Assessment of Serum Ferritin, Folate, Vitamin B12, C-reactive Protein, D-dimer and Homocysteine in Patients with Severe and Critical Covid-19 Infection
et al., Indian Journal of Forensic Medicine & Toxicology, doi:10.37506/ijfmt.v15i4.18454, Sep 2021
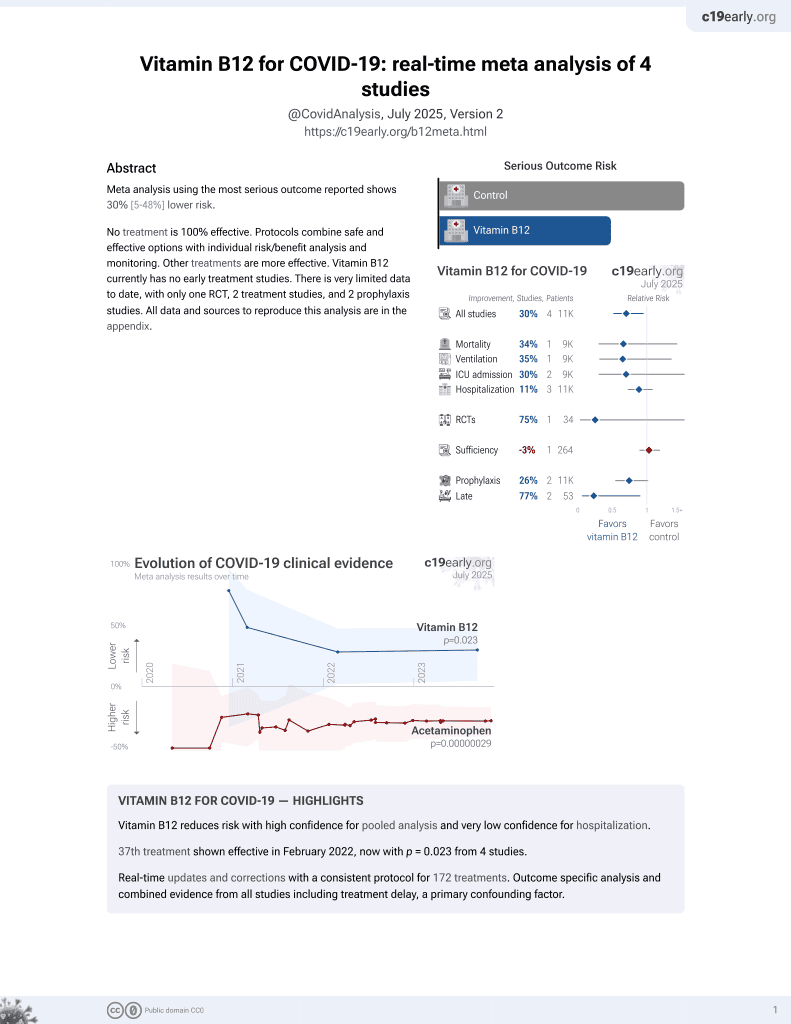
38th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2022, now with p = 0.023 from 4 studies.
Lower risk for recovery.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
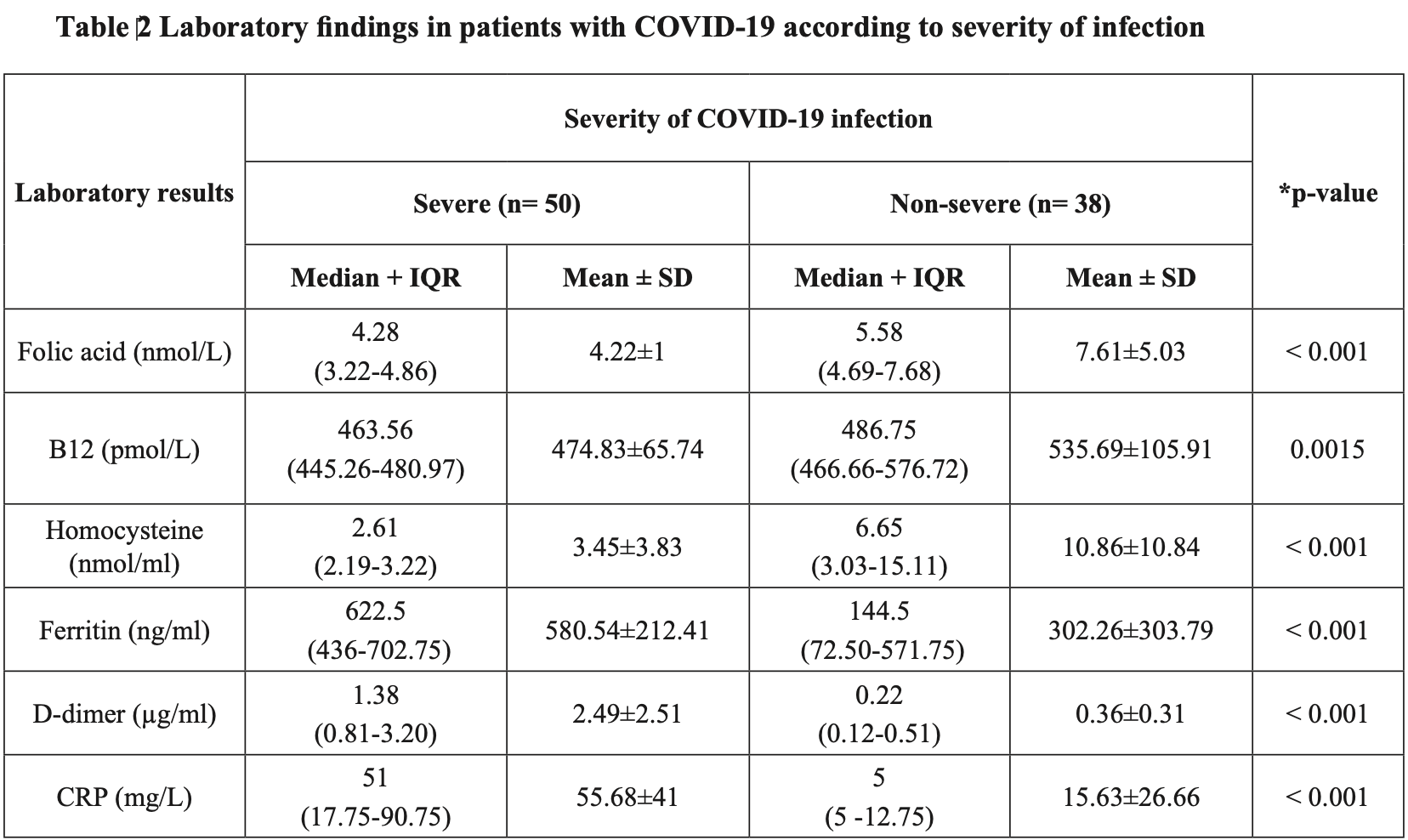
Analysis of 88 COVID-19 patients showing lower folic acid and vitamin B12 levels in severe vs. non-severe cases.
Study covers vitamin B9 and vitamin B12.
Al-Alwan et al., 5 Sep 2021, retrospective, Iraq, peer-reviewed, 3 authors, study period October 2020 - December 2020.
Assessment of Serum Ferritin, Folate, Vitamin B12, C-reactive Protein, D-dimer and Homocysteine in Patients with Severe and Critical Covid-19 Infection
Background: Corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic need urgent measurement and correlation of laboratory parameters in severe and non-severe cases. Serum ferritin, folic acid, vitamin B12, C-reactive protein, D-dimer and homocysteine was measured in patients who were infected with COVID-19.
Aim of the Study : To evaluate the usefulness of serum ferritin, folate, B12, C-reactive protein, D-dimer and homocysteine level as biomarkers for prediction of patients with severe and critical COVID-19 infection.
Subject, Material, Method: A cross sectional study was conducted at AL-Kindy hospital, Baghdad, Iraq from October 2020 to December 2020. Serum ferritin, folate, Vitamin B12, C-reactive protein, homocysteine and blood D-dimer were measured in 88 patients who suffered from COVID-19 infection, 50 cases with severe infection and 38 with non-severe infection. The age range of patients between 20-59 years old. Samples were collected from AL-Kindy hospital, Baghdad. Result: Serum folic acid was significantly low in severe group than in non-severe group, while serum ferritin, CRP and blood D-dimer were high in severe group than in non-severe group.
Conclusion: In this study, measurement of serum ferritin, CRP and blood D-dimer were important in follow up of patients who infected with the novel virus as the level of them were higher in severe than in nonsevere cases. Folic acid has role in determining the severity of COVID-19 infection bacause level was low in patients with severe than non-severe infection.
