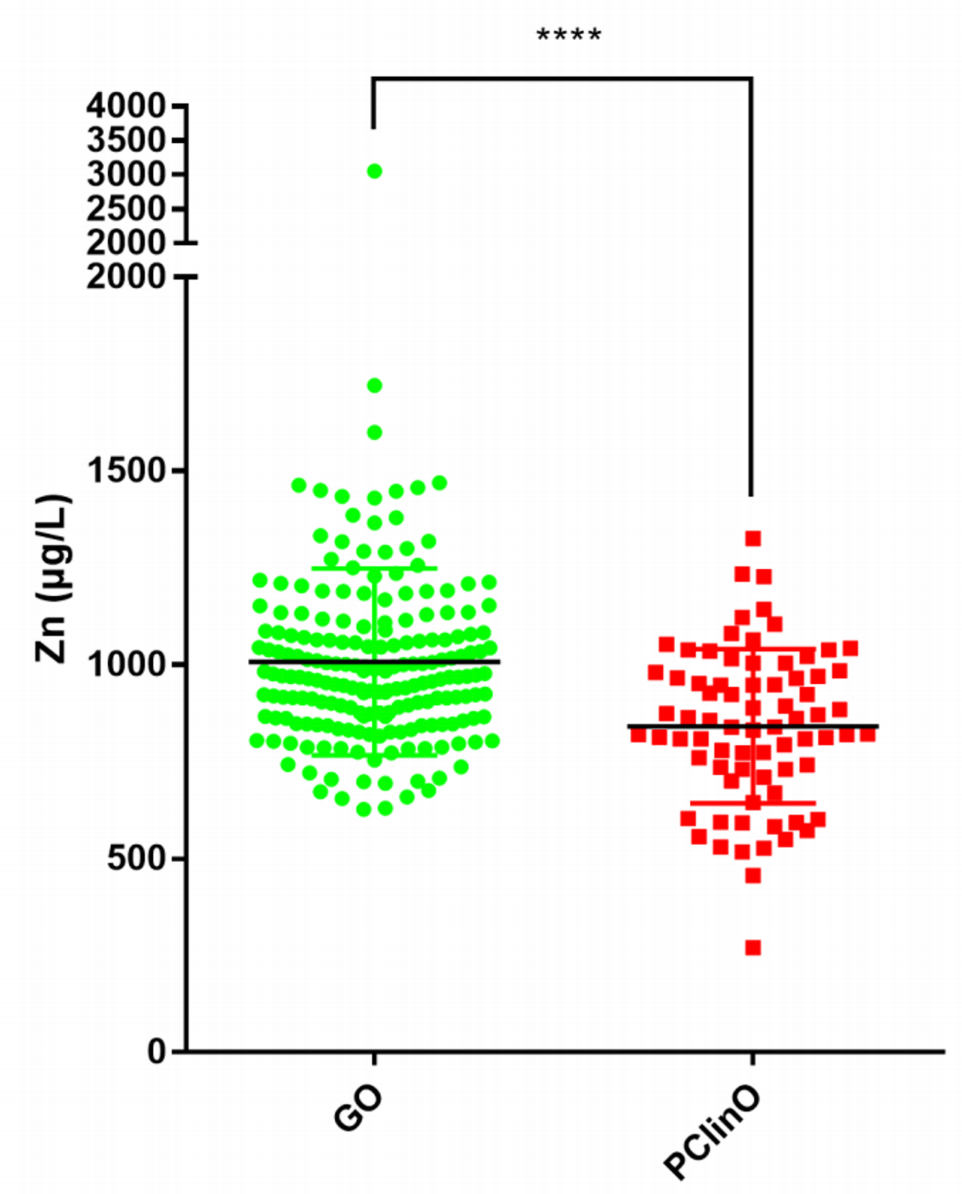
Retrospective 275 patients showing zinc levels significantly lower in patients with poor outcomes, 840 vs. 970 µg/L, p< 0.0001.
Dubourg et al., 13 Feb 2021, peer-reviewed, 8 authors.
Low blood zinc concentrations in patients with poor clinical outcome during SARS-CoV-2 infection: is there a need to supplement with zinc COVID-19 patients?
Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection, doi:10.1016/j.jmii.2021.01.012
Among 275 patients with COVID-19, we found that median blood zinc level was significantly lower in patients with poor clinical outcome (N Z 75) as compared to patients with good clinical outcome (N Z 200) (840 mg/L versus 970 mg/L; p < 0.0001), suggesting that zinc supplementation could be useful for patients with severe COVID-19.
Declaration of competing interest None to declare.
Appendix A. Supplementary data Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmii.2021.01.012.
