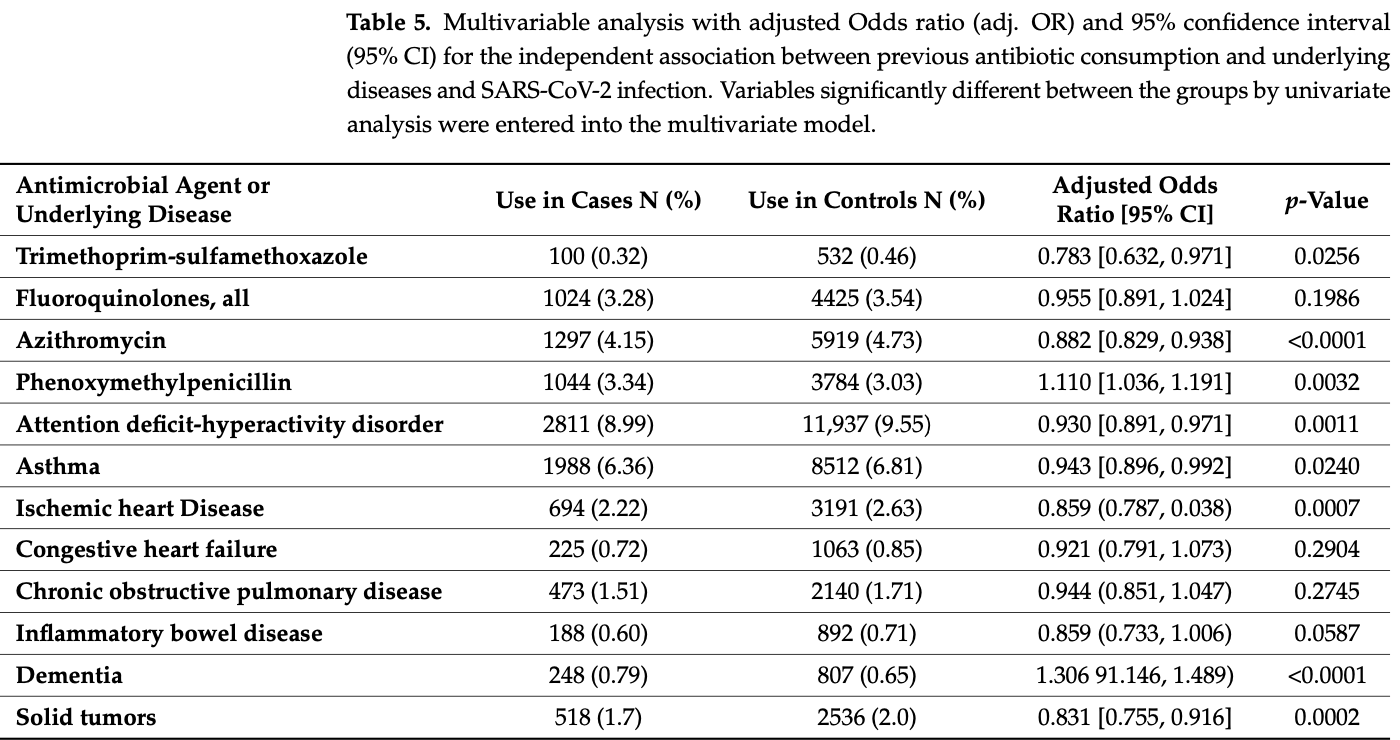
The Association between Previous Antibiotic Consumption and SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Population-Based Case-Control Study
et al., Antibiotics, doi:10.3390/antibiotics12030587, Mar 2023
Retrospective 31,260 COVID-19 cases and 125,039 matched controls, showing lower risk of COVID-19 with previous azithromycin use.
|
risk of case, 11.8% lower, OR 0.88, p < 0.001, treatment 1,297 of 31,260 (4.1%) cases,
5,919 of 125,039 (4.7%) controls, NNT 47, adjusted per study, case control OR, multivariable.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Dugot et al., 15 Mar 2023, retrospective, Israel, peer-reviewed, 7 authors, study period 1 March, 2020 - 31 December, 2020.