Conflict of Interest: No Source of Funding: Self funded Ethical Clearance: Not Required
References
Cheng, Li, Li, Liu, Yan et al., Ferritin in the corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A systematic review and metaanalysis, Journal of clinical laboratory analysis
Dae-Gyun Ahn, Shin, Kim, Lee, Kim, Current Status of Epidemiology, Diagnosis, Therapeutics, and Vaccines for Novel Corona virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), Microbiol Biotechnology
Dalbeni, Bevilacqua, Excessive vitamin B12 and poor outcome in COVID-19 pneumonia. Nutrition, metabolism & cardiovascular diseases
He, Wang, Li, Shi, Main Clinical Features of COVID-19 and Potential Prognostic and Therapeutic Value of the Microbiota in SARS-CoV-2 Infections, Frontiers in microbiology
Kien, Wee, COVID-19's toll on the elderly and those with diabetes mellitus -Is vitamin B12 deficiency an accomplice?, Medical hypotheses
Li, Zhao, Wei, Dynamic relationship between D-dimer and COVID-19 severity, British journal of haematology
Liu, Li, Xu, Wu, Luo et al., Prognostic value of interleukin-6, C-reactive protein, and procalcitonin in patients with COVID-19, Journal of clinical virology
Luo, Zhou, Yan, Guo, Wang, Prognostic value of C-reactive protein in patients with COVID-19, Clinical infectious diseases
Michael, Helena Santos De Oliveira, Benoit, Plebania, Lippia, Hematologic, biochemical and immune biomarker abnormalities associated with severe illness and mortality in corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a meta-analysis, Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine
Phua, Weng, Ling, Egi, Lim, Intensive care management of corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19): challenges and recommendations, The lancet respiratory medicine
Ponti, Ruini, Tomasi, Homocysteine as a potential predictor of cardiovascular risk in patients with COVID-19, Med Hypotheses
Vargas, Cortés-Rojo, Ferritin levels and COVID-19, Pan American journal of public health
Vidali, Morosetti, Cossu, Luisa, Luisi, D-dimer as an indicator of prognosis in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a systematic review, European respiratory journal open research
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.37506/ijfmt.v15i4.18454",
"ISSN": [
"0973-9130",
"0973-9122"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.37506/ijfmt.v15i4.18454",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background: Corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic need urgent measurement and correlationof laboratory parameters in severe and non-severe cases. Serum ferritin, folic acid, vitamin B12, C-reactiveprotein, D-dimer and homocysteine was measured in patients who were infected with COVID-19.Aim of the Study : To evaluate the usefulness of serum ferritin, folate, B12, C-reactive protein, D-dimer andhomocysteine level as biomarkers for prediction of patients with severe and critical COVID-19 infection.Subject, Material, Method: A cross sectional study was conducted at AL-Kindy hospital, Baghdad, Iraqfrom October 2020 to December 2020. Serum ferritin, folate, Vitamin B12, C-reactive protein, homocysteineand blood D-dimer were measured in 88 patients who suffered from COVID-19 infection, 50 cases withsevere infection and 38 with non-severe infection. The age range of patients between 20-59 years old.Samples were collected from AL-Kindy hospital, Baghdad.Result: Serum folic acid was significantly low in severe group than in non-severe group, while serumferritin, CRP and blood D-dimer were high in severe group than in non-severe group.Conclusion: In this study, measurement of serum ferritin, CRP and blood D-dimer were important in followup of patients who infected with the novel virus as the level of them were higher in severe than in nonseverecases. Folic acid has role in determining the severity of COVID-19 infection bacause level was lowin patients with severe than non-severe infection.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nawar Mazin AL-Alwan",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zainab A. Razak Al-Sharifi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abbas Hashim Abdulsalam",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Indian Journal of Forensic Medicine & Toxicology",
"container-title-short": "Indian Journal of Forensic Medicine & Toxicology",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-05T08:48:54Z",
"timestamp": 1662367734000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-26T18:59:25Z",
"timestamp": 1708973965000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-20T12:35:31Z",
"timestamp": 1716208531213
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issue": "4",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
5
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "4",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
5
]
]
}
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://medicopublication.com/index.php/ijfmt/article/download/18454/16088",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://medicopublication.com/index.php/ijfmt/article/download/18454/16088",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "22708",
"original-title": [],
"page": "353-358",
"prefix": "10.37506",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
5
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "Institute of Medico-legal Publications Private Limited",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://medicopublication.com/index.php/ijfmt/article/view/18454"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Assessment of Serum Ferritin, Folate, Vitamin B12, C-reactive Protein, D-dimer and Homocysteine in Patients with Severe and Critical Covid-19 Infection",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "15"
}
alalwan