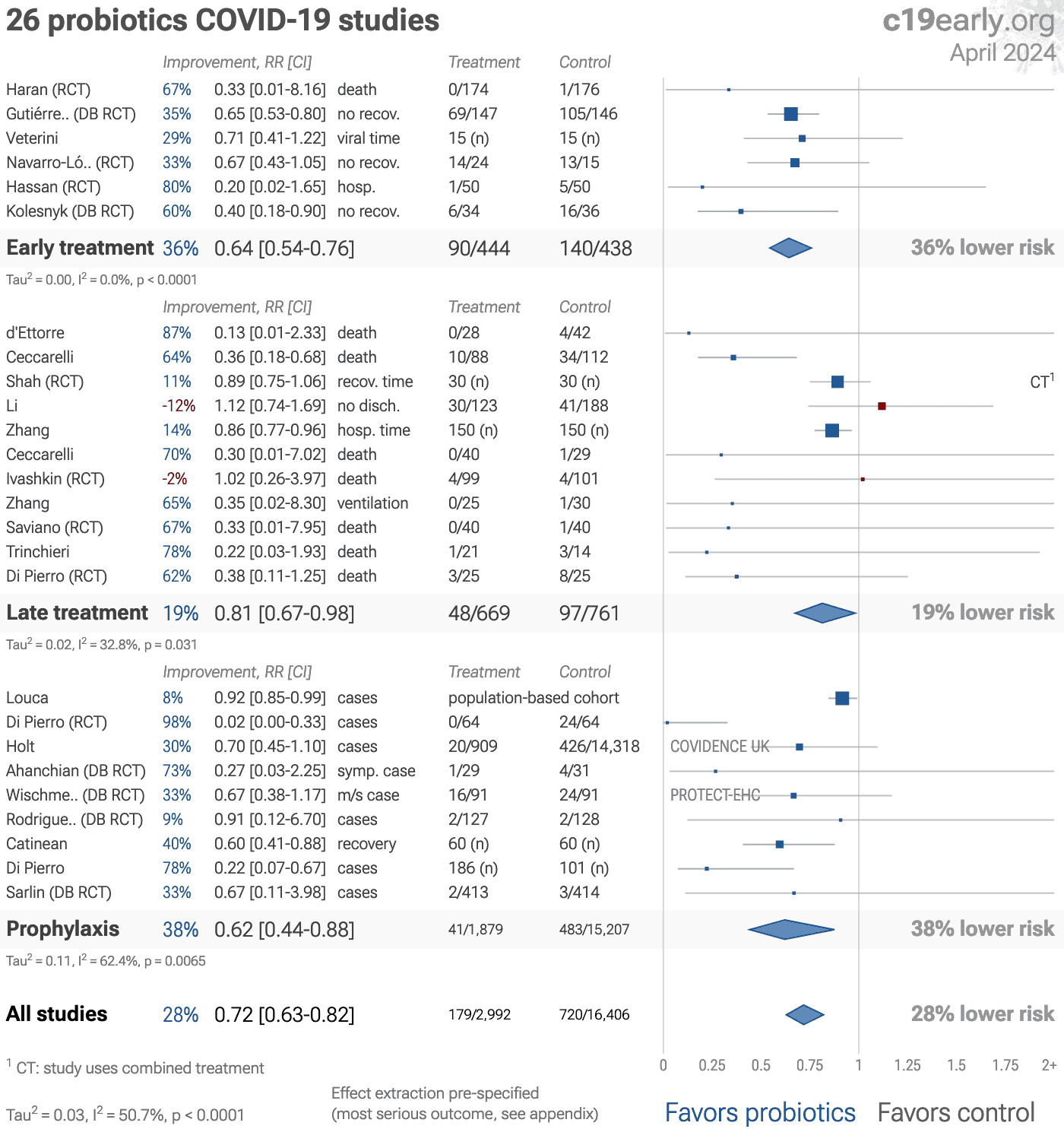
Significantly lower risk is seen for mortality, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and cases. 13 studies from 12 independent teams in 9 countries show significant benefit.
Meta analysis using the most serious outcome reported shows 28% [18‑36%] lower risk. Results are similar for Randomized Controlled Trials, higher quality studies, and peer-reviewed studies. Better results are seen with early treatment.
Results are very robust — in exclusion sensitivity analysis 25 of 28 studies must be excluded to avoid finding statistically significant efficacy in pooled analysis.
Probiotic efficacy depends on the specific strains used. Specific microbes may decrease or increase COVID-19 risk1.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols combine safe and effective options with individual risk/benefit analysis and monitoring. Other treatments are more effective. Dietary sources may be preferred. The quality of non-prescription supplements varies widely2-4. Many probiotic supplements may not include labeled ingredients5. All data and sources to reproduce this analysis are in the appendix.
Other meta analyses show significant improvements with probiotics for hospitalization6 and recovery6,7.
2 meta analyses show significant improvements with probiotics for hospitalization
1 and
recovery
1,2.
Covid Analysis et al., May 2025, preprint, 1 author.