Bromhexine for COVID-19: real-time meta analysis of 7 studies
, Dec 2025
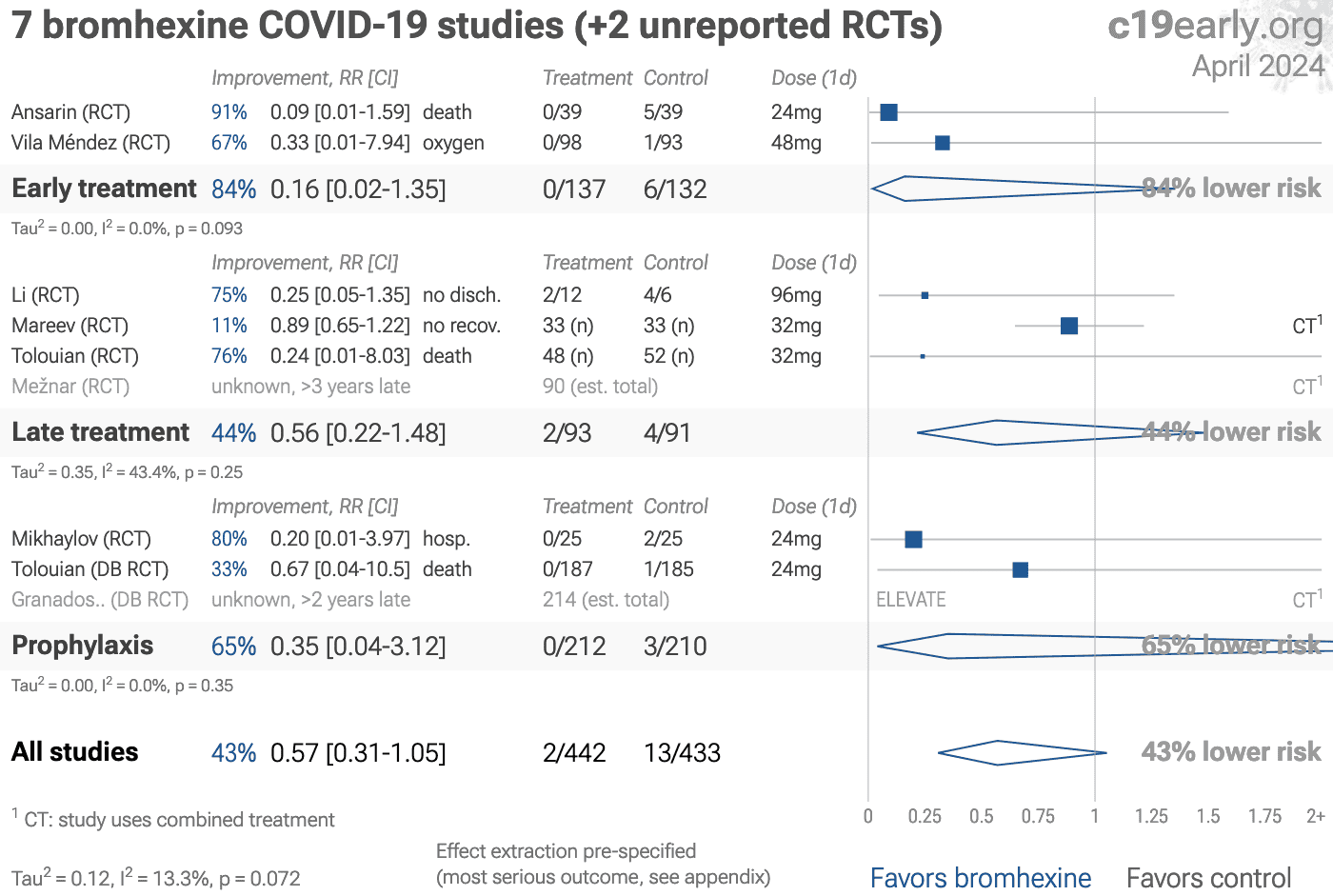
Significantly lower risk is seen for ventilation and ICU admission. 3 studies from 3 independent teams in 2 countries show significant benefit.
Meta analysis using the most serious outcome reported shows 43% [-5‑69%] lower risk, without reaching statistical significance. Results are similar for peer-reviewed studies. Early treatment is more effective than late treatment. Currently all studies are RCTs.
Control Bromhexine
2 RCTs with 304 patients have not reported results (up to 5 years late)1,2.
Bromhexine efficacy may vary depending on the degree of TMPRSS-dependent fusion for different variants3,4.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols combine safe and effective options with individual risk/benefit analysis and monitoring. All data and sources to reproduce this analysis are in the appendix.
Covid Analysis et al., Dec 2025, preprint, 1 author.