Contact: matan.dugot@gmail.com (corresponding author), emarzon@leumit.co.il, shaias@ariel.ac.il.
The Association between Previous Antibiotic Consumption and SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Population-Based Case-Control Study
Antibiotics, doi:10.3390/antibiotics12030587
Background: The susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection is complex and not yet fully elucidated, being related to many variables; these include human microbiome and immune status, which are both affected for a long period by antibiotic use. We therefore aimed to examine the association of previous antibiotic consumption and SARS-CoV-2 infection in a large-scale population-based study with control of known confounders. Methods: A matched case-control study was performed utilizing the electronic medical records of a large Health Maintenance Organization. Cases were subjects with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection (n = 31,260), matched individually (1:4 ratio) to controls without a positive SARS-CoV-2 test (n = 125,039). The possible association between previous antibiotic use and SARS-CoV-2 infection was determined by comparing antibiotic consumption in the previous 6 and 12 months between the cases and controls. For each antibiotic consumed we calculated the odds ratio (OR) for documented SARS-CoV-2 infection, 95% confidence interval (CI), and p-value using univariate and multivariate analyses. Results: The association between previous antibiotic consumption and SARS-CoV-2 infection was complex and bi-directional. In the multivariate analysis, phenoxymethylpenicillin was associated with increased rate of SARS-CoV-2 infection (OR 1.110, 95% CI: 1.036-1.191) while decreased rates were associated with previous consumption of trimethoprim-sulfonamides (OR 0.783, 95% CI: 0.632-0.971) and azithromycin (OR 0.882, 95% CI: 0.829-0.938). Fluroquinolones were associated with decreased rates (OR 0.923, 95% CI: 0.861-0.989) only in the univariate analysis. Previous consumption of other antibiotics had no significant association with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Conclusions: Previous consumption of certain antibiotic agents has an independent significant association with increased or decreased rates of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Plausible mechanisms, that should be further elucidated, are mainly antibiotic effects on the human microbiome and immune modulation.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Adams, Katz, Grandpre, Population-Based Estimates of Chronic Conditions Affecting Risk for Complications from Coronavirus Disease, United States, Emerg. Infect. Dis, doi:10.3201/eid2608.200679
De Castilhos, Zamir, Hippchen, Rohrbach, Schmidt et al., Severe Dysbiosis and Specific Haemophilus and Neisseria Signatures as Hallmarks of the Oropharyngeal Microbiome in Critically III Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Patients, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciab902
Deng, Zhou, Hou, Silver, Wong et al., The Prevalence of Depression, Anxiety, and Sleep Disturbances in COVID-19 Patients: A Meta-Analysis, Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1111/nyas.14506
Finlay, Amato, Azad, Blaser, Bosch et al., The Hygiene Hypothesis, the COVID Pandemic, and Consequences for the Human Microbiome, doi:10.1073/pnas.2010217118
Galley, Dhillon, Paterson, Webster, Effect of Ciprofloxacin on the Activation of the Transcription Factors Nuclear Factor KappaB, Activator Protein-1 and Nuclear Factor-Interleukin-6, and Interleukin-6 and Interleukin-8 MRNA Expression in a Human Endothelial Cell Line, Clin. Sci, doi:10.1042/CS20000073
Gang, Wang, Xue, Zhang, Microbiota and COVID-19: Long-Term and Complex Influencing Factors, Front. Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2022.963488
Green, Merzon, Vinker, Golan-Cohen, Israel et al., A Higher Frequency of Physical Activity Is Associated with Reduced Rates of SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Eur. J. Gen. Pract, doi:10.1080/13814788.2022.2138855
Green, Merzon, Vinker, Golan-Cohen, Magen, COVID-19 Susceptibility in Bronchial Asthma, J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract, doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2020.11.020
Gregory, Slaughter, Duffus, Smith, Lestourgeon et al., COVID-19 Severity Is Tripled in the Diabetes Community: A Prospective Analysis of the Pandemic's Impact in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc20-2260
Guh, Kutty, Clostridioides Difficile Infection, Ann. Intern. Med, doi:10.7326/AITC201810020
Gupta, Singh, Mani, Dysbiosis of human microbiome and infectious diseases, Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci
Hemmi, Makino, Yokoo, Kano, Asami et al., Consumption of yogurt fermented with Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus OLL1073R-1 augments serum antibody titers against seasonal influenza vaccine in healthy adults, Biosci. Microbiota Food Health, doi:10.12938/bmfh.2022-037
