Sotrovimab reduced COVID-19 risk: real-time meta analysis of 28 studies (Version 48)
, Jan 2026
Sotrovimab for COVID-19
44th treatment shown to reduce risk in
August 2022, now with p = 0.00054 from 28 studies, recognized in 42 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,300+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
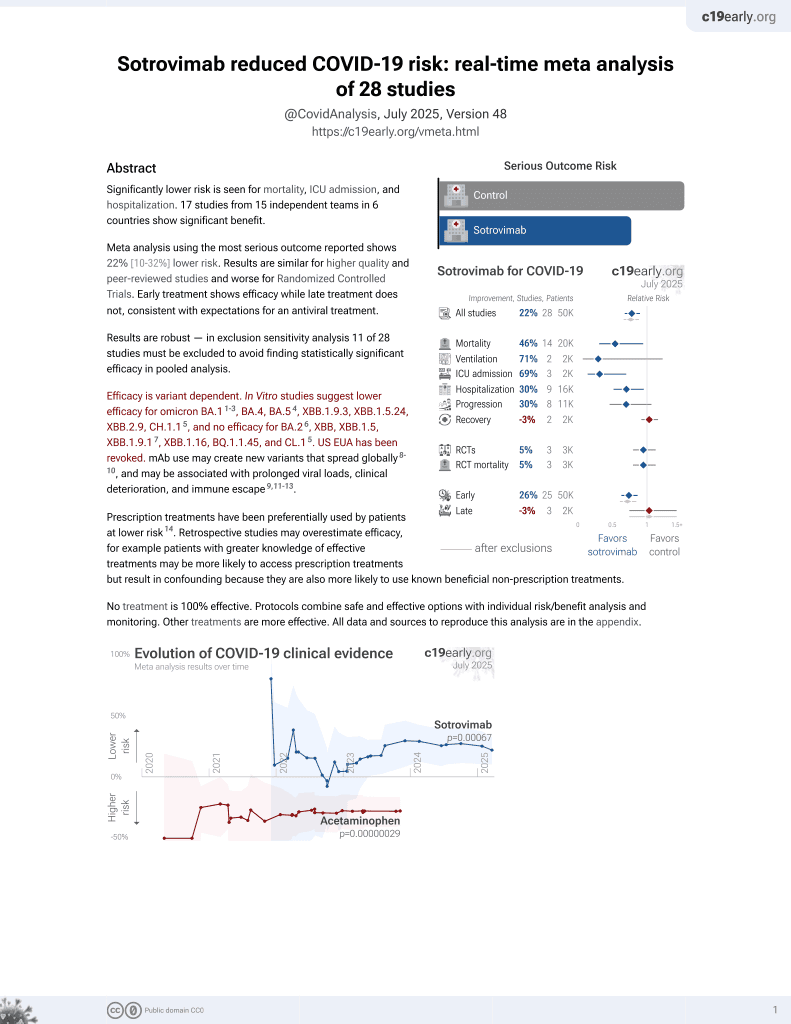
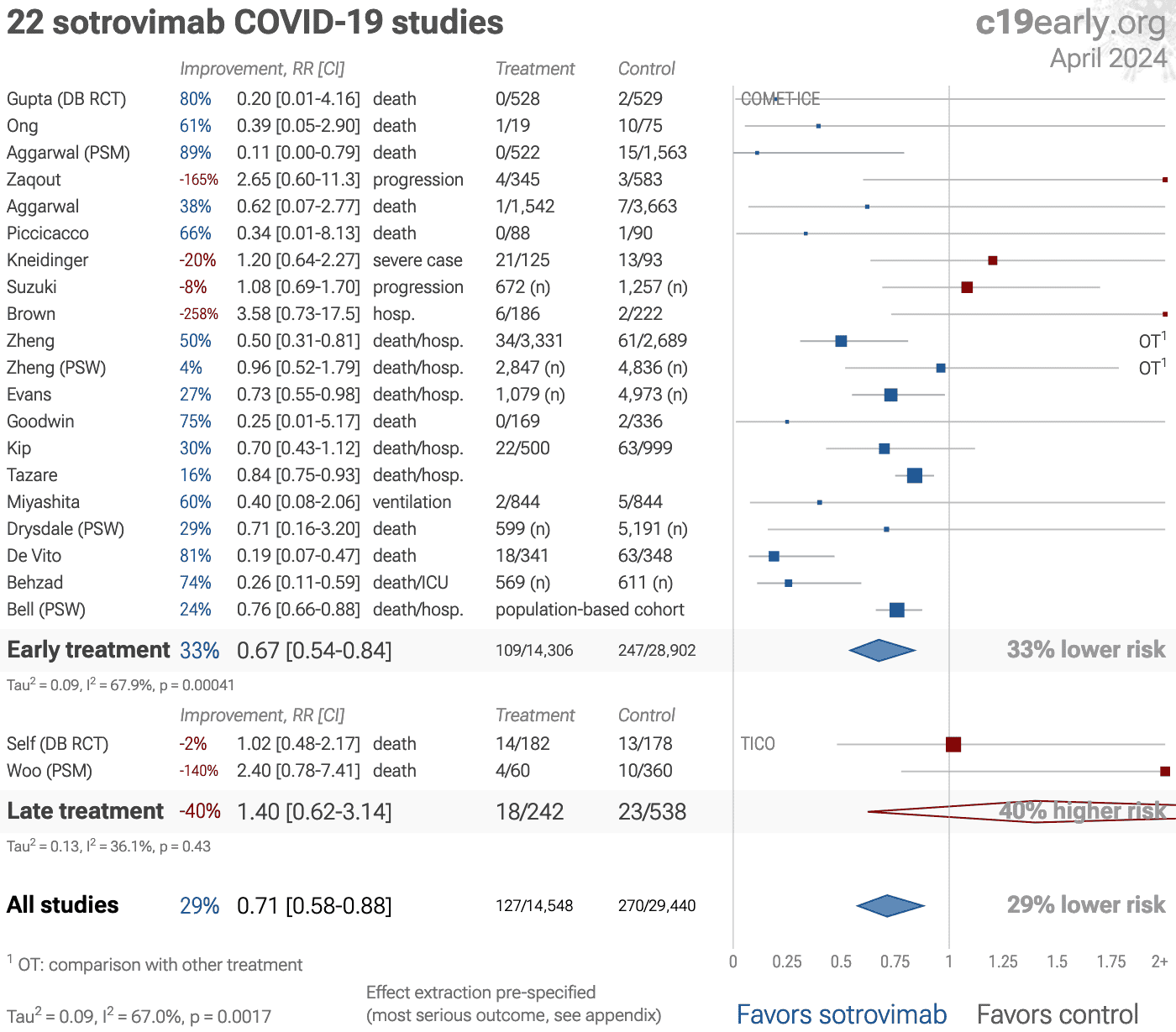
Significantly lower risk is seen for mortality, ICU admission, and hospitalization. 17 studies from 15 independent teams in 6 countries show significant benefit.
Meta analysis using the most serious outcome reported shows 22% [10‑32%] lower risk. Results are similar for higher quality and peer-reviewed studies and worse for Randomized Controlled Trials. Early treatment shows efficacy while late treatment does not, consistent with expectations for an antiviral treatment.
Results are robust — in exclusion sensitivity analysis 13 of 28 studies must be excluded to avoid finding statistically significant efficacy in pooled analysis.
Control Sotrovimab
Efficacy is variant dependent. In Vitro studies suggest lower efficacy for omicron BA.11-3, BA.4, BA.54, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5.24, XBB.2.9, CH.1.15, and no efficacy for BA.26, XBB, XBB.1.5, ХВВ.1.9.17, XBB.1.16, BQ.1.1.45, and CL.15. US EUA has been revoked. mAb use may create new variants that spread globally8-10, and may be associated with prolonged viral loads, clinical deterioration, and immune escape9,11-14.
Prescription treatments have been preferentially used by patients at lower risk15. Retrospective studies may overestimate efficacy, for example patients with greater knowledge of effective treatments may be more likely to access prescription treatments but result in confounding because they are also more likely to use known beneficial non-prescription treatments.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols combine safe and effective options with individual risk/benefit analysis and monitoring. Other treatments are more effective. All data and sources to reproduce this analysis are in the appendix.
Covid Analysis et al., Jan 2026, preprint, 1 author.