Improved sleep reduces COVID-19 risk: real-time meta analysis of 16 studies
, Jan 2026
Sleep for COVID-19
17th treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2021, now with p = 0.00000000084 from 16 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,300+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
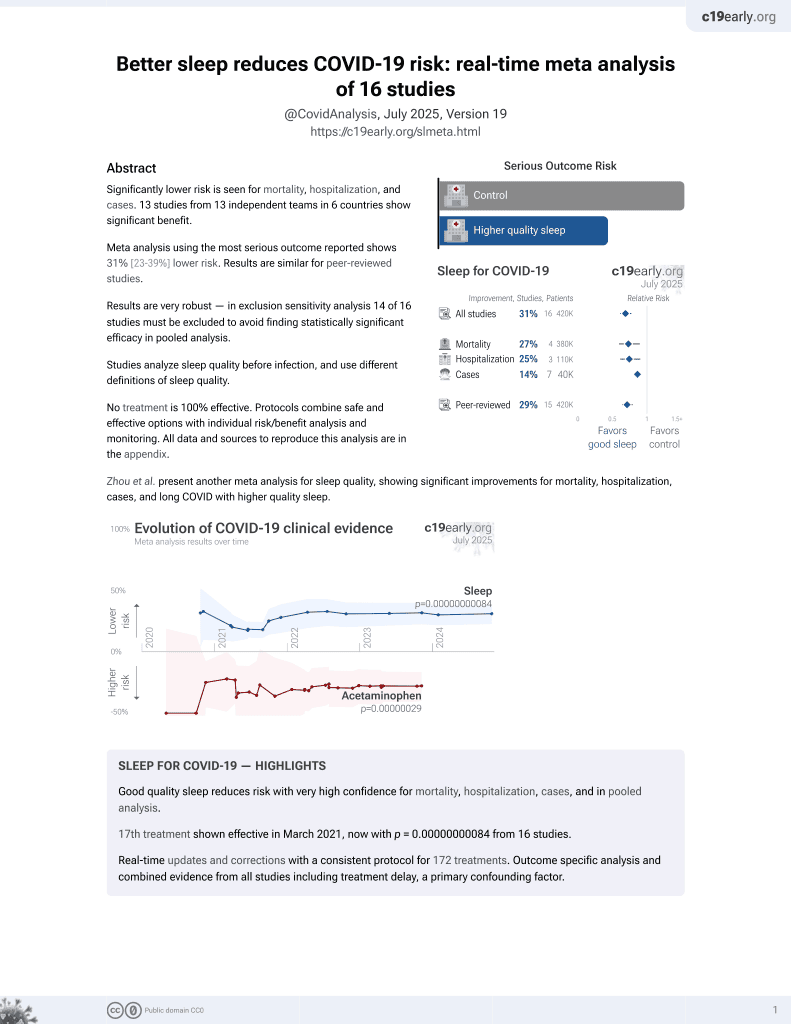
Significantly lower risk is seen for mortality, hospitalization, and cases. 13 studies from 13 independent teams in 6 countries show significant benefit.
Meta analysis using the most serious outcome reported shows 31% [23‑39%] lower risk. Results are similar for peer-reviewed studies.
Results are very robust — in exclusion sensitivity analysis 14 of 16 studies must be excluded to avoid finding statistically significant efficacy in pooled analysis.
Control Improved sleepSleep
Studies analyze sleep quality before infection, and use different definitions of sleep quality.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols combine safe and effective options with individual risk/benefit analysis and monitoring. All data and sources to reproduce this analysis are in the appendix.
Zhou et al. present another meta analysis for sleep quality, showing significant improvements for mortality, hospitalization, cases, and long COVID with improved sleep.
Covid Analysis et al., Jan 2026, preprint, 1 author.