Hernández-Terán, Vega-Sánchez, Mejía-Nepomuceno, Serna-Muñoz, Rodríguez-Llamazares et al., Microbiota composition in the lower respiratory tract is associated with severity in patients with acute respiratory distress by influenza, Virol. J, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-01979-3
Hu, Liu, Fan, Zheng, Wen et al., Multi-omics association analysis reveals interactions between the oropharyngeal microbiome and the metabolome in pediatric patients with influenza A virus pneumonia, Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2022.1011254
Huang, Lu, Huang, Wang, Ling et al., Obesity in Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154378
Jackson, Brown, Shahab, Steptoe, Fancourt, Smoking and Inequalities: A Study of 53 002 Adults in the UK, Tob. Control, doi:10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2020-055933
Joshee, Vatti, Chang, Long-Term Effects of COVID-19, Mayo Clin. Proc, doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.12.017
Karampela, Dalamaga, Could Respiratory Fluoroquinolones, Levofloxacin and Moxifloxacin Prove to Be Beneficial as an Adjunct Treatment in COVID-19?, Arch. Med. Res, doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.06.004
Kournoutou, Dinos, Azithromycin through the Lens of the COVID-19 Treatment, Antibiotics, doi:10.3390/antibiotics11081063
Liu, Cao, Du, Zhi, Prevalence of Comorbid Asthma and Related Outcomes in COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract, doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2020.11.054
Ludvigsson, Systematic Review of COVID-19 in Children Shows Milder Cases and a Better Prognosis than Adults, Acta Paediatr, doi:10.1111/apa.15270
Mainguy-Seers, Vargas, Labrecque, Bédard, Hélie et al., Randomised Study of the Immunomodulatory Effects of Azithromycin in Severely Asthmatic Horses, Vet. Rec, doi:10.1136/vr.105260
Marciniec, Beberok, Pęcak, Boryczka, Wrześniok, Ciprofloxacin and Moxifloxacin Could Interact with SARS-CoV-2 Protease: Preliminary in Silico Analysis, Pharmacol. Rep, doi:10.1007/s43440-020-00169-0
Mcdonald, Effects of Short-and Long-Course Antibiotics on the Lower Intestinal Microbiome as They Relate to Traveller's Diarrhea, J. Travel Med, doi:10.1093/jtm/taw084
Merenstein, Bushman, Collman, Alterations in the Respiratory Tract Microbiome in COVID-19: Current Observations and Potential Significance, Microbiome, doi:10.1186/s40168-022-01342-8
Merenstein, Liang, Whiteside, Cobián-Güemes, Merlino et al., Signatures of COVID-19 Severity and Immune Response in the Respiratory Tract Microbiome, MBio, doi:10.1128/mBio.01777-21
Merzon, Tworowski, Gorohovski, Vinker, Golan Cohen et al., Low Plasma 25(OH) Vitamin D Level Is Associated with Increased Risk of COVID-19 Infection: An Israeli Population-Based Study, FEBS J, doi:10.1111/febs.15495
Merzon, Weiss, Cortese, Rotem, Schneider et al., The Association between ADHD and the Severity of COVID-19 Infection, J. Atten. Disord, doi:10.1177/10870547211003659
Merzon, Weiss, Krone, Cohen, Ilani et al., Clinical and Socio-Demographic Variables Associated with the Diagnosis of Long COVID Syndrome in Youth: A Population-Based Study, Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph19105993
Moreira-Rosário, Marques, Pinheiro, Araújo, Ribeiro et al., Gut Microbiota Diversity and C-Reactive Protein Are Predictors of Disease Severity in COVID-19 Patients, Front. Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2021.705020
Msemburi, Karlinsky, Knutson, Aleshin-Guendel, Chatterji et al., The WHO Estimates of Excess Mortality Associated with the COVID-19 Pandemic, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-05522-2
Niu, Cui, Yang, Li, Yao et al., Microbiota-derived acetate enhances host antiviral response via NLRP3, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-023-36323-4
Patangia, Anthony Ryan, Dempsey, Paul Ross, Stanton, Impact of Antibiotics on the Human Microbiome and Consequences for Host Health, MicrobiologyOpen, doi:10.1002/mbo3.1260
Quadery, John, Samuel, Ramanna, Chattopadhyay et al., Improved Outcomes with Trimethoprim or Cotrimoxazole in Patients with Severe COVID-19: A District Hospital Experience, Soc. Sci. Res. Netw
Quadery, John, Sinha, Bhattacharjee, Bose et al., Cotrimoxazole in Hospitalised Patients with Severe COVID-19-Interim Results from the CoTroxCov Study, Eur. Respir. J
Ramirez, Guarner, Bustos Fernandez, Maruy, Sdepanian et al., Antibiotics as Major Disruptors of Gut Microbiota, Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2020.572912
Reinold, Farahpour, Fehring, Dolff, Konik et al., A Pro-Inflammatory Gut Microbiome Characterizes SARS-CoV-2 Infected Patients and a Reduction in the Connectivity of an Anti-Inflammatory Bacterial Network Associates with Severe COVID-19, Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2021.747816
Sagie, Na'amnih, Frej, Cohen, Alpert et al., Correlates of Hospitalizations in Internal Medicine Divisions among Israeli Adults of Different Ethnic Groups with Hypertension, Diabetes and Cardiovascular Diseases, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0215639
