N-acetylcysteine reduces COVID-19 risk: real-time meta analysis of 25 studies
, Dec 2025
15th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2021, now with p = 0.0000032 from 25 studies, recognized in 3 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,300+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
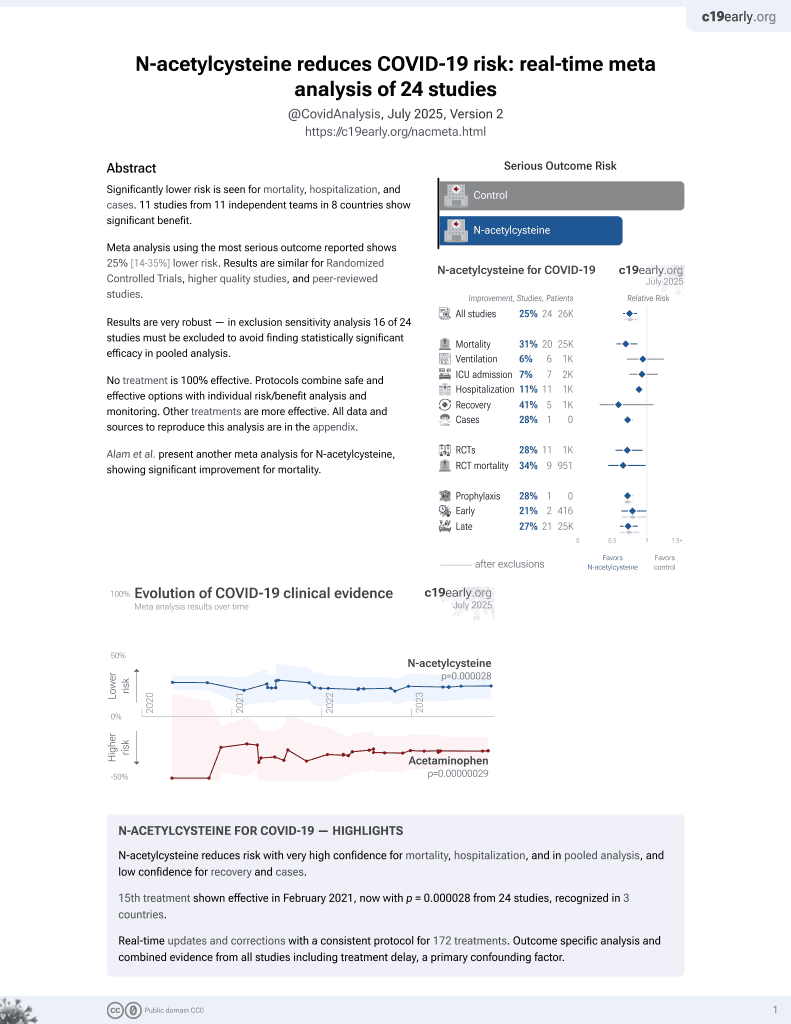
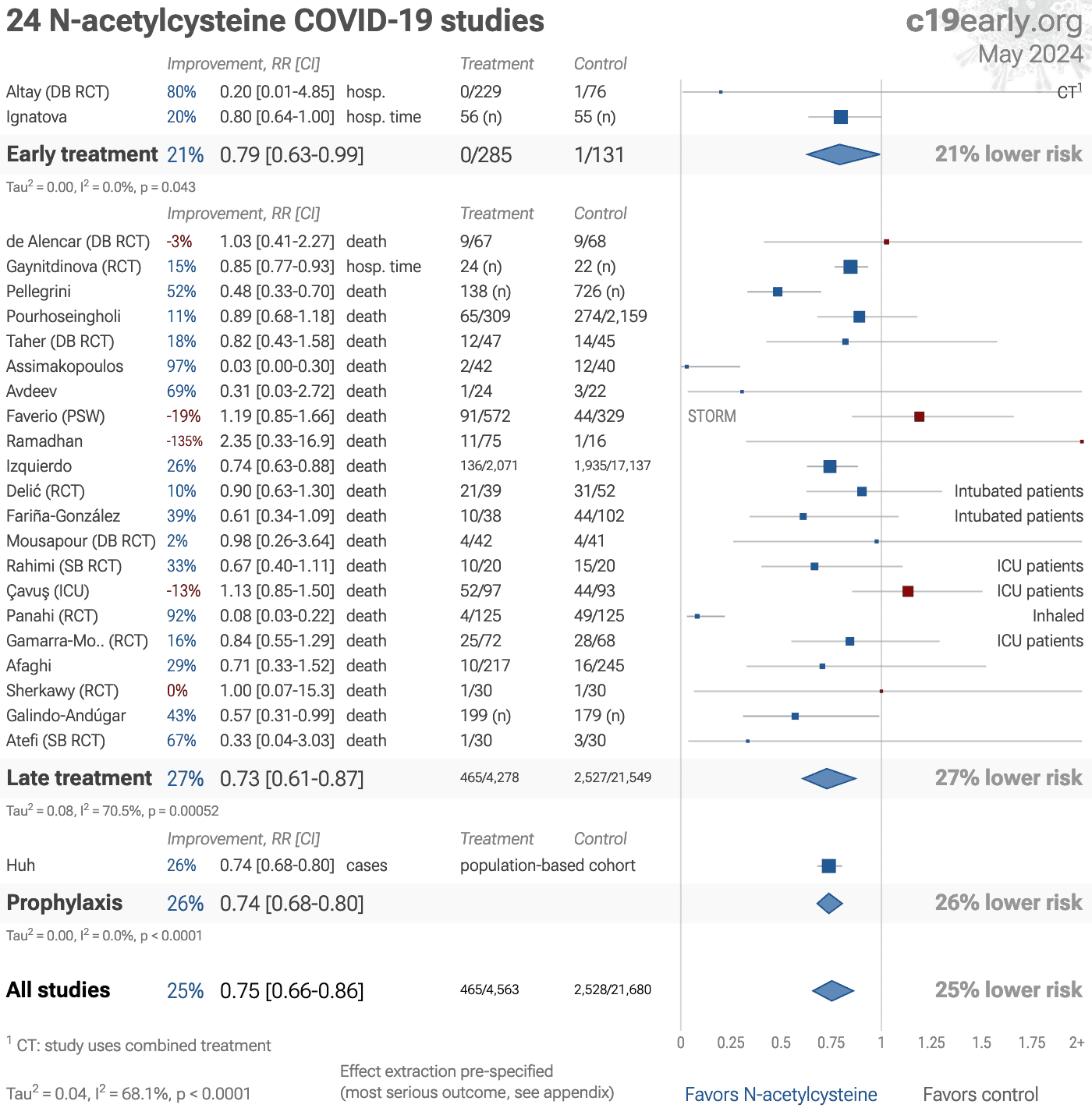
Significantly lower risk is seen for mortality, hospitalization, recovery, and cases. 12 studies from 12 independent teams in 9 countries show significant benefit.
Meta analysis using the most serious outcome reported shows 23% [14‑32%] lower risk. Results are similar for Randomized Controlled Trials, higher quality studies, and peer-reviewed studies.
Results are very robust — in exclusion sensitivity analysis 17 of 25 studies must be excluded to avoid finding statistically significant efficacy in pooled analysis.
Control N-acetylcysteineN-acetylcys..
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols combine safe and effective options with individual risk/benefit analysis and monitoring. Other treatments are more effective. All data and sources to reproduce this analysis are in the appendix.
Other meta analyses show significant improvement with N-acetylcysteine for mortality1,2.
Covid Analysis et al., Dec 2025, preprint, 1 author.