Haematological parameters in COVID-19 patients: association with severity of the disease
et al., Archives of Razi Institute, doi:10.22092/ARI.2022.358363.2208, May 2022
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000028 from 47 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
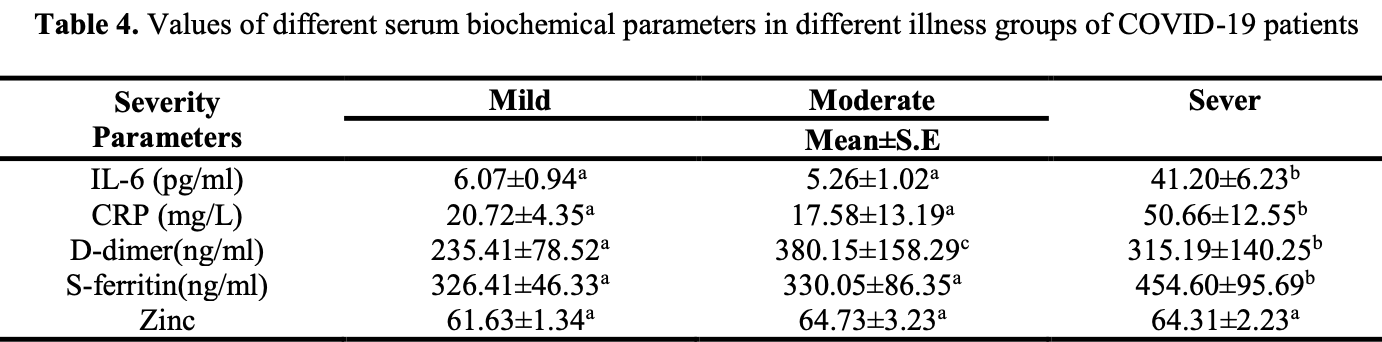
Retrospective 76 COVID-19 patients in Iraq, showing no significant difference in zinc levels based on severity.
Abdulla et al., 31 May 2022, multiple countries, peer-reviewed, 3 authors, study period September 2020 - March 2021.
Contact: alhussainybio@yahoo.com.
Hematological Parameters in COVID-19 Patients: Association with Severity of the Disease
doi:10.22092/ARI.2022.358363.2208
Introduction The novel coronavirus (COVID-19) is responsible for severe acute respiratory coronavirus syndrome (SARS-CoV-2; previously known as 2019-nCoV) and has symptoms ranging from extremely mild to lifethreatening (1). On January 30, 2020, the World Health Organization declared COVID-19 a global public health emergency due to the disease's rapid spread, which was already seen in December 2019 and January 2020 (2). Some complications include pneumonia, acute severe respiratory distress syndrome, renal insufficiency, and death (3). Excessive inflammatory responses to SARS-CoV-2 are thought to impact disease severity and mortality in COVID-19-infected patients significantly. It has been linked to high levels of circulating cytokines, severe lymphopenia, and significant mononuclear cell infiltration in the lungs, spleen, heart, kidney, and lymph nodes (2). The World Health Organization (WHO) classified cases into three severity levels based on clinical symptoms: mild, severe, and critical. The Creactive protein (CRP) is a systemic inflammatory response characterized by increased pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin-6. It can be triggered by
Authors' Contribution
Ethics The study protocol was reviewed by the University Committee on health studies which uses the guidelines of MOH and MOHSER, and approved under number 389 in / 2020.