Schild, Knobloch, Yakin, Jungck, Urban et al., IL-5 Release of CD4+ Non-Effector Lymphocytes Is Increased in COPD-Modulating Effects of Moxifloxacin and Dexamethasone, Int. Immunopharmacol
Schult, Reitmeier, Koyumdzhieva, Lahmer, Middelhoff et al., Gut Bacterial Dysbiosis and Instability Is Associated with the Onset of Complications and Mortality in COVID-19, Gut Microbes, doi:10.1080/19490976.2022.2031840
Seligman, Ferranna, Bloom, Social Determinants of Mortality from COVID-19: A Simulation Study Using NHANES, PLoS Med, doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1003490
Shalit, Kletter, Halperin, Waldman, Vasserman et al., Immunomodulatory Effects of Moxifloxacin in Comparison to Ciprofloxacin and G-CSF in a Murine Model of Cyclophosphamide-Induced Leukopenia+, Eur. J Haematol, doi:10.1034/j.1600-0609.2001.066005287.x
Shapiro, Yavne, Shepshelovich, Predicting Which Patients Are at Risk for Clinical Deterioration in COVID-19: A Review of the Current Models in Use, Isr. Med. Assoc. J
Siddiqui, Das, Alapan, Cotrimoxazole in the Domiciliary Management of Patients with Severe COVID-19: A Case Series, J. Indian Med. Assoc
Tran, Sugamata, Hirose, Suzuki, Noguchi et al., Azithromycin, a 15-Membered Macrolide Antibiotic, Inhibits Influenza A(H1N1)Pdm09 Virus Infection by Interfering with Virus Internalization Process, J. Antibiot, doi:10.1038/s41429-019-0204-x
Treskova-Schwarzbach, Haas, Reda, Pilic, Borodova et al., Pre-Existing Health Conditions and Severe COVID-19 Outcomes: An Umbrella Review Approach and Meta-Analysis of Global Evidence, BMC Med, doi:10.1186/s12916-021-02058-6
Venditto, Haydar, Abdel-Latif, Gensel, Anstead et al., Immunomodulatory Effects of Azithromycin Revisited: Potential Applications to COVID-19, Front. Immunol
Verity, Okell, Dorigatti, Winskill, Whittaker et al., Estimates of the Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Model-Based Analysis, Lancet Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30243-7
Yamamoto, Saito, Tamura, Prawisuda, Mizutani et al., The Human Microbiome and COVID-19: A Systematic Review, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0253293
Yang, Bhargava, Mccloskey, Mao, Palsson et al., Antibiotic-Induced Changes to the Host Metabolic Environment Inhibit Drug Efficacy and Alter Immune Function, Cell Host Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.chom.2017.10.020
Yuhas, Berent, Ashkenazi, Effect of Rifampin on Production of Inflammatory Mediators in HepG2 Liver Epithelial Cells, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother, doi:10.1128/AAC.05149-11
Zuo, Zhang, Lui, Yeoh, Li et al., Alterations in Gut Microbiota of Patients with COVID-19 during Time of Hospitalization, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.06.048
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antibiotics12030587",
"ISSN": [
"2079-6382"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030587",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background: The susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection is complex and not yet fully elucidated, being related to many variables; these include human microbiome and immune status, which are both affected for a long period by antibiotic use. We therefore aimed to examine the association of previous antibiotic consumption and SARS-CoV-2 infection in a large-scale population-based study with control of known confounders. Methods: A matched case–control study was performed utilizing the electronic medical records of a large Health Maintenance Organization. Cases were subjects with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection (n = 31,260), matched individually (1:4 ratio) to controls without a positive SARS-CoV-2 test (n = 125,039). The possible association between previous antibiotic use and SARS-CoV-2 infection was determined by comparing antibiotic consumption in the previous 6 and 12 months between the cases and controls. For each antibiotic consumed we calculated the odds ratio (OR) for documented SARS-CoV-2 infection, 95% confidence interval (CI), and p-value using univariate and multivariate analyses. Results: The association between previous antibiotic consumption and SARS-CoV-2 infection was complex and bi-directional. In the multivariate analysis, phenoxymethylpenicillin was associated with increased rate of SARS-CoV-2 infection (OR 1.110, 95% CI: 1.036–1.191) while decreased rates were associated with previous consumption of trimethoprim-sulfonamides (OR 0.783, 95% CI: 0.632–0.971) and azithromycin (OR 0.882, 95% CI: 0.829–0.938). Fluroquinolones were associated with decreased rates (OR 0.923, 95% CI: 0.861–0.989) only in the univariate analysis. Previous consumption of other antibiotics had no significant association with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Conclusions: Previous consumption of certain antibiotic agents has an independent significant association with increased or decreased rates of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Plausible mechanisms, that should be further elucidated, are mainly antibiotic effects on the human microbiome and immune modulation.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"antibiotics12030587"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Adelson School of Medicine, Ariel University, Ariel 40700, Israel"
