Zinc reduces COVID-19 risk: real-time meta analysis of 47 studies
, Dec 2025
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000028 from 47 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,300+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
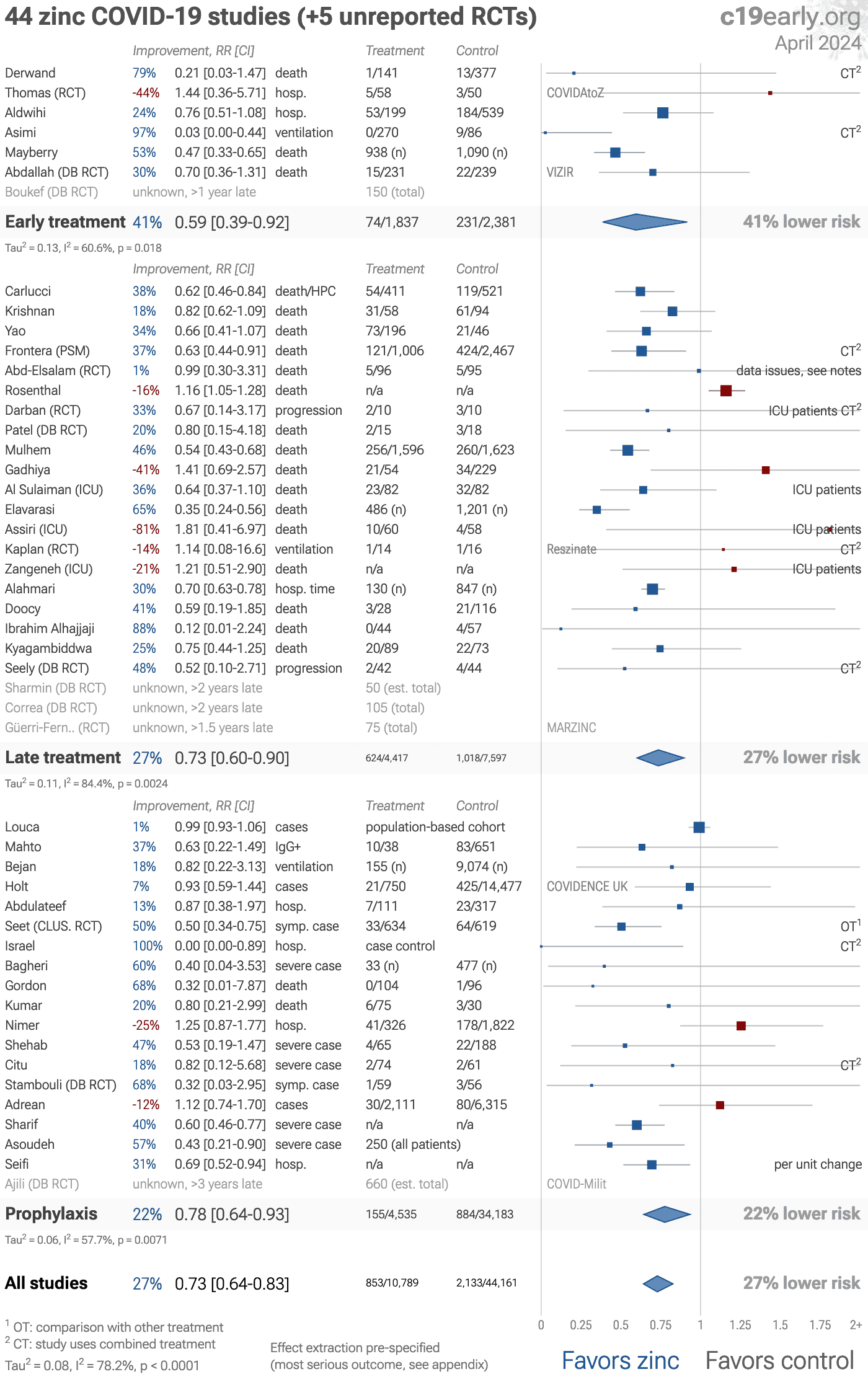
Significantly lower risk is seen for mortality, ventilation, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance. 20 studies from 19 independent teams in 10 countries show significant benefit.
Meta analysis using the most serious outcome reported shows 28% [18‑36%] lower risk. Results are similar for Randomized Controlled Trials, higher quality studies, peer-reviewed studies, and after excluding studies using combined treatment.
24 sufficiency studies analyze outcomes based on serum levels, showing 69% [60‑76%] lower risk for patients with higher zinc levels.
Results are robust — in exclusion sensitivity analysis 22 of 47 studies must be excluded to avoid finding statistically significant efficacy in pooled analysis.
Control Zinc
8 studies use combined treatments. After exclusion the risk reduction is 27% [17‑35%] compared to 28% [18‑36%].
4 RCTs with 900 patients have not reported results (up to 5 years late).
The European Food Safety Authority has found evidence for a causal relationship between the intake of zinc and optimal immune system function1,2. Over-supplementation may be detrimental3. Bioaccessibility of supplements varies widely4.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols combine safe and effective options with individual risk/benefit analysis and monitoring. Other treatments are more effective. Dietary sources may be preferred. The quality of non-prescription supplements varies widely5-7. All data and sources to reproduce this analysis are in the appendix.
6 other meta analyses show significant improvements with zinc for mortality8-12, severity13, and cases13.
1.
Tabatabaeizadeh, S., Zinc supplementation and COVID-19 mortality: a meta-analysis, European Journal of Medical Research, doi:10.1186/s40001-022-00694-z.
2.
Olczak-Pruc et al., The effect of zinc supplementation on the course of COVID-19 – A systematic review and meta-analysis, Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine, doi:10.26444/aaem/155846.
3.
Xie et al., Micronutrient perspective on COVID-19: Umbrella review and reanalysis of meta-analyses, Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, doi:10.1080/10408398.2023.2174948.
4.
Abuhelwa, Z., Do Zinc Supplements Reduce Mortality in Patients with COVID-19?, Translation: The University of Toledo Journal of Medical Sciences, doi:10.46570/utjms.vol11-2023-749.
Covid Analysis et al., Dec 2025, preprint, 1 author.