Conflict of Interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
Bajgain, Badal, Bajgain, Santana, Prevalence of comorbidities among individuals with COVID-19: A rapid review of current literature, Am J Infect Control
Cekerevac, Turnic, Draginic, Andjic, Zivkovic et al., Predicting severity and intrahospital mortality in COVID-19: the place and role of oxidative stress, Oxid Med Cell Longev
Chan, Rout, Use of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratios in COVID-19, J Clin Med Res
Commission, Translation: Diagnosis and treatment protocol for novel coronavirus pneumonia (trial version 7)
Coperchini, Chiovato, Croce, Magri, Rotondi, The cytokine storm in COVID-19: An overview of the involvement of the chemokine/chemokine-receptor system, Cytokine Growth Factor Rev
Fa, Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and lymphocyte-to-C-reactive protein ratio in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a meta-analysis, J Med Virol
Fox, Akmatbekov, Harbert, Li, Brown et al., Pulmonary and cardiac pathology in African American patients with COVID-19: an autopsy series from New Orleans, Lancet Respir Med
Gao, Xu, Sun, Wang, Guo et al., A systematic review of asymptomatic infections with COVID-19, J Microbiol Immunol Infect
Gennaro, Pizzol, Marotta, Antunes, Racalbuto et al., Coronavirus diseases (COVID-19) current status and future perspectives: a narrative review, Int J Environ Res Public Health
Gong, Dong, Xia, Huang, Wang et al., Correlation analysis between disease severity and inflammation-related parameters in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia, MedRxiv
Honore, Hoste, Molnár, Jacobs, Boyau et al., Cytokine removal in human septic shock: where are we and where are we going?, Ann Intensive Care
Klein, Morgan, The impact of sex and gender on immunotherapy outcomes, Biol Sex Differ
Kwon, Jang, Kim, Lee, Nam et al., The usefulness of C-reactive protein and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio for predicting the outcome in hospitalized patients with liver cirrhosis, BMC Gastroenterol
Lai, Shih, Ko, Tang, Hsueh, Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19): The epidemic and the challenges, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Le, Li, Yuan, Shord, Nie et al., FDA approval summary: tocilizumab for treatment of chimeric antigen receptor T cell-induced severe or life-threatening cytokine release syndrome, Oncologist
Lin, Ding, Xie, Sun, Li et al., Asymptomatic novel coronavirus pneumonia patient outside Wuhan: the value of CT images in the course of the disease, Clin Imaging
Liu, Du, Chen, Peng, Wang, Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as an independent risk factor for mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, J Infect
Liu, Li, Xu, Wu, Luo et al., Prognostic value of interleukin-6, C-reactive protein, and procalcitonin in patients with COVID-19, J Clin Virol
Mo, Xing, Xiao, Deng, Zhao et al., Clinical characteristics of refractory COVID-19 pneumonia in Wuhan, Clin Infect Dis
Moore, June, Cytokine release syndrome in severe COVID-19, Science
Mousavi, Rostami, Rostami, Mousavi, Mirhoseini, Hematologic predictors of mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a comparative study, Hematology
Ns, Abdulla, Kunwar, Mohammed, Mohammed et al., Coronaviruses seven outbreaks associated with OC43, 229E, severe acute respiratory syndrome-CoV1, NL63, HKU1, Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus, and severe acute respiratory syndrome-CoV2. Drug Invent Today
Organization, Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): situation report
Peckham, De Gruijter, Raine, Radziszewska, Ciurtin et al., Male sex identified by global COVID-19 meta-analysis as a risk factor for death and ITU admission, Nat Commun
Pimentel, Redfern, Hatch, Young, Tarassenko et al., Trajectories of vital signs in patients with COVID-19, Resuscitation
Querol-Ribelles, Tenias, Grau, Querol-Borras, Climent et al., Plasma d-dimer levels correlate with outcomes in patients with communityacquired pneumonia, Chest
Quismondo, Manso, Colmenares, Alos, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality from COVID-19 in patients with haematological malignancies, Eur J Haematol
Ruan, Yang, Wang, Jiang, Song, Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China, Intensive Care Med
Sanchez-Pina, Rodriguez, Castro, None
Soni, Evaluation of eosinopenia as a diagnostic and prognostic indicator in COVID-19 infection, Int J Lab Hematol
Usul, Şan, Bekgöz, Şahin, Role of hematological parameters in COVID-19 patients in the emergency room, Biomark Med
Velavan, Meyer, The COVID-19 epidemic. Tropical medicine & international health
Wang, C-reactive protein levels in the early stage of COVID-19, Med Mal Infect
Wang, Wang, Qu, Wang, Zhou et al., The RNA genome of hepatitis E virus robustly triggers an antiviral interferon response, Hepatology
Warusevitane, Karunatilake, Sim, Smith, Roffe, Early diagnosis of pneumonia in severe stroke: clinical features and the diagnostic role of C-reactive protein, PloS one
Wool, Miller, The impact of COVID-19 disease on platelets and coagulation, Pathobiology
Xu, Shi, Wang, Zhang, Huang et al., Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome, Lancet Respir Med
Zahorec, Hulin, Zahorec, Rationale Use of Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio for early diagnosis and stratification of COVID-19, Bratisl Lek Listy
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.22092/ari.2022.358363.2208",
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.22092/ari.2022.358363.2208",
"author": [
{
"family": "Ali. Abdulla",
"given": "Anwar"
},
{
"family": "Abdulaali Abed",
"given": "Thekra"
},
{
"family": "Fadhel Abbas Awadh",
"given": "Eman"
}
],
"container-title": "Archives of Razi Institute",
"container-title-short": "Archives of Razi Institute",
"issue": "Online First",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5
]
]
},
"journalAbbreviation": "Archives of Razi Institute",
"language": "eng",
"publisher": "Razi Vaccine & Serum Research Institute",
"publisher-place": "IR",
"title": "Haematological parameters in COVID-19 patients: association with severity of the disease",
"type": "article-journal"
}