}
],
"family": "Dugot",
"given": "Matan",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Adelson School of Medicine, Ariel University, Ariel 40700, Israel"
},
{
"name": "Leumit Health Services, Tel Aviv 64738, Israel"
}
],
"family": "Merzon",
"given": "Eugene",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7244-0679",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Adelson School of Medicine, Ariel University, Ariel 40700, Israel"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ashkenazi",
"given": "Shai",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Leumit Health Services, Tel Aviv 64738, Israel"
},
{
"name": "Sackler Faculty of Medicine, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv 69978, Israel"
}
],
"family": "Vinker",
"given": "Shlomo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9435-7152",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Leumit Health Services, Tel Aviv 64738, Israel"
},
{
"name": "Sackler Faculty of Medicine, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv 69978, Israel"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Green",
"given": "Ilan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Leumit Health Services, Tel Aviv 64738, Israel"
},
{
"name": "Sackler Faculty of Medicine, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv 69978, Israel"
}
],
"family": "Golan-Cohen",
"given": "Avivit",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4389-8896",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Leumit Health Services, Tel Aviv 64738, Israel"
},
{
"name": "Sackler Faculty of Medicine, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv 69978, Israel"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Israel",
"given": "Ariel",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Antibiotics",
"container-title-short": "Antibiotics",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-15T09:53:44Z",
"timestamp": 1678874024000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-15T13:10:04Z",
"timestamp": 1678885804000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-16T04:45:25Z",
"timestamp": 1678941925135
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
15
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-15T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1678838400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2079-6382/12/3/587/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "587",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
15
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
15
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"key": "ref_1",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization (2023, February 04). WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-05522-2",
"article-title": "The WHO Estimates of Excess Mortality Associated with the COVID-19 Pandemic",
"author": "Msemburi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "130",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "613",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30243-7",
"article-title": "Estimates of the Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Model-Based Analysis",
"author": "Verity",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "669",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.12.017",
"article-title": "Long-Term Effects of COVID-19",
"author": "Joshee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "579",
"journal-title": "Mayo Clin. Proc.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/apa.15270",
"article-title": "Systematic Review of COVID-19 in Children Shows Milder Cases and a Better Prognosis than Adults",
"author": "Ludvigsson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1088",
"journal-title": "Acta Paediatr.",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Predicting Which Patients Are at Risk for Clinical Deterioration in COVID-19: A Review of the Current Models in Use",
"author": "Shapiro",
"first-page": "699",
"journal-title": "Isr. Med. Assoc. J.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph19105993",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_7",
"unstructured": "Merzon, E., Weiss, M., Krone, B., Cohen, S., Ilani, G., Vinker, S., Cohen-Golan, A., Green, I., Israel, A., and Schneider, T. (2022). Clinical and Socio-Demographic Variables Associated with the Diagnosis of Long COVID Syndrome in Youth: A Population-Based Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 19."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.1003888",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_8",