References
Andreani, Bideau, Duflot, Jardot, Rolland et al., In vitro testing of combined hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin on SARS-CoV-2 shows synergistic effect, Microb Pathog
Carlucci, Ahuja, Petrilli, Rajagopalan, Jones et al., Zinc sulfate in combination with a zinc ionophore may improve outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, J Med Microbiol
Derwand, Scholz, Zelenko, COVID-19 outpatients: early risk-stratified treatment with zinc plus low-dose hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin: a retrospective case series study, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Frank, Hughes, Bankson, Roberts, Effects of anticoagulants and contemporary blood collection containers on aluminum, copper, and zinc results, Clin Chem
Gautret, Lagier, Parola, Hoang, Meddeb et al., Clinical and microbiological effect of a combination of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin in 80 COVID-19 patients with at least a six-day follow up: a pilot observational study, Trav Med Infect Dis
Jothimani, Kailasam, Danielraj, Nallathambi, Ramachandran et al., COVID-19: poor outcomes in patients with Zinc deficiency, Int J Infect Dis
Lagier, Million, Gautret, Colson, Cortaredona et al., Outcomes of 3,737 COVID-19 patients treated with hydroxychloroquine/azithromycin and other regimens in Marseille, France: a retrospective analysis, Trav Med Infect Dis
Velthuis, Van Den Worm, She, Sims, Baric et al., Zn(2þ) inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture, PLoS Pathog
Wang, Song, Efficacy of zinc given as an adjunct to the treatment of severe pneumonia: a meta-analysis of randomized, double-blind and placebo-controlled trials, Clin Res J
Wessels, Rolles, Rink, The potential impact of zinc supplementation on COVID-19 pathogenesis, Front Immunol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jmii.2021.01.012",
"ISSN": [
"1684-1182"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmii.2021.01.012",
"alternative-id": [
"S1684118221000268"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Low blood zinc concentrations in patients with poor clinical outcome during SARS-CoV-2 infection: is there a need to supplement with zinc COVID-19 patients?"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmii.2021.01.012"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2021 Taiwan Society of Microbiology. Published by Elsevier Taiwan LLC."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dubourg",
"given": "Grégory",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lagier",
"given": "Jean-Christophe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6125-2805",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Brouqui",
"given": "Philippe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Casalta",
"given": "Jean-Paul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4728-7400",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Jacomo",
"given": "Véronique",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8006-7704",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "La Scola",
"given": "Bernard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rolain",
"given": "Jean-Marc",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Raoult",
"given": "Didier",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection",
"container-title-short": "Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-15T17:23:57Z",
"timestamp": 1613409837000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-15T15:47:39Z",
"timestamp": 1657900059000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-13T07:49:28Z",
"timestamp": 1715586568739
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 13,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1633046400000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-03T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1612310400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1684118221000268?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1684118221000268?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "997-1000",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104228",
"article-title": "In vitro testing of combined hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin on SARS-CoV-2 shows synergistic effect",
"author": "Andreani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "104228",
"journal-title": "Microb Pathog",
"key": "10.1016/j.jmii.2021.01.012_bib1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101663",
"article-title": "Clinical and microbiological effect of a combination of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin in 80 COVID-19 patients with at least a six-day follow up: a pilot observational study",
"author": "Gautret",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101663",
"journal-title": "Trav Med Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.jmii.2021.01.012_bib2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101791",
"article-title": "Outcomes of 3,737 COVID-19 patients treated with hydroxychloroquine/azithromycin and other regimens in Marseille, France: a retrospective analysis",
"author": "Lagier",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101791",
"journal-title": "Trav Med Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.jmii.2021.01.012_bib3",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106214",
"article-title": "COVID-19 outpatients: early risk-stratified treatment with zinc plus low-dose hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin: a retrospective case series study",
"author": "Derwand",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "106214",
"journal-title": "Int J Antimicrob Agents",
"key": "10.1016/j.jmii.2021.01.012_bib4",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "The potential impact of zinc supplementation on COVID-19 pathogenesis",
"author": "Wessels",
"first-page": "11",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.jmii.2021.01.012_bib5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176",
"article-title": "Zn(2+) inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture",
"author": "te Velthuis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog",
"key": "10.1016/j.jmii.2021.01.012_bib6",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/crj.12646",
"article-title": "Efficacy of zinc given as an adjunct to the treatment of severe pneumonia: a meta-analysis of randomized, double-blind and placebo-controlled trials",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "857",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Clin Res J",
"key": "10.1016/j.jmii.2021.01.012_bib7",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.014",
"article-title": "COVID-19: poor outcomes in patients with Zinc deficiency",
"author": "Jothimani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "343",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.jmii.2021.01.012_bib8",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/clinchem/47.6.1109",
"article-title": "Effects of anticoagulants and contemporary blood collection containers on aluminum, copper, and zinc results",
"author": "Frank",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1109",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Clin Chem",
"key": "10.1016/j.jmii.2021.01.012_bib9",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1099/jmm.0.001250",
"article-title": "Zinc sulfate in combination with a zinc ionophore may improve outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Carlucci",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1228",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "J Med Microbiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.jmii.2021.01.012_bib10",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 10,
"references-count": 10,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1684118221000268"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Low blood zinc concentrations in patients with poor clinical outcome during SARS-CoV-2 infection: is there a need to supplement with zinc COVID-19 patients?",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "54"
}
