Vitamin A for COVID-19: real-time meta analysis of 22 studies (15 treatment studies and 7 sufficiency studies)
, Dec 2025
Vitamin A for COVID-19
48th treatment shown to reduce risk in
June 2023, now with p = 0.0052 from 15 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,300+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
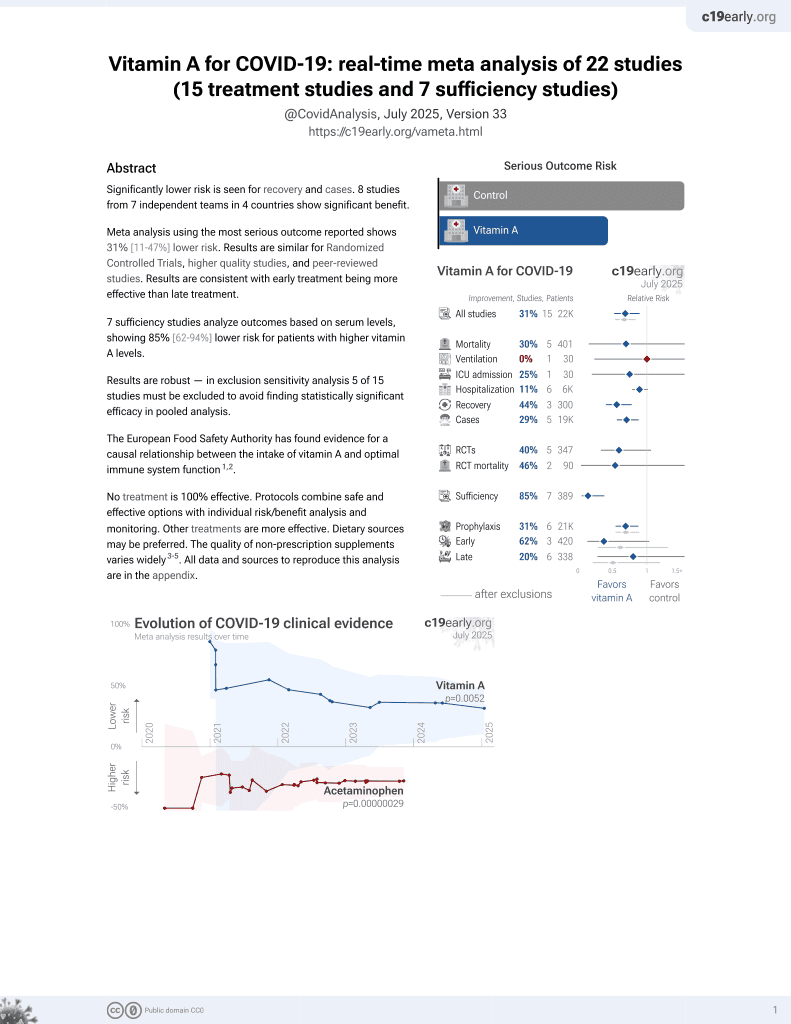
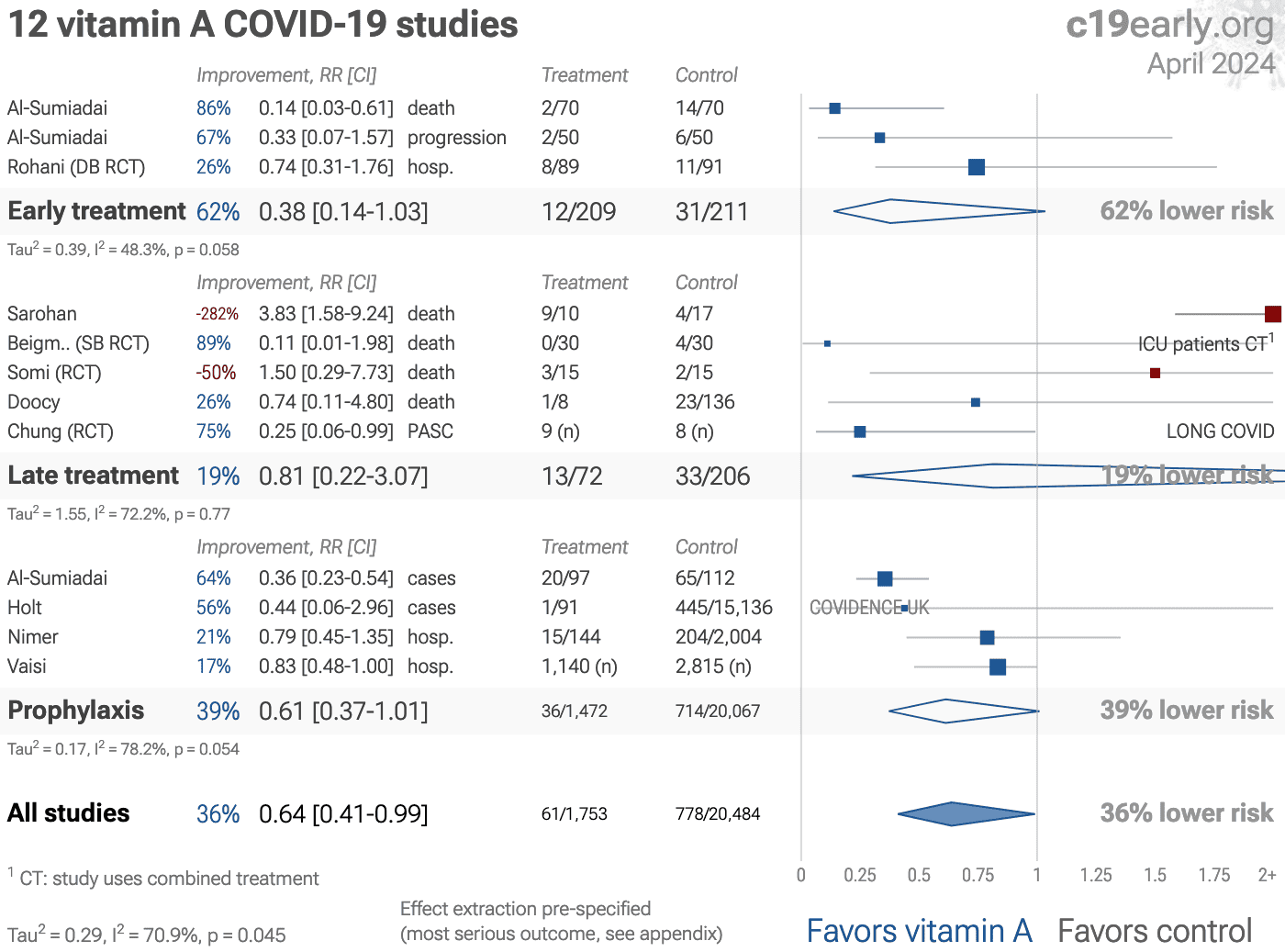
Significantly lower risk is seen for recovery and cases. 8 studies from 7 independent teams in 4 countries show significant benefit.
Meta analysis using the most serious outcome reported shows 31% [11‑47%] lower risk. Results are similar for Randomized Controlled Trials, higher quality studies, and peer-reviewed studies. Results are consistent with early treatment being more effective than late treatment.
7 sufficiency studies analyze outcomes based on serum levels, showing 85% [62‑94%] lower risk for patients with higher vitamin A levels.
Results are robust — in exclusion sensitivity analysis 5 of 15 studies must be excluded to avoid finding statistically significant efficacy in pooled analysis.
Control Vitamin A
The European Food Safety Authority has found evidence for a causal relationship between the intake of vitamin A and optimal immune system function1,2.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols combine safe and effective options with individual risk/benefit analysis and monitoring. Other treatments are more effective. Dietary sources may be preferred. The quality of non-prescription supplements varies widely3-5. All data and sources to reproduce this analysis are in the appendix.
Covid Analysis et al., Dec 2025, preprint, 1 author.