"unstructured": "Seligman, B., Ferranna, M., and Bloom, D.E. (2021). Social Determinants of Mortality from COVID-19: A Simulation Study Using NHANES. PLoS Med., 18."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2020-055933",
"article-title": "COVID-19, Smoking and Inequalities: A Study of 53 002 Adults in the UK",
"author": "Jackson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e111",
"journal-title": "Tob. Control.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154378",
"article-title": "Obesity in Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "154378",
"journal-title": "Metabolism",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "113",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/febs.15495",
"article-title": "Low Plasma 25(OH) Vitamin D Level Is Associated with Increased Risk of COVID-19 Infection: An Israeli Population-Based Study",
"author": "Merzon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3693",
"journal-title": "FEBS J.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "287",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12916-021-02058-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_12",
"unstructured": "Treskova-Schwarzbach, M., Haas, L., Reda, S., Pilic, A., Borodova, A., Karimi, K., Koch, J., Nygren, T., Scholz, S., and Schönfeld, V. (2021). Pre-Existing Health Conditions and Severe COVID-19 Outcomes: An Umbrella Review Approach and Meta-Analysis of Global Evidence. BMC Med., 19."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaip.2020.11.054",
"article-title": "Prevalence of Comorbid Asthma and Related Outcomes in COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "693",
"journal-title": "J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc20-2260",
"article-title": "COVID-19 Severity Is Tripled in the Diabetes Community: A Prospective Analysis of the Pandemic’s Impact in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes",
"author": "Gregory",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "526",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3201/eid2608.200679",
"article-title": "Population-Based Estimates of Chronic Conditions Affecting Risk for Complications from Coronavirus Disease, United States",
"author": "Adams",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1831",
"journal-title": "Emerg. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/nyas.14506",
"article-title": "The Prevalence of Depression, Anxiety, and Sleep Disturbances in COVID-19 Patients: A Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Deng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "90",
"journal-title": "Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "1486",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/10870547211003659",
"article-title": "The Association between ADHD and the Severity of COVID-19 Infection",
"author": "Merzon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "491",
"journal-title": "J. Atten. Disord.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0253293",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_18",
"unstructured": "Yamamoto, S., Saito, M., Tamura, A., Prawisuda, D., Mizutani, T., and Yotsuyanagi, H. (2021). The Human Microbiome and COVID-19: A Systematic Review. PLoS ONE, 16."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mBio.01777-21",
"article-title": "Signatures of COVID-19 Severity and Immune Response in the Respiratory Tract Microbiome",
"author": "Merenstein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0177721",
"journal-title": "MBio",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2021.747816",
"article-title": "A Pro-Inflammatory Gut Microbiome Characterizes SARS-CoV-2 Infected Patients and a Reduction in the Connectivity of an Anti-Inflammatory Bacterial Network Associates with Severe COVID-19",
"author": "Reinold",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "747816",
"journal-title": "Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.06.048",
"article-title": "Alterations in Gut Microbiota of Patients with COVID-19 during Time of Hospitalization",
"author": "Zuo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1302",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2021.705020",
"article-title": "Gut Microbiota Diversity and C-Reactive Protein Are Predictors of Disease Severity in COVID-19 Patients",
"author": "Marques",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "705020",
"journal-title": "Front. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/19490976.2022.2031840",
"article-title": "Gut Bacterial Dysbiosis and Instability Is Associated with the Onset of Complications and Mortality in COVID-19",
"author": "Schult",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2031840",
"journal-title": "Gut Microbes",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2022.963488",
"article-title": "Microbiota and COVID-19: Long-Term and Complex Influencing Factors",
"author": "Gang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "963488",
"journal-title": "Front. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2020.572912",
"article-title": "Antibiotics as Major Disruptors of Gut Microbiota",
"author": "Ramirez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "572912",
"journal-title": "Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mbo3.1260",
"article-title": "Impact of Antibiotics on the Human Microbiome and Consequences for Host Health",
"author": "Patangia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1260",
"journal-title": "MicrobiologyOpen",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jtm/taw084",
"article-title": "Effects of Short- and Long-Course Antibiotics on the Lower Intestinal Microbiome as They Relate to Traveller’s Diarrhea",
"author": "McDonald",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S35",
"journal-title": "J. Travel Med.",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2017.10.020",
"article-title": "Antibiotic-Induced Changes to the Host Metabolic Environment Inhibit Drug Efficacy and Alter Immune Function",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "757",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.574425",
"article-title": "Immunomodulatory Effects of Azithromycin Revisited: Potential Applications to COVID-19",
"author": "Venditto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "574425",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/vr.105260",
"article-title": "Randomised Study of the Immunomodulatory Effects of Azithromycin in Severely Asthmatic Horses",
"author": "Vargas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "143",
"journal-title": "Vet. Rec.",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "185",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2010.12.013",
"article-title": "IL-5 Release of CD4+ Non-Effector Lymphocytes Is Increased in COPD—Modulating Effects of Moxifloxacin and Dexamethasone",
"author": "Schild",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "444",
"journal-title": "Int. Immunopharmacol.",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/CS20000073",
"article-title": "Effect of Ciprofloxacin on the Activation of the Transcription Factors Nuclear Factor KappaB, Activator Protein-1 and Nuclear Factor-Interleukin-6, and Interleukin-6 and Interleukin-8 MRNA Expression in a Human Endothelial Cell Line",
"author": "Galley",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "405",
"journal-title": "Clin. Sci.",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "99",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1034/j.1600-0609.2001.066005287.x",
"article-title": "Immunomodulatory Effects of Moxifloxacin in Comparison to Ciprofloxacin and G-CSF in a Murine Model of Cyclophosphamide-Induced Leukopenia+",
"author": "Shalit",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "287",
"journal-title": "Eur. J Haematol.",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.05149-11",
"article-title": "Effect of Rifampin on Production of Inflammatory Mediators in HepG2 Liver Epithelial Cells",
"author": "Yuhas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5541",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/AITC201810020",
"article-title": "Clostridioides Difficile Infection",
"author": "Guh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "ITC49",
"journal-title": "Ann. Intern. Med.",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "169",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0215639",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_36",
"unstructured": "Sagie, S., Na’amnih, W., Frej, J., Cohen, D., Alpert, G., and Muhsen, K. (2019). Correlates of Hospitalizations in Internal Medicine Divisions among Israeli Adults of Different Ethnic Groups with Hypertension, Diabetes and Cardiovascular Diseases. PLoS ONE, 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40168-022-01342-8",
"article-title": "Alterations in the Respiratory Tract Microbiome in COVID-19: Current Observations and Potential Significance",
"author": "Merenstein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "165",
"journal-title": "Microbiome",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Severe Dysbiosis and Specific Haemophilus and Neisseria Signatures as Hallmarks of the Oropharyngeal Microbiome in Critically III Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Patients",
"author": "Zamir",
"first-page": "e1063",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2010217118",
"article-title": "The Hygiene Hypothesis, the COVID Pandemic, and Consequences for the Human Microbiome",
"author": "Finlay",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2010217118",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/bs.pmbts.2022.06.016",
"article-title": "Dysbiosis of human microbiome and infectious diseases",
"author": "Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "33",
"journal-title": "Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci.",
"key": "ref_40",
"volume": "192",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-023-36323-4",
"article-title": "Microbiota-derived acetate enhances host antiviral response via NLRP3",
"author": "Niu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "642",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12985-023-01979-3",
"article-title": "Microbiota composition in the lower respiratory tract is associated with severity in patients with acute respiratory distress by influenza",
"author": "Campos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "19",
"journal-title": "Virol. J.",
"key": "ref_42",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12938/bmfh.2022-037",
"article-title": "Consumption of yogurt fermented with Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus OLL1073R-1 augments serum antibody titers against seasonal influenza vaccine in healthy adults",
"author": "Hemmi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "73",
"journal-title": "Biosci. Microbiota Food Health",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2022.1011254",
"article-title": "Multi-omics association analysis reveals interactions between the oropharyngeal microbiome and the metabolome in pediatric patients with influenza A virus pneumonia",
"author": "Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1011254",
"journal-title": "Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_44",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/13814788.2022.2138855",
"article-title": "A Higher Frequency of Physical Activity Is Associated with Reduced Rates of SARS-CoV-2 Infection",
"author": "Green",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Gen. Pract.",
"key": "ref_45",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antibiotics11081063",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_46",
"unstructured": "Kournoutou, G.G., and Dinos, G. (2022). Azithromycin through the Lens of the COVID-19 Treatment. Antibiotics, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41429-019-0204-x",
"article-title": "Azithromycin, a 15-Membered Macrolide Antibiotic, Inhibits Influenza A(H1N1)Pdm09 Virus Infection by Interfering with Virus Internalization Process",
"author": "Tran",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "759",
"journal-title": "J. Antibiot.",
"key": "ref_47",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2139/ssrn.3626443",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_48",
"unstructured": "Quadery, S.R., John, T., Samuel, T., Ramanna, S., Chattopadhyay, G., Malapanjudi, C., Sodha, A., Lawrence, R., Dutta, S., and Varney, V. (2023, February 03). Improved Outcomes with Trimethoprim or Cotrimoxazole in Patients with Severe COVID-19: A District Hospital Experience. Available online: http://medicinaycirugiaoralymaxilofacial.info/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/Improved.pdf."
},
{
"article-title": "Cotrimoxazole in the Domiciliary Management of Patients with Severe COVID-19: A Case Series",
"author": "Siddiqui",
"first-page": "34",
"journal-title": "J. Indian Med. Assoc.",
"key": "ref_49",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Cotrimoxazole in Hospitalised Patients with Severe COVID-19—Interim Results from the CoTroxCov Study",
"author": "Quadery",
"first-page": "1544",
"journal-title": "Eur. Respir. J.",
"key": "ref_50",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s43440-020-00169-0",
"article-title": "Ciprofloxacin and Moxifloxacin Could Interact with SARS-CoV-2 Protease: Preliminary in Silico Analysis",
"author": "Marciniec",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1553",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol. Rep.",
"key": "ref_51",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.06.004",
"article-title": "Could Respiratory Fluoroquinolones, Levofloxacin and Moxifloxacin Prove to Be Beneficial as an Adjunct Treatment in COVID-19?",
"author": "Karampela",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "741",
"journal-title": "Arch. Med. Res.",
"key": "ref_52",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaip.2020.11.020",
"article-title": "COVID-19 Susceptibility in Bronchial Asthma",
"author": "Green",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "684",
"journal-title": "J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract.",
"key": "ref_53",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 53,
"references-count": 53,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2079-6382/12/3/587"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pharmacology (medical)",
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)",
"General Pharmacology, Toxicology and Pharmaceutics",
"Biochemistry",
"Microbiology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The Association between Previous Antibiotic Consumption and SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Population-Based Case-Control Study",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "12"
}
dugot